Define the architecture, components, and functionality of Data Deduplication
Most organizations and businesses, including Contoso, must deal with processing and storing an increasing volume of data. While there are solutions that allow you to offload and archive data to cloud, in many cases, it's necessary to maintain it in on-premises datacenters. Efficient management of storing such data requires proper tools. When using Windows Server, you have the option of using for this purpose Data Deduplication.
What is Data Deduplication?
Data Deduplication is a role service of Windows Server that identifies and removes duplications within data without compromising data integrity. This achieves the goals of storing more data and using less physical disk space.
To reduce disk utilization, Data Deduplication scans files, then divides those files into chunks, and retains only one copy of each chunk. After deduplication, files are no longer stored as independent streams of data. Instead, Data Deduplication replaces the files with stubs that point to data blocks that it stores in a common chunk store. The process of accessing deduplicated data is completely transparent to users and apps.
In many cases, Data Duplication increases overall disk performance, because multiple files can share one chunk cached in memory. This way, it might be possible to retrieve data from these files by performing fewer read operations, which compensates for a small performance impact when reading deduplicated files. Data deduplication has no impact on the performance of disk writes because it applies to data that is already on the disk.

What are the components of Data Deduplication?
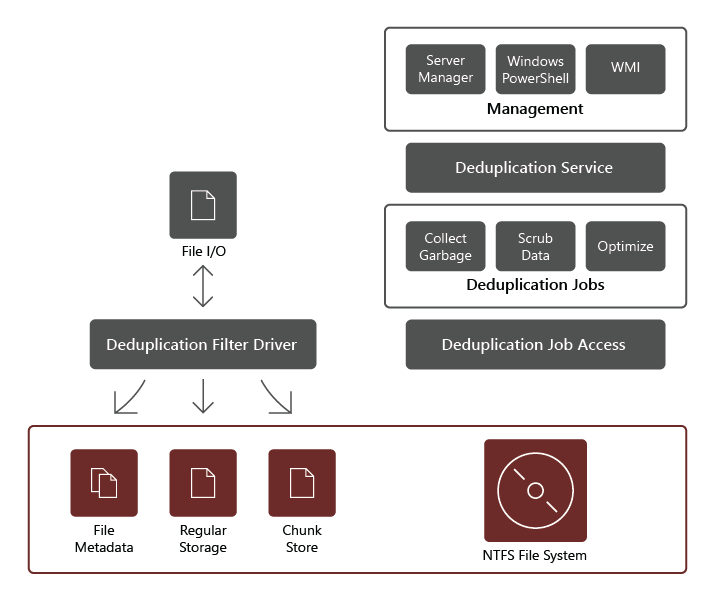
The Data Deduplication role service consists of the following components:
- Filter driver. This component redirects read requests to the chunks that are part of the file being requested. There is one filter driver for every volume.
- Deduplication service. This component manages the following jobs:
- Deduplication and compression. These jobs process files according to the data deduplication policy for the volume. After initial optimization of a file, if the file is then modified and meets the data deduplication policy threshold for optimization, the file will be optimized again.
- Garbage Collection. This job processes deleted or modified data on the volume so that any data chunks no longer being referenced are cleaned up, yielding free disk space. By default, Garbage Collection runs weekly, however, you might also consider invoking it after deleting many files.
- Scrubbing. This job relies on such resiliency features as checksum validation and metadata consistency checking to identify and, whenever possible, automatically resolve data integrity issues.
Note
Because of the additional validation capabilities, deduplication can detect and report early signs of data corruption.
- Unoptimization. This job reverses deduplication on all the optimized files on the volume. Some of the common scenarios for using this type of job include troubleshooting issues with deduplicated data or migration of data to another system that doesn't support Data Deduplication.
Note
Before you start this job, you should use the Disable-DedupVolume Windows PowerShell cmdlet to disable further data deduplication activity on one or more volumes.
Note
After disabling Data Deduplication, the volume remains in the deduplicated state, and the existing deduplicated data remains accessible; however, the server stops running optimization jobs for the volume, and it doesn't deduplicate the new data. Afterwards, you could use the unoptimization job to undo the existing deduplicated data on a volume. At the end of a successful de-optimization job, all the data deduplication metadata is deleted from the volume.
Important
When using the unoptimization job, make sure to verify that the volume hosting this data has enough free space, because all the deduplicated files will revert to their original size.
Scope of Data Deduplication
Data Deduplication process all the data on a selected volume, with a few exceptions, including:
- Files that don't meet the deduplication policy you configure.
- Files in folders that you explicitly exclude from the scope of deduplication.
- System state files.
- Alternate data streams.
- Encrypted files.
- Files with extended attributes.
- Files smaller than 32 KB.
Note
Since Windows Server 2019, Resilient File System (ReFS) supports data deduplication for volumes of up to 64 terabytes (TB) in size and files of up to 4 TB in size. It also relies on a variable-size chunk store that includes optional compression to maximize disk space savings, while the multiple-threaded post-processing architecture keeps performance impact at minimum.