How Azure Front Door works
In this unit, you learn how Azure Front Door works and how it:
- Helps provide fast, secure, and scalable access to your web applications.
- Helps protect your cloud-based apps.
- Provides high-bandwidth content.
Azure Front Door optimizes access times to content. In the following diagram, users are connecting to content hosted in the custom domain contoso.com. Azure Front Door is implemented at multiple edge locations. Azure Front Door provides CDN features that optimize access to backend contents, while the firewall helps to secure that access.
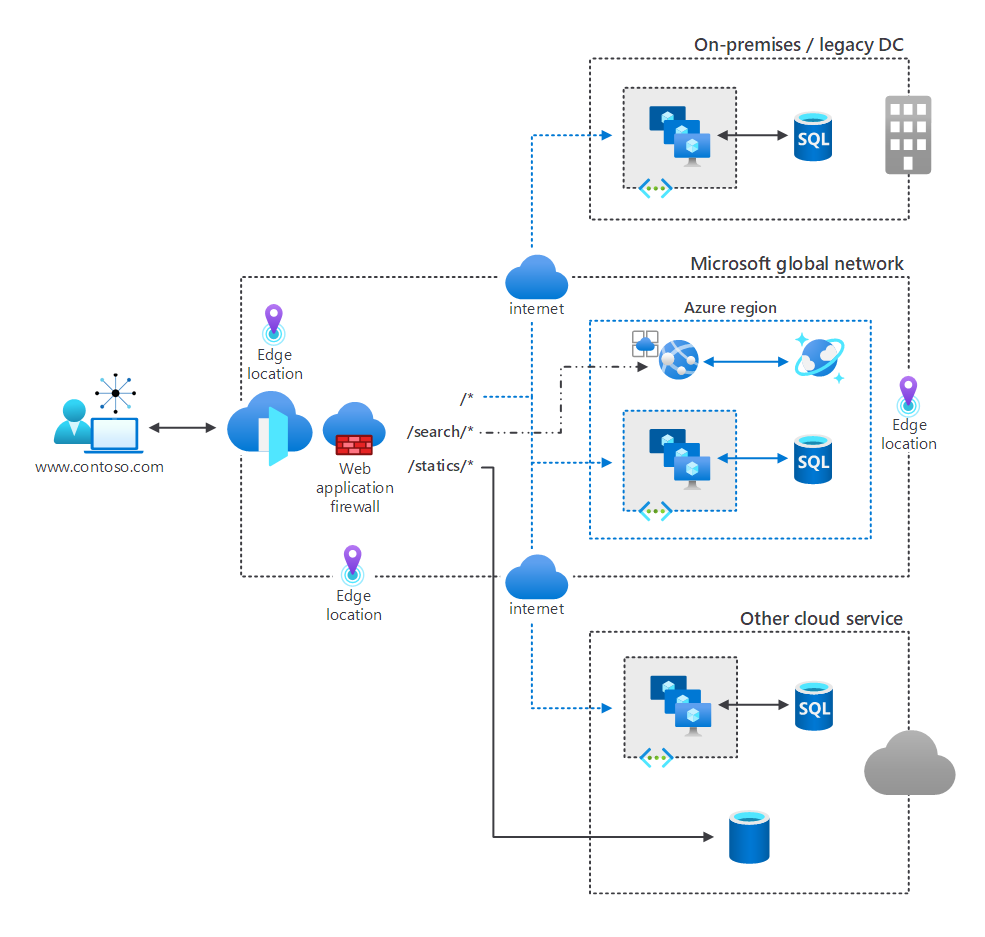
How Azure Front Door optimizes content delivery
Azure Front Door uses the anycast protocol with split TCP at layer 7 to route HTTP/S client requests to the most available and fastest application backend. The way Azure Front Door routes requests depend on the routing method you select, and on backend health. Azure Front Door supports four routing methods, as the following table describes:
| Routing method | Description |
|---|---|
| Latency | Helps ensure requests are sent to the lowest latency backends, within an acceptable sensitivity range. |
| Priority | Uses administrator-assigned priorities to your backends when you want to configure a primary backend to service all traffic. |
| Weighted | Uses administrator-assigned weights to your backends when you want to distribute traffic across a set of backends. |
| Session Affinity | Allows you to configure session affinity for your frontend hosts or domains. This helps ensure requests from the same end user are sent to the same backend. |
Azure Front Door also provides backend health monitoring options. Azure Front Door periodically assesses the health of each of your configured backends. Responses from these backends enable Azure Front Door to determine to which backend resources your client requests can be routed.
Note
Azure Front Door is resilient to failures, including failures of an entire Azure region due to the many edge locations strategically placed around the world.
A CDN is a distributed collection of web servers. These servers deliver web-based content to users. To help minimize latency, CDN's use point-of-presence locations that are next to users, to cache content.
Azure Front Door provides the following key CDN features:
- Dynamic site acceleration
- CDN caching rules
- HTTPS custom domain support
- Azure diagnostics logs
- File compression
- Geo-filtering
How Azure Front Door helps secure content
Azure Front Door provides web-application firewall capabilities to help protect your web applications from exploits and vulnerabilities. Managing security for your applications can be challenging because web applications are increasingly targeted.
Azure Front Door operates at the network's edge, close to potential attacks. This helps prevent attacks before they can enter your network. Azure Front Door's web application firewall is based on policies you can associate with one or more instances of Azure Front Door. These firewall policies consist of:
- Managed rule sets, which are a collection of preconfigured rules
- Custom rules that you can configure
Note
If present, custom rules are processed first.
A rule consists of:
- A condition, which determines whether a rule applies to traffic.
- A priority, which determines the order in which a rule gets processed, based on importance.
- An action, which can be Allow, Block, Log, or Redirect.
- A mode. There are two modes:
- Detection: Azure Web Application Firewall only monitors and logs when in this mode. However, it takes no other action.
- Prevention: Azure Web Application Firewall takes the defined action while in this mode.
In the next unit, let's consider the factors that will help you determine which Azure Front Door tier is most appropriate for your organizational needs.