What are the Azure IoT Suite preconfigured solutions?
The Azure IoT Suite preconfigured solutions are implementations of common IoT solution patterns that you can deploy to Azure using your subscription. You can use the preconfigured solutions:
- As a starting point for your own IoT solutions.
- To learn about common patterns in IoT solution design and development.
Each preconfigured solution is a complete, end-to-end implementation that uses simulated devices to generate telemetry.
You can download the complete source code to customize and extend the solution to meet your specific IoT requirements.
The following table shows how the solutions map to specific IoT features:
| Solution | Data ingestion | Device identity | Device management | Command and control | Rules and actions | Predictive analytics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remote monitoring | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | - |
| Predictive maintenance | Yes | Yes | - | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Connected factory | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | - |
- Data ingestion: Ingress of data at scale to the cloud.
- Device identity: Manage unique device identities and control device access to the solution.
- Device management: Manage device metadata and perform operations such as device reboots and firmware upgrades.
- Command and control: To cause the device to take an action, send messages to a device from the cloud.
- Rules and actions: To act on specific device-to-cloud data, the solution back end uses rules.
- Predictive analytics: The solution back end analyzes device-to-cloud data to predict when specific actions should take place. For example, analyzing aircraft engine telemetry to determine when engine maintenance is due.
Remote Monitoring preconfigured solution overview
We have chosen to discuss the remote monitoring preconfigured solution in this article because it illustrates many common design elements that the other solutions share.
The following diagram illustrates the key elements of the remote monitoring solution. The following sections provide more information about these elements.
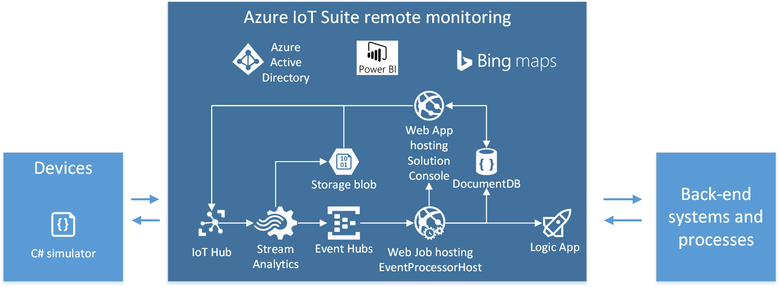
Devices
When you deploy the remote monitoring preconfigured solution, four simulated devices are pre-provisioned in the solution that simulate a cooling device. These simulated devices have a built-in temperature and humidity model that emits telemetry. These simulated devices are included to:
- Illustrate the end-to-end flow of data through the solution.
- Provide a convenient source of telemetry.
- Provide a target for methods or commands if you are a back-end developer using the solution as a starting point for a custom implementation.
The simulated devices in the solution can respond to the following cloud-to-device communications:
- Methods (direct methods): A two-way communication method where a connected device is expected to respond immediately.
- Commands (cloud-to-device messages): A one-way communication method where a device retrieves the command from a durable queue.
For a comparison of these different approaches, see Cloud-to-device communications guidance.
When a device first connects to IoT Hub in the preconfigured solution, it sends a device information message to the hub. This message enumerates the methods the device can respond to. In the remote monitoring preconfigured solution, simulated devices support these methods:
- Initiate Firmware Update: this method initiates an asynchronous task on the device to perform a firmware update. The asynchronous task uses reported properties to deliver status updates to the solution dashboard.
- Reboot: this method causes the simulated device to reboot.
- FactoryReset: this method triggers a factory reset on the simulated device.
When a device first connects to IoT Hub in the preconfigured solution, it sends a device information message to the hub. This message enumerates the commands the device can respond to. In the remote monitoring preconfigured solution, simulated devices support these commands:
- Ping Device: The device responds to this command with an acknowledgement. This command is useful for checking that the device is still active and listening.
- Start Telemetry: Instructs the device to start sending telemetry.
- Stop Telemetry: Instructs the device to stop sending telemetry.
- Change Set Point Temperature: Controls the simulated temperature telemetry values the device sends. This command is useful for testing back-end logic.
- Diagnostic Telemetry: Controls if the device should send the external temperature as telemetry.
- Change Device State: Sets the device state metadata property that the device reports. This command is useful for testing back-end logic.
You can add more simulated devices to the solution that emit the same telemetry and respond to the same methods and commands.
In addition to responding to commands and methods, the solution uses device twins. Devices use device twins to report property values to the solution back end. The solution dashboard uses device twins to set to new desired property values on devices. For example, during the firmware update process the simulated device reports the status of the update using reported properties.
IoT Hub
In this preconfigured solution, the IoT Hub instance corresponds to the Cloud Gateway in a typical IoT solution architecture.
An IoT hub receives telemetry from the devices at a single endpoint. An IoT hub also maintains device-specific endpoints where each device can retrieve the commands that are sent to it.
The IoT hub makes the received telemetry available through the service-side telemetry read endpoint.
The device management capability of IoT Hub enables you to manage your device properties from the solution portal and schedule jobs that perform operations such as:
- Rebooting devices
- Changing device states
- Firmware updates
Azure Stream Analytics
The preconfigured solution uses three Azure Stream Analytics (ASA) jobs to filter the telemetry stream from the devices:
- DeviceInfo job - outputs data to an Event hub that routes device registration-specific messages to the solution device registry. This device registry is an Azure Cosmos DB database. These messages are sent when a device first connects or in response to a Change device state command.
- Telemetry job - sends all raw telemetry to Azure blob storage for cold storage and calculates telemetry aggregations that display in the solution dashboard.
- Rules job - filters the telemetry stream for values that exceed any rule thresholds and outputs the data to an Event hub. When a rule fires, the solution portal dashboard view displays this event as a new row in the alarm history table. These rules can also trigger an action based on the settings defined on the Rules and Actions views in the solution portal.
In this preconfigured solution, the ASA jobs form part of to the IoT solution back end in a typical IoT solution architecture.
Event processor
In this preconfigured solution, the event processor forms part of the IoT solution back end in a typical IoT solution architecture.
The DeviceInfo and Rules ASA jobs send their output to Event hubs for delivery to other back-end services. The solution uses an EventProcessorHost instance, running in a WebJob, to read the messages from these Event hubs. The EventProcessorHost uses:
- The DeviceInfo data to update the device data in the Cosmos DB database.
- The Rules data to invoke the Logic app and update the alerts display in the solution portal.
Device identity registry, device twin, and Cosmos DB
Every IoT hub includes a device identity registry that stores device keys. IoT Hub uses this information authenticate devices - a device must be registered and have a valid key before it can connect to the hub.
A device twin is a JSON document managed by the IoT Hub. A device twin for a device contains:
- Reported properties sent by the device to the hub. You can view these properties in the solution portal.
- Desired properties that you want to send to the device. You can set these properties in the solution portal.
- Tags that exist only in the device twin and not on the device. You can use these tags to filter lists of devices in the solution portal.
This solution uses device twins to manage device metadata. The solution also uses a Cosmos DB database to store additional solution-specific device data such as the commands supported by each device and the command history.
The solution must also keep the information in the device identity registry synchronized with the contents of the Cosmos DB database. The EventProcessorHost uses the data from DeviceInfo stream analytics job to manage the synchronization.
Solution portal
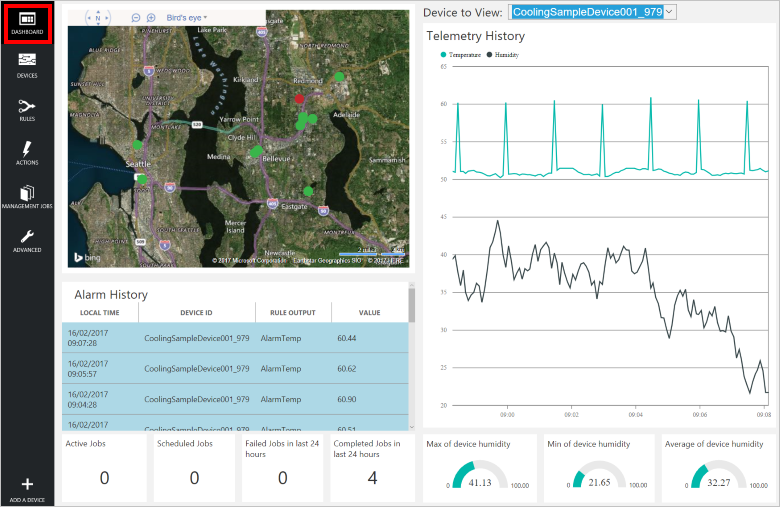
The solution portal is a web-based UI that is deployed to the cloud as part of the preconfigured solution. It enables you to:
- View telemetry and alarm history in a dashboard.
- Provision new devices.
- Manage and monitor devices.
- Send commands to specific devices.
- Invoke methods on specific devices.
- Manage rules and actions.
- Schedule jobs to run on one or more devices.
In this preconfigured solution, the solution portal forms part of the IoT solution back end and part of the Processing and business connectivity in the typical IoT solution architecture.
Next steps
For more information about IoT solution architectures, see Microsoft Azure IoT services: Reference Architecture.
Now you know what a preconfigured solution is, you can get started by deploying the remote monitoring preconfigured solution: Get started with the preconfigured solutions.