Explore the fundamentals of PKI and AD CS
To obtain certificates for your AD DS infrastructure, you can request them from a public CA or issue them by using your own infrastructure. To implement your own CA, you can use AD CS, which is the path that Contoso chose to take. AD CS is an identity technology in Windows Server that allows you to implement PKI for your organization.
What is PKI?
PKI is the combination of software, encryption technologies, processes, and services that enables an organization to secure its data, communications, and business transactions. PKI relies on the exchange of digital certificates between authenticated users and trusted resources. You use certificates to secure data and to manage identification credentials from users and computers both within and outside of your organization.
What is AD CS?
You can implement a PKI solution by using the AD CS Windows Server role. AD CS provides all PKI-related components as role services. Each role service is responsible for a specific portion of the certificate infrastructure while working together to form a complete solution.
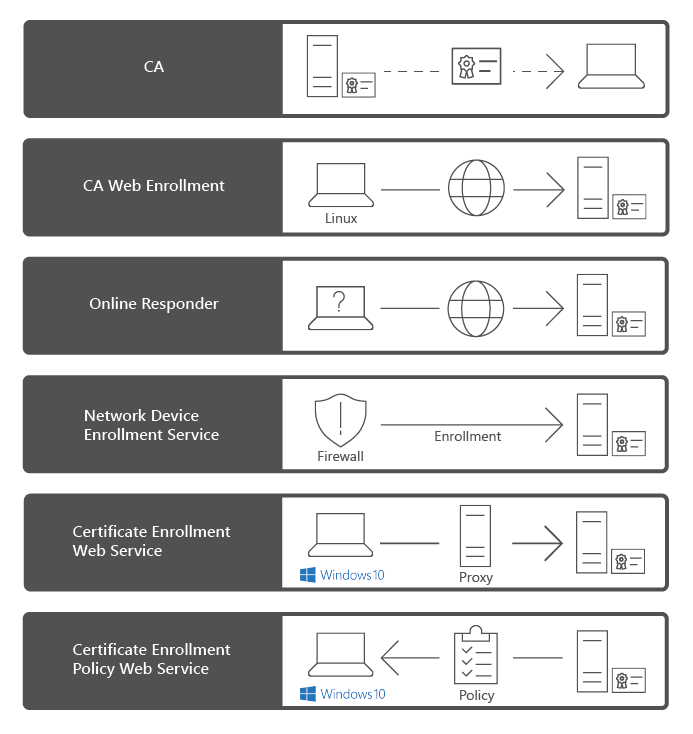
The AD CS role includes the following role services:
Certification Authority. The main purposes of CAs are to issue certificates, to revoke certificates, and to publish authority information access (AIA) and revocation information. The first CA you deploy becomes the root of your internal PKI. Subsequently, you can deploy subordinate CAs, positioned within the PKI hierarchy, with the root CA at its top. Subordinate CAs implicitly trust the root CA and, by implication, certificates it issues.
Note
You have the option of deploying multiple internal CA hierarchies, each with its own root.
Certification Authority Web Enrollment. This component provides a method to issue and renew certificates in scenarios where users use devices that are not joined to the domain or are running operating systems other than Windows.
Online Responder. You can use this component to configure and manage Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) validation and revocation checking. An Online Responder decodes revocation status requests for specific certificates, evaluates the status of those certificates, and returns a signed response that has the requested certificate status information.
Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES). With this component, routers, switches, and other network devices can obtain certificates from AD CS.
Certificate Enrollment Web Service (CES). This component works as a proxy client between a computer running Windows and the CA. CES enables users, computers, or applications to connect to a CA by using web services to:
- Request, renew, and install issued certificates.
- Retrieve certificate revocation lists (CRLs).
- Download a root certificate.
- Enroll over the internet or across forests.
- Renew certificates automatically for computers that are part of untrusted AD DS domains or are not joined to a domain.
Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service. This component enables users to obtain certificate enrollment policy information. Combined with CES, it enables policy-based certificate enrollment in scenarios where user devices are not joined to the domain or can't connect to a domain controller.