Exercise - Build a neural network to classify space rocks
We'll build a neural network (or deep learning network) to learn the associations between features and each rock type. Features can include things like curves, edges, and texture.
Neurons and wired networks
Neural networks process information similar to how our brains work. Our brains have neurons or nerve cells that transmit and process information from our senses. Many nerve cells are arranged as a network of nerves in the brain. The nerves pass electrical impulses from one neuron to the next in the network.
Neural networks have millions of neurons and nerves. To build a functional neural network, we wire the neurons and nerves together in two steps:
- Step A: Build all the neurons.
- Step B: Wire the neurons in an appropriate way. (There are thousands of ways to wire neurons.)
In our model, we'll collect the features for a rock from an image and store them as a linear sequence of parameters. This step builds a single neuron. Every new image that's analyzed is another neuron. We supply the training data for our computer to build all the neurons.
Then we'll tell the computer to combine the sequences into a matrix. The matrix represents the best pattern we have to describe the features for types of space rock. This matrix is a wired network.
We'll train our model to predict the rock type. We'll compare the rock features in a new image with the matrix pattern. Each time we run the model, the matrix grows and the prediction accuracy improves. Our goal is to test the model and achieve a prediction accuracy close to 100%.
Check your working environment
Before you can add new code to your AI model, we need to make sure your development environment is still active.
If you closed your Anaconda prompt, or Visual Studio Code, you need to restart them. You'll need to configure your environment to continue to work on your AI model.
If your Anaconda prompt is still open from your work for the previous module, and you haven't closed Visual Studio Code, continue to the section, Create a neural network.
Verify your Anaconda environment (myenv)
If you closed your Anaconda prompt after you completed the exercises in the previous module, follow these steps to restart your environment.
Start the Anaconda prompt application (or terminal on Mac).
At the Anaconda prompt, enter the following command to activate your environment:
conda activate myenvUse the following command to check the torchvision package installation:
conda install -c pytorch torchvisionThe system should report that all requested packages are already installed. You can ignore warnings about the Anaconda (conda) version.
Restart Visual Studio and the Python kernel
If you refreshed your Anaconda environment by following the previous steps, or you closed Visual Studio Code after you completed the exercises in the previous module, you need to restart the application and Python myenv kernel.
Restart Visual Studio Code.
Open the Jupyter Notebook file that you created earlier.
In the previous exercises, we used the Jupyter Notebook file ClassifySpaceRockProgram.ipynb.
Start the Jupyter Python
myenvkernel. At the upper-right and lower-left corners of Visual Studio, change to the Anaconda environment('myenv')that you created earlier.
Rerun cells in your Jupyter Notebook file
If you refreshed your Anaconda environment or restarted Visual Studio Code, you need to run the existing cells in your Jupyter Notebook file before you can add new code cells.
To rerun the cells in your Jupyter Notebook file, start from the first cell in the Notebook file.
Run each cell in the Notebook in order, from the first cell in the file to the last.
If there are no errors, continue to the next section, Create a neural network.
Troubleshoot environment errors
Here are some tips to help troubleshoot errors in the setup process:
If you receive errors when running existing cells in your Jupyter Notebook file, make sure you followed all the steps in this section:
- Restart your Anaconda environment. Activate
myenv. Check the torchvision installation. - Restart Visual Studio Code. Restart the Jupyter
myenvPython kernel. - Run the existing cells in your Jupyter Notebook file, from the first cell to the last.
- Restart your Anaconda environment. Activate
If you receive an error about a specific command or library, you might need to refresh a library through your Anaconda prompt environment. Make sure the Anaconda prompt environment indicates that all libraries are downloaded and installed. Follow the steps to Download the Python AI libraries as described in an earlier module.
If you see errors in Visual Studio Code, try restarting the application, restarting the
myenvkernel, and running the existing cells in the Jupyter Notebook file.If possible, try to complete the exercises for all modules in the Learning path in a single session. Try not to close your Anaconda prompt environment or Visual Studio Code.
Create a neural network
After you confirm your environment is active, you're ready to create a neural network for your AI model.
Detect the device type
We need to help your computer determine the most efficient way to create the deep learning network. First, we need to find the type of device you're using: CPU or GPU. The PyTorch APIs offer support to form a neural network according to the device type.
Add the following code in a new cell, and then run the cell.
# Determine if you're using a CPU or a GPU device to build the deep learning network device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") model = models.resnet50(pretrained=True)After the system detects your device, it downloads the appropriate model structures to the PyTorch installation location on your computer.
Build neurons and wire the network
Let's add code to your Jupyter Notebook file to build the neurons and wire the network.
Add the following code in a new cell, and then run the cell.
# Build all the neurons for param in model.parameters(): param.requires_grad = False # Wire the neurons together to create the neural network model.fc = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(2048, 512), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.2), nn.Linear(512, 2), nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)) criterion = nn.NLLLoss() optimizer = optim.Adam(model.fc.parameters(), lr=0.003) # Add the neural network to the device model.to(device) print('done')When the build completes, the output for the command shows that the process is complete:
done
The neural network goes back and forth many times until it learns the best associations (wiring) between features and rock types.
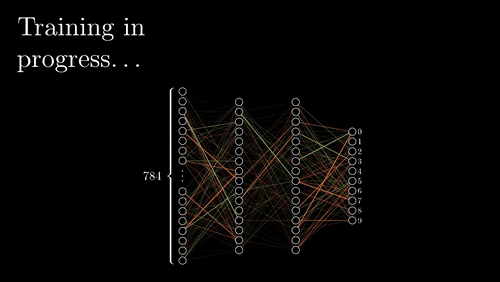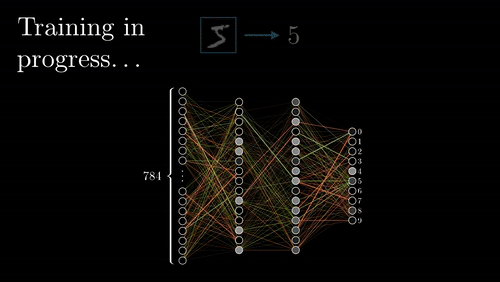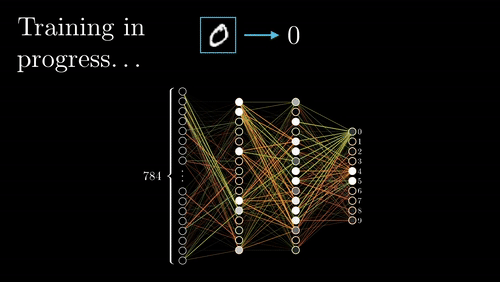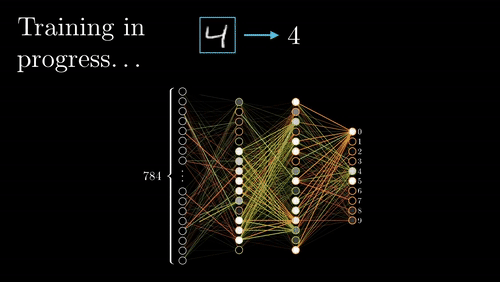
Visualization credit: Grant Sanderson, https://www.3blue1brown.com/.