Manage mail flow in hybrid Exchange deployments
A hybrid deployment is typically configured to share a common SMTP email namespace. This design requires routing messages between an organization's on-premises Exchange servers and Exchange Online. For this reason, you must consider how to organize the email flow to and from the Internet, and between Exchange Online and the Exchange Server on-premises.
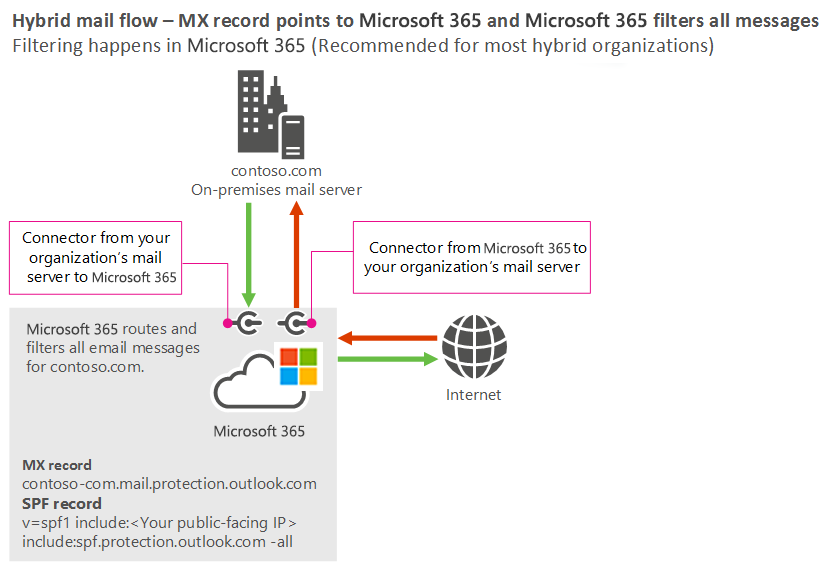
Inbound email flow from the Internet
Inbound email can be delivered to Exchange Server on-premises, or you can target the mail exchanger (MX) resource record to Exchange Online. The method you choose depends on your organization’s requirements. The following are some considerations for each scenario:
- Inbound to Exchange Server on-premises. Use this option if you want to keep full control of your email domains, such as message tracking and journaling of messages in your company. Configure the MX resource record to point to your organization’s SMTP smart host so that the hybrid deployment automatically forwards all messages for mailboxes that are located on Exchange Online. If you currently use a third-party mail filter in front of your on-premises environment, then this scenario also applies.
- Inbound to Exchange Online. Use this option if you want Microsoft to handle your email domains, and you want to automatically take advantage of the anti-virus and anti-spam scanning engines from Exchange Online Protection. To configure this scenario, point the MX resource record to Exchange Online Protection. Exchange Online automatically delivers messages that are located on Exchange Server on-premises by using the Exchange Server that you define when you run the Hybrid Deployment Wizard.
Outbound email flow to the Internet
Like inbound email flow, you can configure outbound email flow from your domain to the Internet, by using one of the following options:
- Deliver Internet-bound messages directly. Use this option to send any outbound message that is targeted to the Internet directly from either Exchange Online or Exchange Server on-premises. If the mailbox is located on Exchange Online, the Internet messages are delivered directly to the target SMTP domain without passing through the Exchange Server on-premises environment. Messages sent from on-premises mailboxes are routed directly to Internet recipients without passing through Exchange Online. The benefit of this option is that the message traffic is optimized, but the drawback is that it’s harder to track messages to the Internet because not every message flows through the on-premises Exchange servers.
- Route all Internet-bound messages through your on-premises Exchange servers. This option forces Exchange Online to send any message that is targeted to the Internet through the Exchange Server on-premises environment first. The on-premises Exchange servers then route the message to the Internet and deliver the message. The benefit of this option is that all messages pass through the Exchange servers, so you can use message tracking, journaling, and other compliance features.
- Route all Internet-bound messages through ExchangeOnline. This option forces the on-premises Exchange servers to send any message that is targeted to the Internet through Exchange Online first.
Email flow between Exchange Online and the Exchange Server on-premises organization
Email flow between Exchange Online and an Exchange Server on-premises organization uses SMTP send and receive connectors that the HCW configures automatically. The connectors enforce the requirement that messages be encrypted by using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol.
Further reading. For more information, see Manage mail flow with mailboxes in multiple locations (Exchange Online and on-premises).