Explore server and database audit
Azure SQL auditing tracks database events and writes them to an audit log in your Azure Storage account, Log Analytics workspace or Event Hubs. In addition, it enables you to maintain regulatory compliance, analyze activity patterns, and identify deviations that may indicate security violations.
You can define server-level and database-level policies. Server policies automatically cover new and existing databases in Azure.
- If server auditing is enabled, the database will be audited, regardless of the database auditing settings.
- In addition to enabling auditing on the server, you can also enable it on the database. This allows both audits to exist simultaneously; the server policy and the database policy.
It is best not to enable both server auditing and database auditing together, unless:
- A different storage account, retention period or Log Analytics Workspace is used for a specific database.
- An audit is needed for a specific database that differs from the rest on the server, such as different event types or categories.
For all the other cases, we recommend that you enable only server-level auditing and leave the database-level auditing disabled for all databases.
The default auditing policy for SQL Database includes the following set of action groups:
| Action group | Definition |
|---|---|
| BATCH_COMPLETED_GROUP | Audits all the queries and stored procedures executed against the database. |
| SUCCESSFUL_DATABASE_AUTHENTICATION_GROUP | This indicates that a principal succeed to log into the database. |
| FAILED_DATABASE_AUTHENTICATION_GROUP | This indicates that a principal failed to log into the database. |
To enable auditing for all databases on an Azure SQL server, select Auditing in the Security section of the main blade for your server.
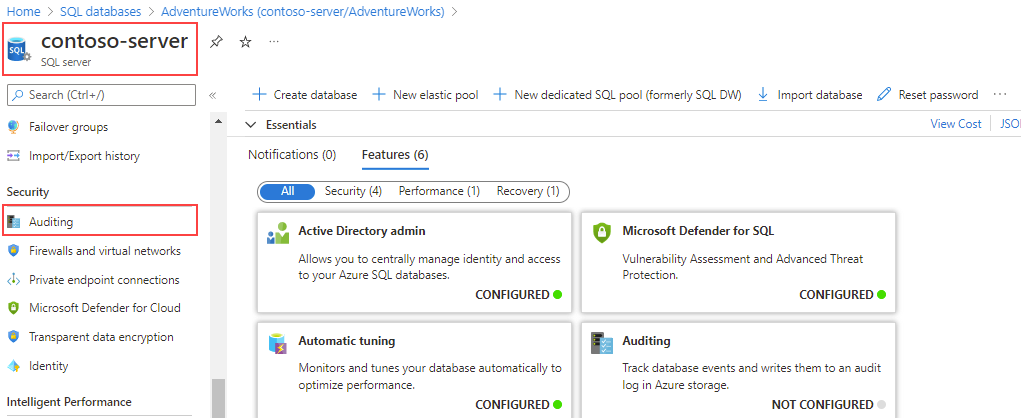
The Auditing page allows you to set the audit log destination and also choose whether to track Microsoft support engineer operations on the same log destination as Azure SQL Auditing or select a different one.
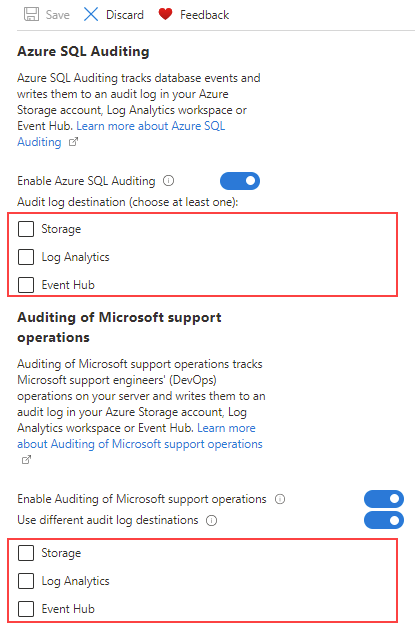
You can review the audit logs of Microsoft Support operations in your Log Analytics workspace by running the following query:
AzureDiagnostics
| where Category == "DevOpsOperationsAudit"
The auditing services for SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance are optimized for availability and performance. SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance may not record some audited events when there is a high rate of activity or high network load.
Note
Auditing on Read-Only replicas is automatically enabled.
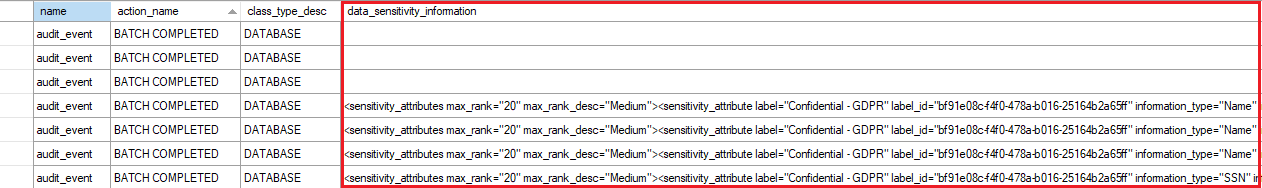
Audit sensitive labels
When combined with data classification, you can also monitor access to sensitive data. Azure SQL Auditing has been enhanced to include a new field in the audit log called data_sensitivity_information.
By logging the sensitivity labels of the data returned by a query, this field provides an easier way to track access to classified columns.
Auditing consists of tracking and recording events that occur in the database engine. Azure SQL auditing simplifies the configuration steps required to enabled it, making it easier to track database activities for SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance.