Define authentication
Authentication is the process of proving that a person is who they say they are. When someone purchases an item with a credit card, they may be required to show an additional form of identification. This proves that they are the person whose name appears on the card. In this example, the user may show a driver’s license that serves as a form of authentication and proves their ID.
When you want to access a computer or device, you'll encounter the same type of authentication. You may get asked to enter a username and password. The username states who you are, but by itself isn't enough to grant you access. When combined with the password, which only that user should know, it allows access to your systems. The username and password are a form of authentication.
Strong authentication methods are essential to maintaining good cybersecurity and ensure that only authorized users can gain access to confidential data and resources.
While authentication will verify the user, it doesn't govern what a user can do once they've been authenticated. Control over what a user can do is called authorization and we'll cover that later in this module.
Authentication methods
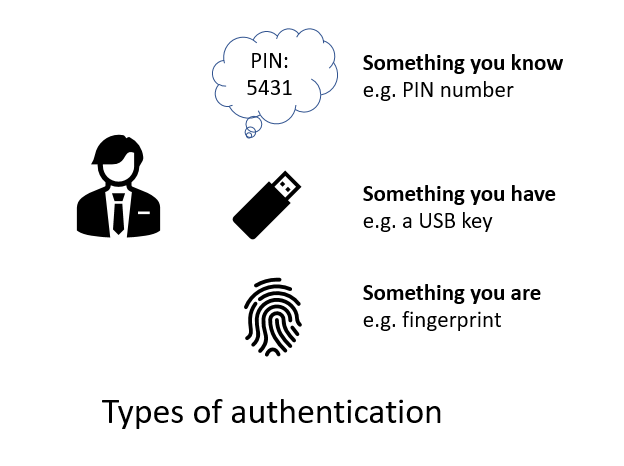
Authentication can be divided into three types: something you know, something you have, and something you are.
- Something you know includes:
- Passwords
- PIN numbers
- Security questions
- Something you have includes:
- Identity cards
- USB keys
- Computers
- Cell phones
- Something you are includes:
- A fingerprint
- Facial recognition
- Retinal scan
- Other forms of biometric ID.
Biometric identification is comprised of physical characteristics that uniquely identify an individual.
Single-factor authentication
Single-factor authentication is a system where only one authentication type is used, making it the least secure but simplest method.
An example of this system is when the user provides something they know, such as a password, to authenticate. Simple passwords are straightforward to remember but easy for criminals to hack. Complex passwords might seem more secure, but they'll be impossible to remember. It's more likely that someone will write down this type of password, making it much less secure.
Another single-factor authentication method is to use something you have. For example, using your cell phone to pay for an item. A tap-to-pay service authenticates the user through something that they have but doesn't require another verification method.
A biometric, something you are, can be used as a single-factor authentication method, but in some common scenarios, it's not necessarily more secure. Consider, for example, when you use a fingerprint to unlock your cell phone. You've probably known instances where the fingerprint might not be readily recognized, so you're given the option to enter a pin. This can make it easier for someone to guess. In most biometric cases, it's used in conjunction with another form of authentication.
Single-factor authentication is convenient but isn't suitable for a highly secure system.
Multifactor authentication
Multifactor authentication is a system where two, or even three, authentication types are used. By providing something that you know, something that you have, and something that you are, the system's security is massively increased. For example, in a multifactor authentication system that uses two types of authentications, you might be asked for a password, and then a number is sent to your cell phone. You input this number, proving that you know the password and have your cell phone. This is a common approach when you use multifactor authentication to access an online bank account. Multifactor authentication reduces the likelihood that a bad actor will be able to get access to confidential information.
As mentioned earlier, biometric authentication is most often used in conjunction with another method of authentication. Consider the example of a bank that has a secured area where it keeps customers’ safety deposit boxes. Before someone can gain access, they're typically required to successfully enter both a password and a fingerprint scan.
Multifactor authentication is an important way users and organizations can improve security. It should be the default approach for authentication.