Introduction
Advancements in mixed reality provide organizations with another tool in offering better customer service. With mixed reality, organizations can provide more accurate interactive support, richer training, and customized sales experiences for customers.
Mixed reality
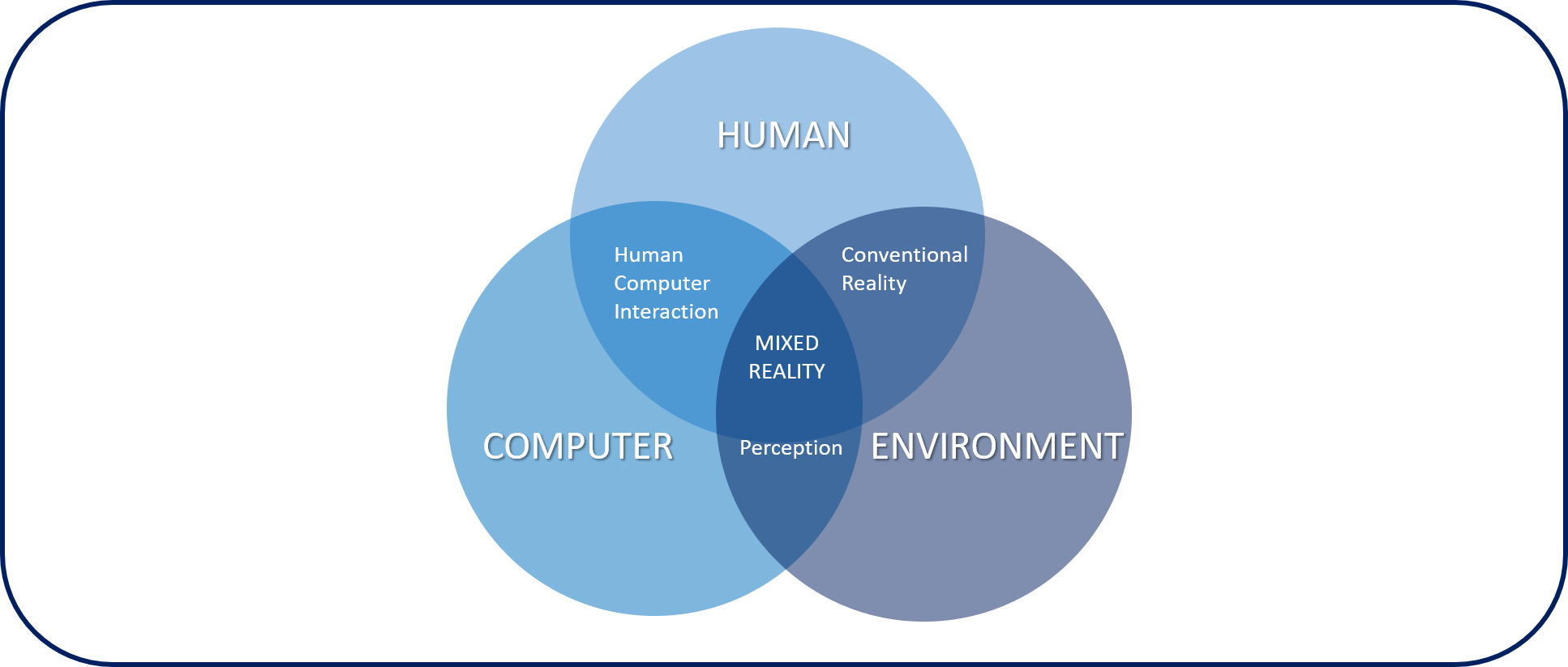
Mixed reality is the result of blending the physical world with the digital world. It represents the next evolution in human, computer, and environmental interaction and unlocks possibilities that, before now, were restricted to human imagination.
Concepts and terms
The following section defines the important concepts and terms that are associated with mixed reality technology.
Mixed reality terminology
The core terms and concepts that define mixed reality are:
Mixed reality is a spectrum - Mixed reality blends the physical world with the digital world. Mixed reality physically anchors holographic images, data, text, and other digital information onto the physical world, enabling you to interact with these holograms.
Hologram - HoloLens 1 and 2 display holograms, which are objects made of light and sound that appear in the world around you as if they were real objects, like the green arrow that is shown in the previous image. Holograms respond to your gaze, gestures, and voice commands and can interact with real-world surfaces around you. With holograms, you can create digital objects that are part of your world.
Spatial anchoring - When a technician or remote collaborator creates drawings or adds arrows, these annotations are anchored in the physical world and stay in place as the Remote Assist user moves around.
HoloLens 2 - HoloLens 2 offers the most comfortable and immersive mixed reality experience available with industry-leading solutions that deliver value in minutes, all enhanced by the reliability, security, and scalability of cloud and AI services from Microsoft. To learn more about HoloLens 2, go to the HoloLens 2 features and technical specs documentation. Compared to HoloLens 1, HoloLens 2 offers a more immersive, ergonomic, and instinctual experience.
Learn more about core concepts in mixed reality technology by selecting the link.
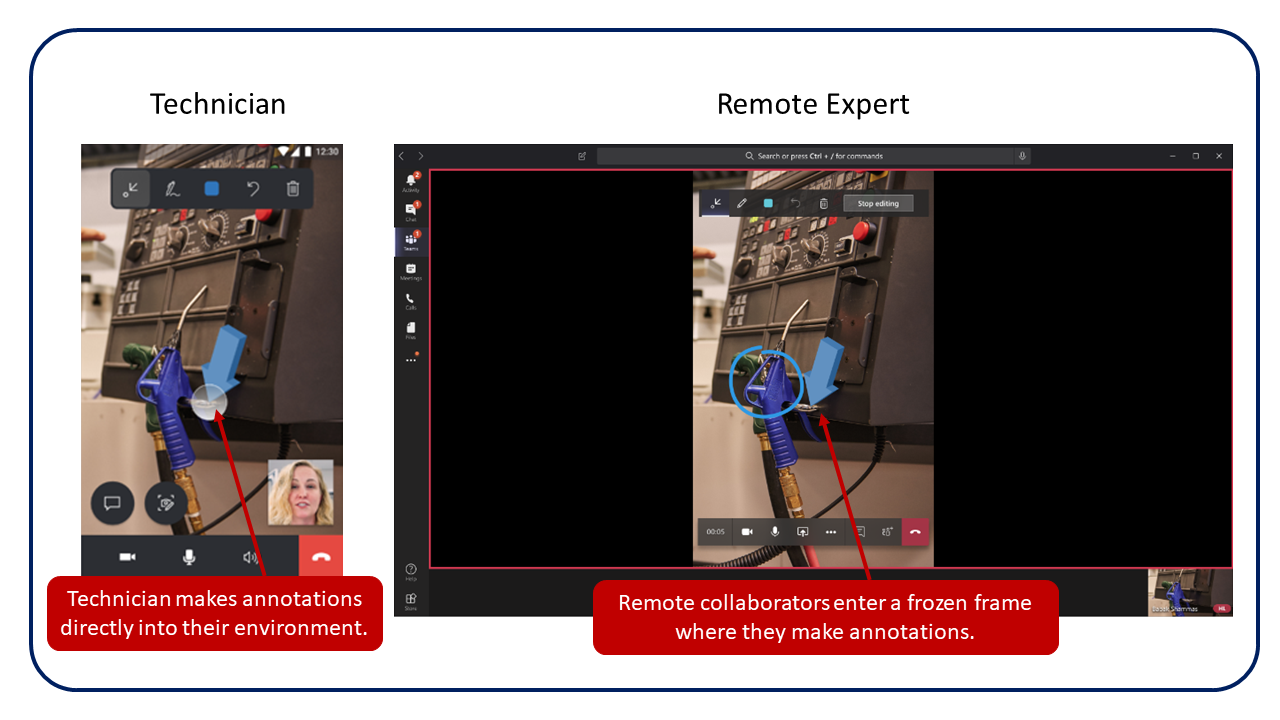
The most common example of mixed reality technology in Remote Assist is annotations, also called drawings, which are a type of hologram. In the following image, the person is using Remote Assist on an Android phone and the green arrow is a mixed reality annotation.
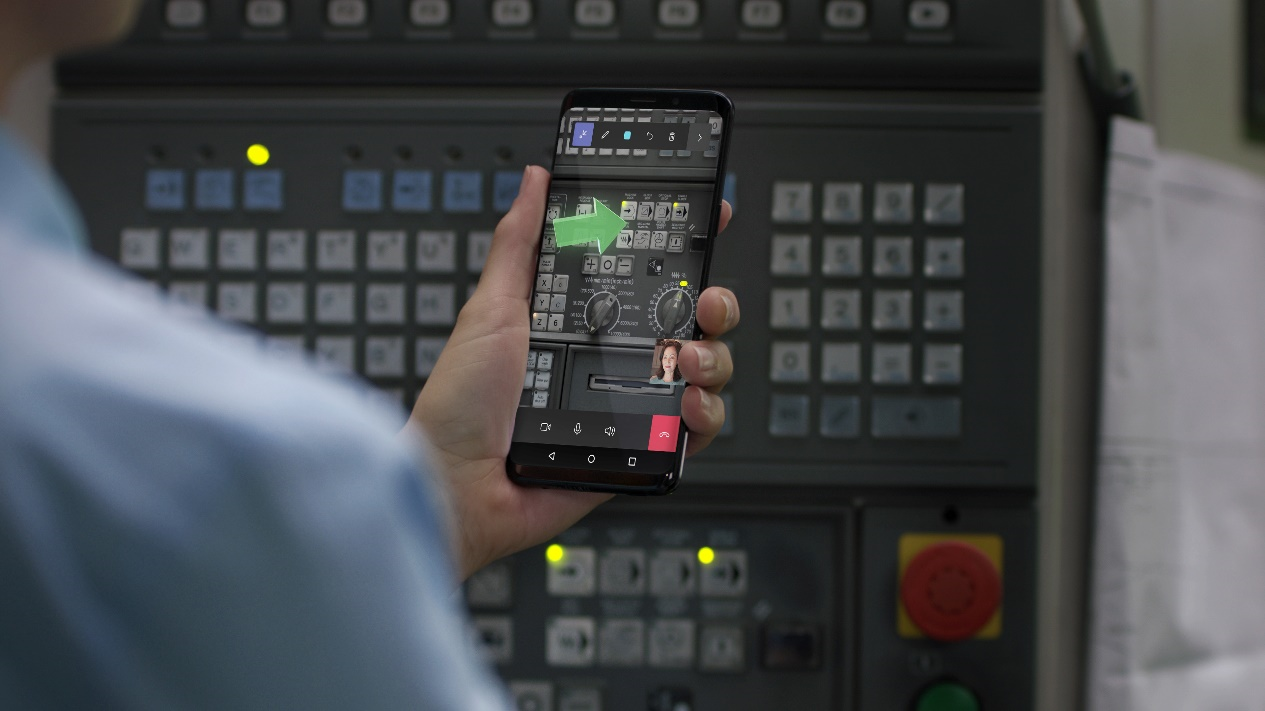

The machine in front of the phone exists in the physical world, the green arrow exists in the digital world, and mixed reality brings them together. Nevertheless, the green arrow is more than an image on a screen because it is anchored in a three-dimensional space, and it will stay in place even if the user moves the phone or walks away. This feature is accomplished with mixed reality technology that maps the 3D area around the mobile phone or HoloLens headset.
Spatial anchoring makes mixed reality more powerful than augmented reality or virtual reality. Augmented reality doesn't model the surrounding 3D space, meaning that the green arrow would disappear if the user moved their phone. Virtual reality is an immersive experience, meaning that the user wouldn't be able to see the physical machine surrounding them (think virtual reality headsets, where the user cannot see anything other than what's displayed in the headset screen).
The purpose of this module is not to make you a mixed reality expert but to highlight these key terms to help you better understand the mixed reality and remote assist concepts that will be referenced throughout the remainder of the module.
Remote Assist terminology
The core terms and concepts that define Remote Assist are:
Technician/frontline worker - A technician refers to the person who performs some type of work for a customer. For example, a technician installs, repairs, inspects, or troubleshoots, and would use Remote Assist on their HoloLens or mobile device to share what they are seeing so that they are able to receive remote assistance to fix the issue.
Remote collaborator expert - A remote collaborator refers to the person who is knowledgeable or has access to knowledge and can assist the technician in resolving an issue. This person uses Microsoft Teams on a PC or mobile device to see what the technician sees and then provides contextual guidance.
Field of view (FOV) - This concept represents the portion of the technician's view that is captured with their phone or HoloLens' camera that is shared with the remote collaborator. The greater the device's field of view, the more holograms you can see simultaneously.
Annotation - A type of hologram that technicians and remote collaborators can draw into a 3D virtual space that helps them see the issue more clearly.
Call - When a technician needs help and wants to share their field of view to receive contextual guidance, they will make a remote assist call to the remote collaborator expert. The technician uses the Remote Assist app on their phone or HoloLens, and the remote collaborator uses Microsoft Teams on their phone or PC.
Mobile device - A mobile phone or tablet (like an iPhone or Samsung Galaxy) that connects to the internet through a wireless network or cellular.
Now that you have a basic understanding of mixed reality and its key concepts, you can learn how Dynamics 365 Remote Assist helps empower technicians to collaborate more efficiently by helping them work together from different locations.
Reasons for Remote Assist
When knowledge isn’t available to the people who need it, time, money, and customer satisfaction are negatively affected.
If a technician tries to troubleshoot a machine and doesn't know how to fix the issue, they would have to call or text someone else for instructions, ask someone else to join them onsite to look at the issue, or they'd have to return another day after doing more research.
These scenarios are problematic because:
Describing issues over phone and text is difficult and time-consuming.
Having someone else travel to your location is expensive and time-consuming.
Returning another day is expensive, time-consuming, and if the issue is critical, can cause severe customer dissatisfaction.
Remote Assist allows people who are onsite and performing work to share their field of view and collaborate with people in other locations. Compared to video chatting, such as with Microsoft Teams or FaceTime, Remote Assist has the added benefits of mixed reality holograms to collaborate in context and connections to Dynamics 365 business applications and processes. Consider Remote Assist as high-powered video sharing with mixed reality technology for enterprise.
Benefits of Remote Assist
The benefits of using Remote Assist are:
Scale expert knowledge - Enable remote collaborators to effectively share their knowledge from anywhere in the world.
Solve problems in real time - Technicians can share their real-time view with experts in remote locations to get the help that they need. This feature reduces travel time and cost and improves the likelihood of fixing an issue during the first visit (referred to and quantified as first-time-fix rate).
Walk the site without being onsite - Remote inspectors can assess product quality without traveling onsite.
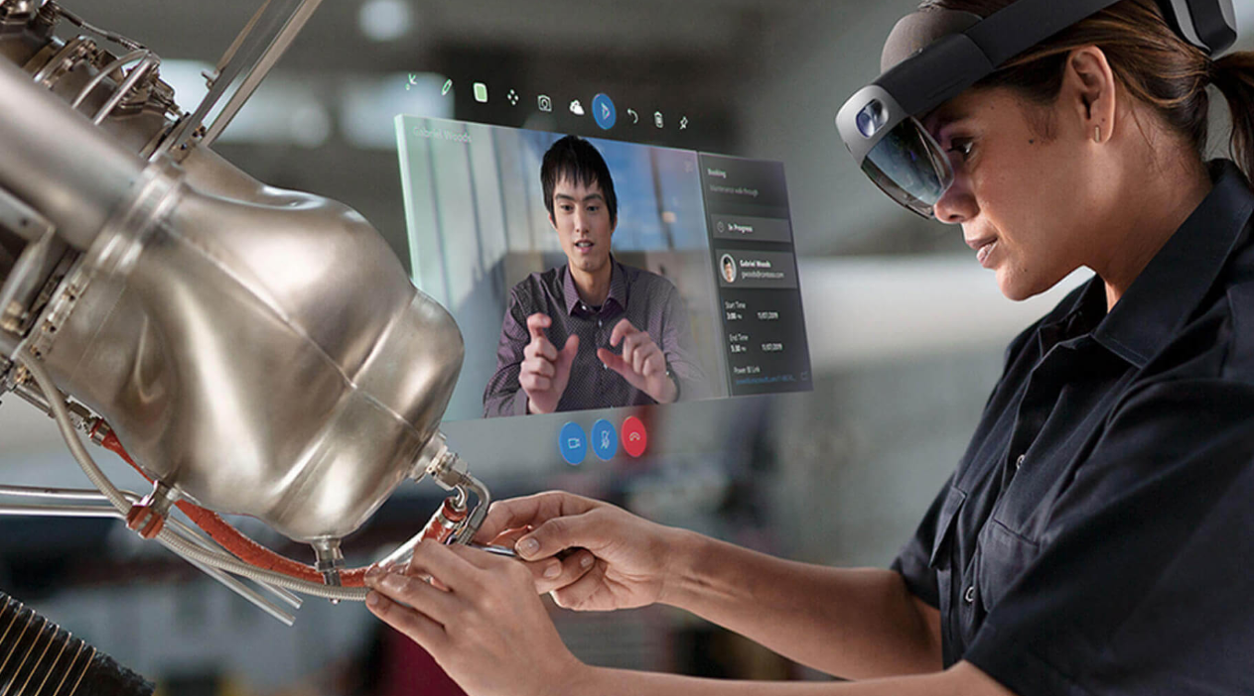

Communicate detailed and complex instructions visually - Rather than communicating instructions through audio call, onsite workers and remote collaborators can use drawings and arrows to refer to specific parts of a machine or asset. These annotations are anchored in the Remote Assist user's space.
Bring critical information into view - Technicians and inspectors can pull in work order information from Dynamics 365 Field Service and call the resource who is assigned to support them. Furthermore, technicians and inspectors no longer need to carry around paper manuals to perform their repair or inspection. If the technician is using Remote Assist on HoloLens, remote collaborators can insert reference images, schematics, and other helpful information on the technician's physical space so they can refer to the schematic while working alert and hands-free on HoloLens. If the technician is using Remote Assist on mobile, remote collaborators can share reference images, schematics, and other helpful information on their mobile device.
Navigate Remote Assist on HoloLens with your voice - Remote Assist on HoloLens provides a hands-free experience by supporting voice commands in these languages for all features, even in a loud, industrial environment.
Offer your customers a differentiated service - When selling your product, you can include a Remote Assist subscription that your customer can use to receive help from product specialists or customer support agents.