Connect Azure Kubernetes Service on Azure Stack HCI to Azure Arc for Kubernetes
With the advent of changes in its technological landscape, Contoso CIO is looking for opportunities to modernize its operational model. The current one lacks consistency, forcing IT staff to deal with multiple, disparate management and monitoring products. This fragmented approach becomes even more problematic because Contoso is preparing for migrating some of its workloads to Azure and containerizing many others. You decide to evaluate to what extent these challenges can be addressed by using Azure Arc.
What is Azure Arc?
Azure Arc consists of a set of technologies that simplify the administration of complex, distributed, hybrid environments. It provides a centralized, scalable, and consistent multi-cloud and on-premises governance, management, and monitoring platform.
From the architectural standpoint, Azure Arc is a cloud-based solution that relies on an agent that customers such as Contoso deploy to their on-premises servers. Each on-premises resource with a locally installed agent has its representation in the form of an Azure resource.
The combination of the agent and an Azure-based resource allows centralized monitoring and management. The state of the cloud-based resource reflects the state of the on-premises servers, which allows for Azure-based monitoring. To manage the workloads running on the on-premises servers, you can use technologies such as Microsoft Azure Policy and Azure VM extensions.
What are the benefits of Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes and AKS on Azure Stack HCI?
Azure Arc enables integration of non-Azure resources with Azure, helping companies such as Contoso to provide a consistent administrative model across on-premises and cloud resources. At the same time, by keeping your resources on-premises, you can continue using your existing management methods as you transition to the new operational model.
Many Azure Arc benefits are independent of the resource type because they reflect the capabilities of Azure Resource Manager. These benefits include:
- The ability to organize all organizational resources by using Azure management groups, subscriptions, resource groups, and tags.
- A single, comprehensive inventory of organizational assets across multi-clouds and on-premises.
- A consolidated view of Azure and Azure Arc-enabled resources by using the Azure portal, Microsoft Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, and Azure REST API.
- Integration with Microsoft Azure Monitor for comprehensive, cloud-based monitoring spanning on-premises datacenters, Azure, and other third-party clouds.
There are also benefits specific to Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes and AKS on Azure Stack HCI, such as:
- Enforcement of run-time policies by using Azure Policy for Kubernetes and centralized reporting of the policy compliance, which allows you to enforce HTTPS ingress in Kubernetes cluster and ensure that pods listen only on secured ports.
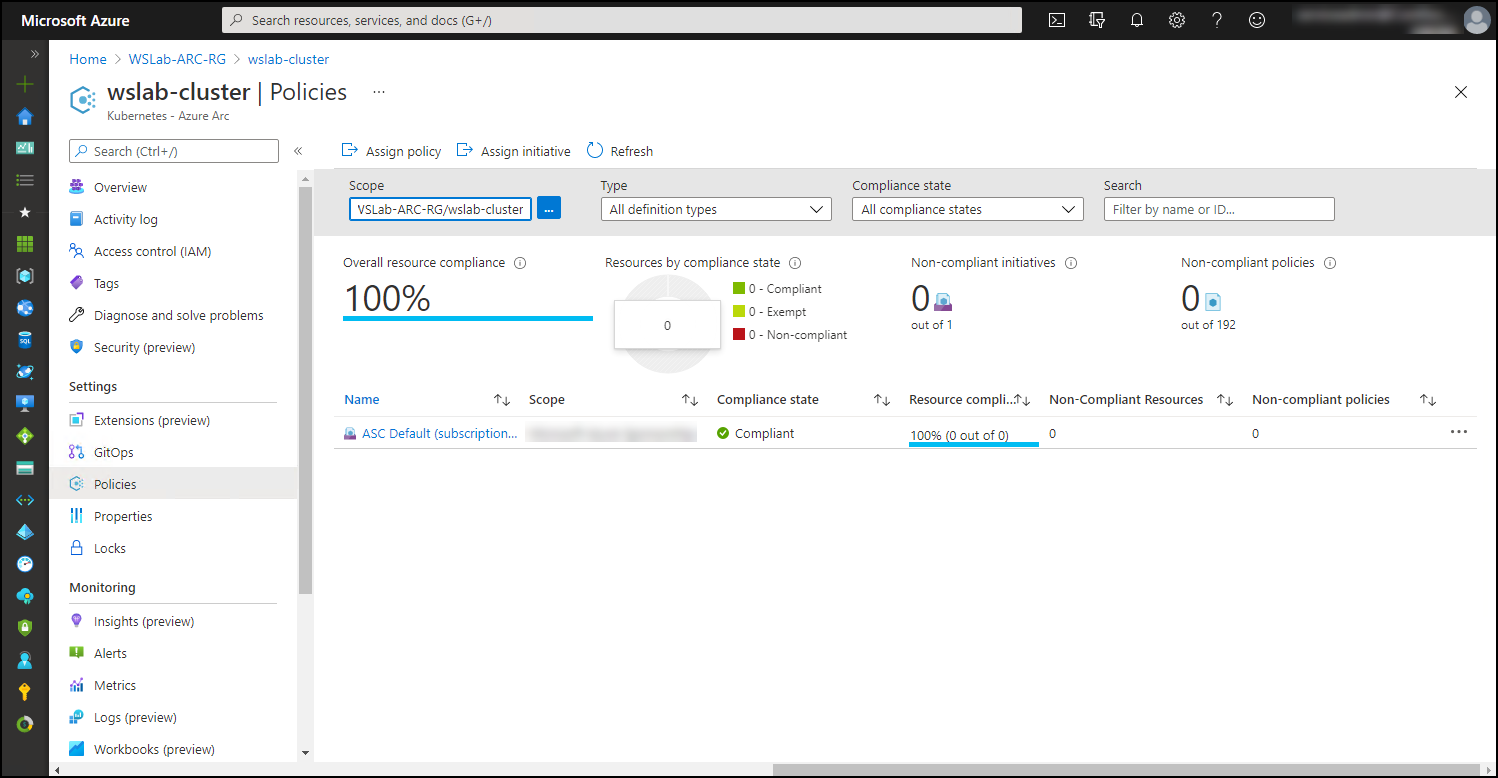
- Support for automated updates to cluster configuration by using GitOps. GitOps is the practice of automatically deploying the code residing in a Git repository. In this scenario, that code describes a YAML-based desired state of the Kubernetes configuration. You can enforce specific GitOps-based configurations by using Azure Policy, which also provides centralized reporting of the policy compliance.
Connect an AKS on Azure Stack HCI cluster to Azure Arc for Kubernetes
In Azure Stack HCI clusters, the Azure Arc agent is already included as part of the operating system of cluster nodes. You activate it by registering your Azure Stack HCI cluster with Azure Arc, which automatically enables Azure monitoring, support, and billing.
For Kubernetes clusters hosted by AKS on Azure Stack HCI, connection to Azure requires deploying containerized agents into a designated cluster namespace (azure-arc). The agents are responsible for maintaining connectivity to Azure, collecting Azure Arc logs and metrics, and processing configuration requests.
Note
For onboarding to succeed, the AKS on Azure Stack HCI cluster must contain at least one operational node in a Linux worker node pool.
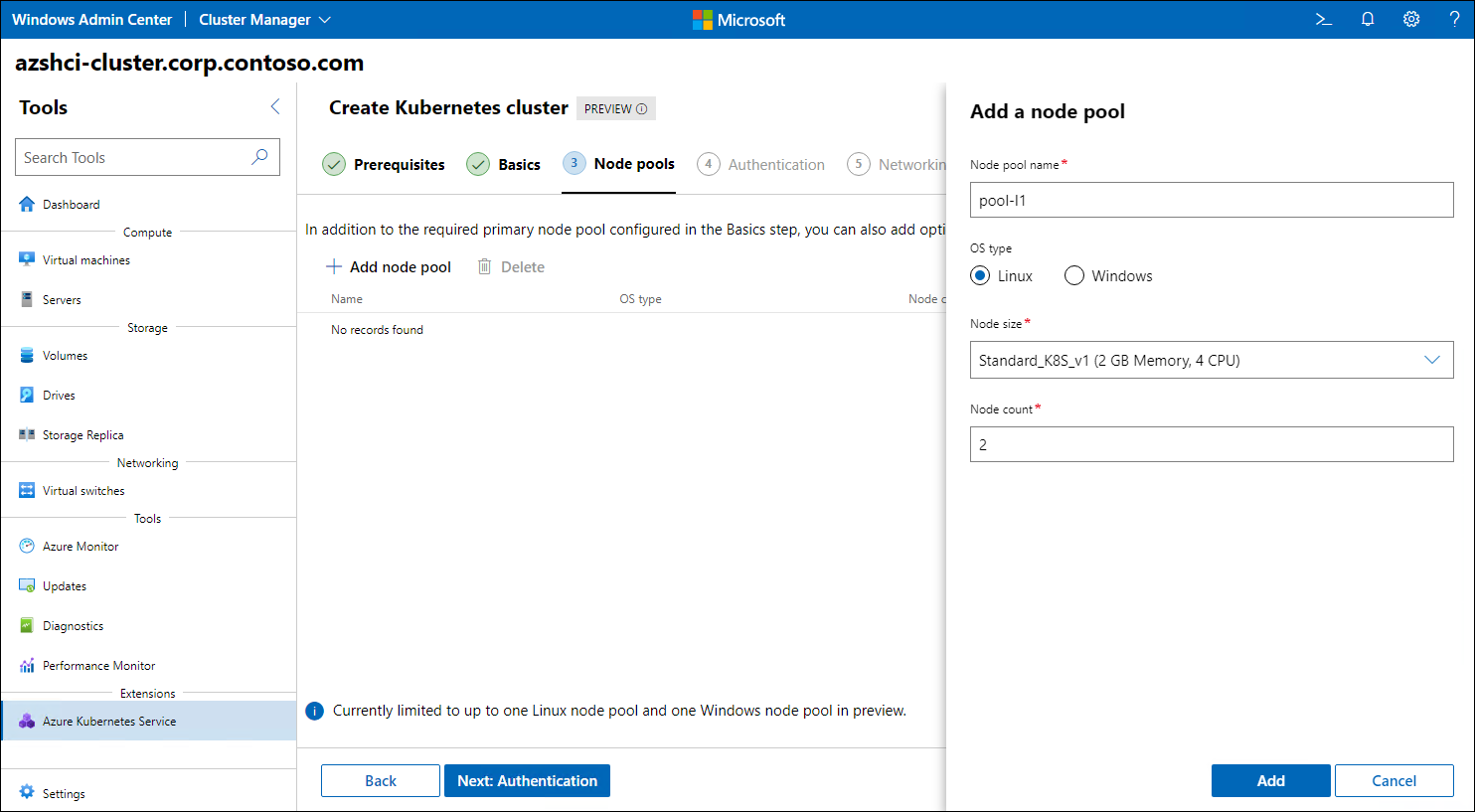
To simplify the onboarding process, use Windows Admin Center. Such onboarding happens automatically if you follow the cluster creation process described in the previous unit of this module. Alternatively, you can script this process by using Azure CLI or PowerShell.
If you choose the scripting approach to connect Kubernetes clusters on an Azure Stack HCI cluster to Azure Arc, run the following sequence of steps from an on-premises computer with connectivity to the Azure Stack HCI cluster and to Azure:
- Install the current version of the Azure CLI version with the Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes CLI extensions and the AKS on Azure Stack HCI PowerShell module.
- Use Azure CLI to sign in to Microsoft Entra ID to access the Azure subscription where you've at least the Contributor role and where you intend to register your Kubernetes clusters.
- Use Azure CLI to register the Microsoft.Kubernetes and Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration Azure Resource Manager resource providers. This step is necessary to implement Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes. Using Azure CLI is a one-time only setup for a given subscription.
- Use Azure CLI to create a resource group that will host the connected cluster resources in an Azure region that supports Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes.
- Use Azure CLI to create a service principal with the Contributor role in the resource group you created in the previous step and record its credentials.
- Use the AKS on Azure Stack HCI PowerShell module to connect the Kubernetes cluster to Azure Arc in the target subscription, authenticating with the service principal credentials. This step deploys the Azure Arc agents for Kubernetes into the azure-arc namespace.