Prepare for disaster recovery with Azure Site Recovery
In the previous unit, we explored the capabilities of Azure Site Recovery. Our next step is to prepare for disaster recovery in our Azure environment.
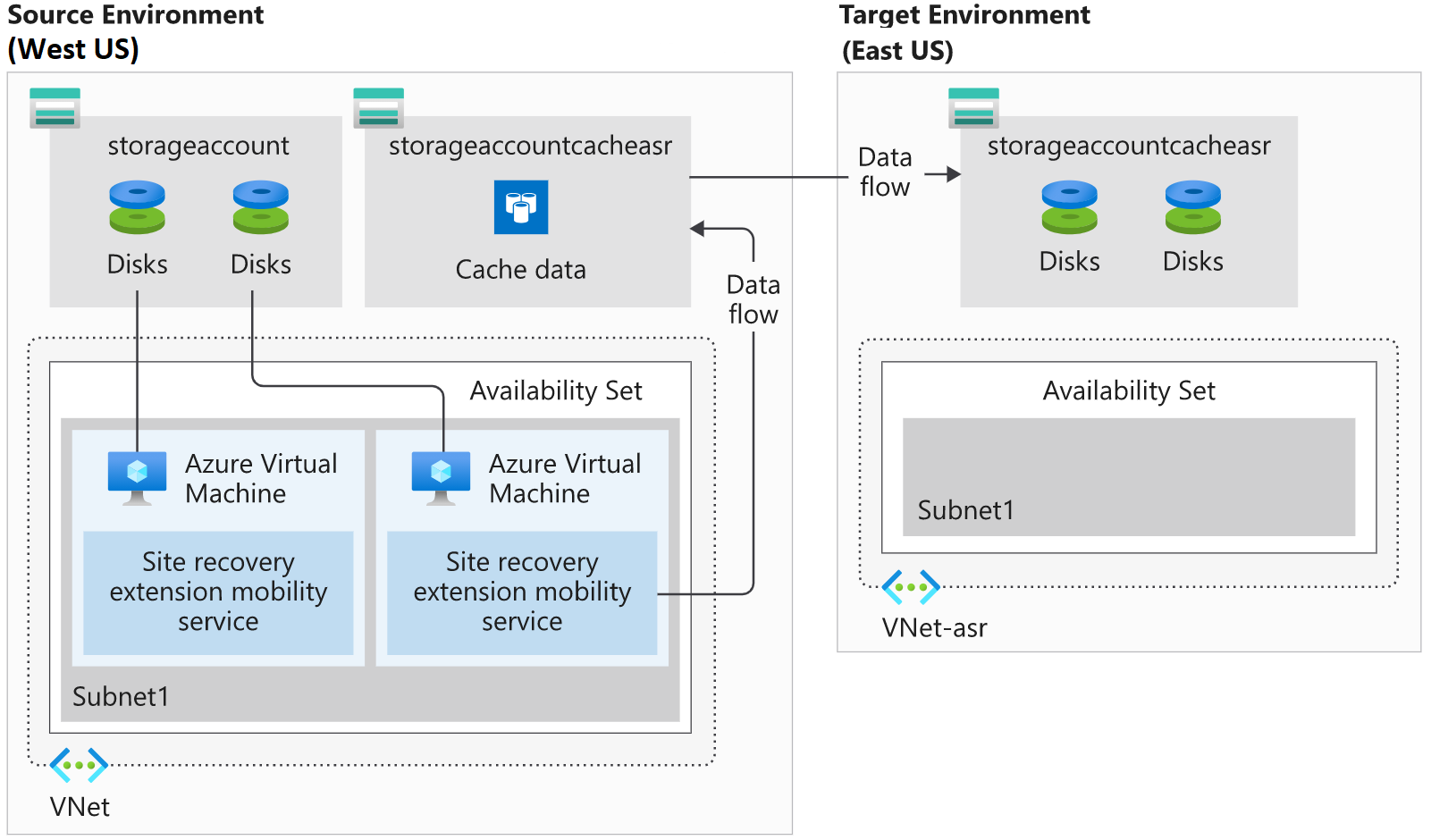
Using our organization's business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) plan, we can run through the Site Recovery configurations and set a preparation plan in motion that fits with our organization's BCDR goals. Let's assume we're using the West US Azure region for our existing solution, and we've decided to use the East US region for replication.
Here, we'll explore how to take advantage of the automated features in Site Recovery to prepare for a disaster-recovery scenario.
Environment setup
We need to set up our environment for exercises in subsequent units. Because this setup takes a few minutes to complete, we'll start the process now, and then we can work through some of the theory while the configuration completes in the background.
Note
If you want to complete the following setup, but you don't have an Azure subscription or prefer not to use your account, you'll need to create a free account before you begin.
Let's assume we have two VMs configured in the organization. We'll configure the following services in the West US region to simulate the configured VMs.
- A virtual network
- Two VMs
- A storage account
We'll also configure a resource group in East US. We'll later configure Site Recovery to use the East US region as our target environment.
Our first step is to create our exercise environment. We'll run a script that creates our company's infrastructure in Azure. After the script completes, we'll have a virtual network, two VMs, and a storage account that we'll use for our Recovery Services vault.
Sign in to the Azure portal with your credentials, and start a Cloud Shell session.
In Cloud Shell toolbar, make sure you're running a Bash session.
Use the following command to copy the Azure Resource Manager JSON templates to create your company's infrastructure:
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftDocs/mslearn-protect-infrastructure-with-azure-site-recovery/master/deploy.json > deploy.jsonRun the following commands to create resource groups and the company's infrastructure:
az group create --name east-coast-rg --location eastus2 az group create --name west-coast-rg --location westus2 az deployment group create \ --name asrDeployment \ --template-file deploy.json \ --parameters storageAccounts_asrcache_name=asrcache$RANDOM \ --resource-group west-coast-rg
Configuring the environment can take up to five minutes to complete. We can continue with the rest of this unit while the deployment completes.
Disaster recovery preparation with Azure Site Recovery
Site Recovery manages and orchestrates our DR process for Azure VMs or on-premises machines. However, to enable it, there are several components we need to configure. We'll need to:
- Add a Recovery Services vault
- Organize target resources
- Configure outbound network connectivity
- Set up replication on existing VMs
What is a Recovery Services vault?
A Recovery Services vault enables Site Recovery to complete disaster recovery replication. These vaults use storage accounts to store data backups, VM configuration settings, and workloads. To meet Site Recovery requirements, we'll provision a Recovery Services vault using the portal or the Azure CLI.
What are the target resources?
Target resources are all the Azure services created after your existing resources replicate. In this scenario, the East US region (target environment) is where all your target resources get created. There are a few considerations to keep in mind when selecting the target resources region:
- Target resources for Site Recovery replication have to be in a different Azure region.
- The storage account that stores the backed-up data must also be in a different region than the resources being protected.
- The target region creates VMs and has enough resources to match the size of the existing VMs.
Configure outbound network connectivity and URLs
Site Recovery requires outbound connectivity on the VMs that you want to replicate.
The required network connectivity is set up for you automatically when using VMs created in Azure. However, when you migrate on-premises VMs to Azure, you might need to update your network connectivity.
Site Recovery doesn't support controlling network connectivity via an authentication proxy. If your organization is using a URL-based firewall proxy to restrict outbound connectivity, you'll need to add access to several URLs.
| URL | Description |
|---|---|
| login.microsoftonline.com | For the Azure Site Recovery URLs to authenticate |
| *.blob.core.windows.net | To write VM data to the source storage account cache |
| *.hypervrecoverymanager.windowsazure.com | For Site Recovery to communicate with the VM |
| *.servicebus.windows.net | For Site Recovery monitoring and diagnostic data from the VM |
If you prefer to control the connectivity using IP addresses instead, you'll need to add the IP address ranges for:
- Azure datacenters
- Site Recovery endpoints
Update Azure VM root certificates
Every Azure VM you want to replicate has to register with Site Recovery. For a VM to register, Site Recovery requires the latest root certificates installed on the VM. On a Windows VM, you'll need to make sure to install all the latest Windows updates. The process for updating root certificates on Linux VMs varies from distribution to distribution. You'll need to follow the guidance the distributor publishes.
Configure account permissions
By default, Site Recovery uses role-based access control (RBAC) in Azure. RBAC enables fine-grained access control and enables you to use several built-in Site Recovery roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Site Recovery Contributor | A contributor has full permissions for Site Recovery operations in a Recovery Services vault, suitable for disaster recovery admins. |
| Site Recovery Operator | An operator has permissions to run and administer Site Recovery failover and failback operations, suitable for disaster recovery operators. |
| Site Recovery Reader | A reader has permissions to view Site Recovery operations, suitable for IT monitoring executives. |
To enable replication on a VM, a user must have permission to create a VM in both the virtual network and resource group.
What is Azure Mobility Service?
Azure Mobility Service needs to be installed on every VM that you replicate. This client is available for Windows and Linux VMs, and will be installed and configured automatically by Site Recovery. If the automatic installation fails, you can install the service manually.
The mobility service works in partnership with Site Recovery to keep an up-to-date cache of the VMs' data. The cache is replicated to the target environment's storage account. The replicated data is used if Site Recovery fails over the environment.