Principle: Climate commitments
Over the years, many terms have been used interchangeably when discussing an approach to reduce emissions. It's essential to have a common understanding of these terms to work towards an agreed goal.
Carbon reduction methodologies
There are many ways to reduce emissions. Understanding the exact reduction mechanism when planning to work toward these targets is essential.
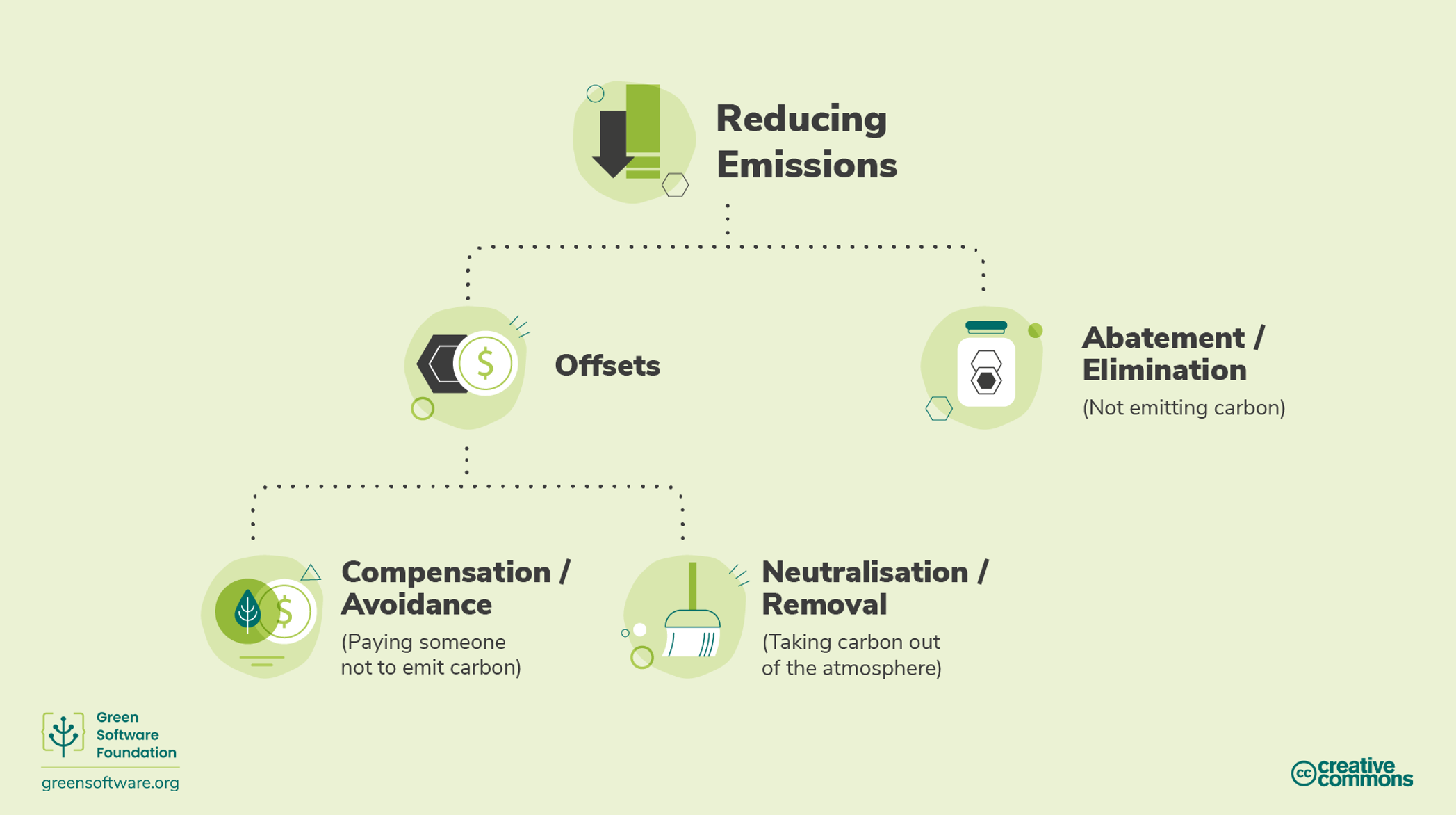
At the highest level, there are offsets or abatement. Offsetting involves reducing emissions elsewhere, whereas reduction or elimination involves not emitting carbon in the first place. It's understood that it's impossible not to emit carbon in today's society, and offsets provide an approach to supplement carbon reduction.
There are two mechanisms to offset; these are compensation and neutralization.
Compensation, sometimes called avoidance, involves paying someone else not to emit carbon. In comparison, neutralization or removal involves taking carbon out of the atmosphere. Examples include enhancing natural carbon sinks such as forest restoration, or direct air capture where carbon is removed from the air.
Climate commitments
There are many different climate-commitment strategies to which an organization can commit. Understanding the various meanings and implications can help identify the right strategy.

Carbon neutral
An organization must measure and match emissions through carbon reduction projects to achieve carbon neutrality. This can include carbon removal projects and carbon avoidance.
PAS 2060 is an internationally recognized carbon neutrality standard. To be carbon neutral, you must cover all emissions in scopes 1 and 2, and all scope 3 emissions that contribute to more than 1% of the total.
Net zero
Net zero means reducing and balancing residual emissions through carbon removals (neutralizations). Net zero, by definition, requires emissions reductions in line with a 1.5°C pathway.
The critical differentiator between net zero and carbon neutral is net zero's focus on abatement/elimination and compensations.
The Science Based Targets initiative is developing the standard for net zero.
For Net zero, 90% of emissions are eliminated and the remaining 10% are permanently neutralized.
Net zero must cover direct and indirect emissions from scopes 1, 2, and 3.