Enable CORS for interactive console in the API Management developer portal
Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is an HTTP-header based mechanism that allows a server to indicate any origins (domain, scheme, or port) other than its own from which a browser should permit loading resources.
To let visitors to the API Management developer portal use the interactive test console in the API reference pages, enable a CORS policy for APIs in your API Management instance. If the developer portal's domain name isn't an allowed origin for cross-domain API requests, test console users will see a CORS error.
For certain scenarios, you can configure the developer portal as a CORS proxy instead of enabling a CORS policy for APIs.
APPLIES TO: Developer | Basic | Standard | Premium
Prerequisites
- Complete the following quickstart: Create an Azure API Management instance
Go to your API Management instance
In the Azure portal, search for and select API Management services.
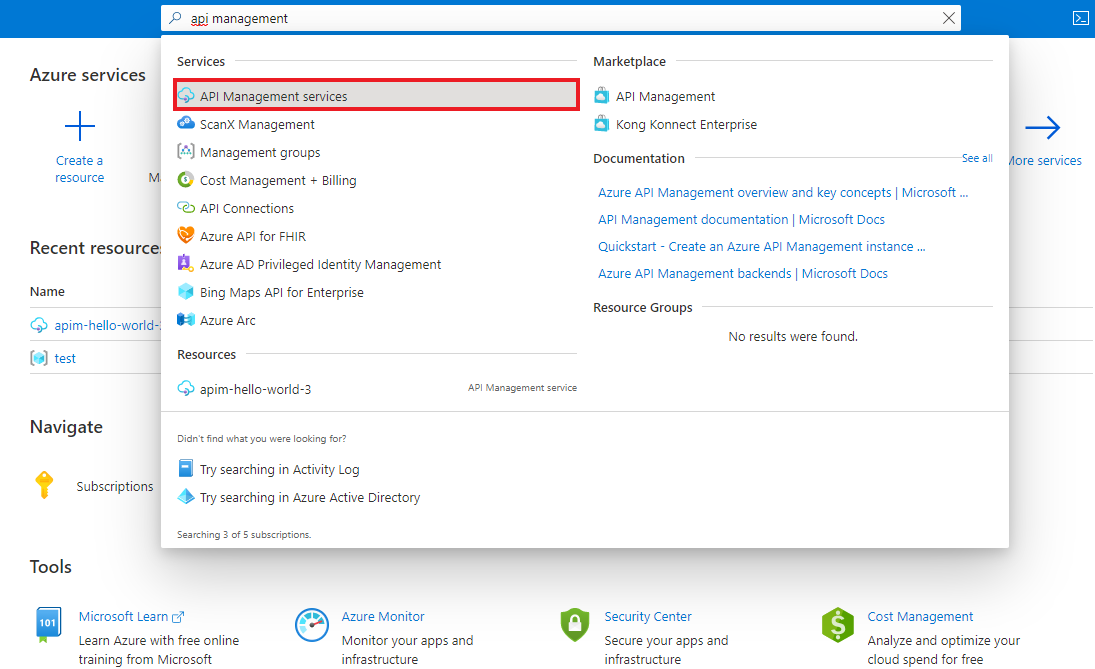
On the API Management services page, select your API Management instance.

Enable CORS policy for APIs
You can enable a setting to configure a CORS policy automatically for all APIs in your API Management instance. You can also manually configure a CORS policy.
Note
Only one CORS policy is executed. If you specify multiple CORS policies (for example, on the API level and on the all-APIs level), your interactive console may not work as expected.
Enable CORS policy automatically
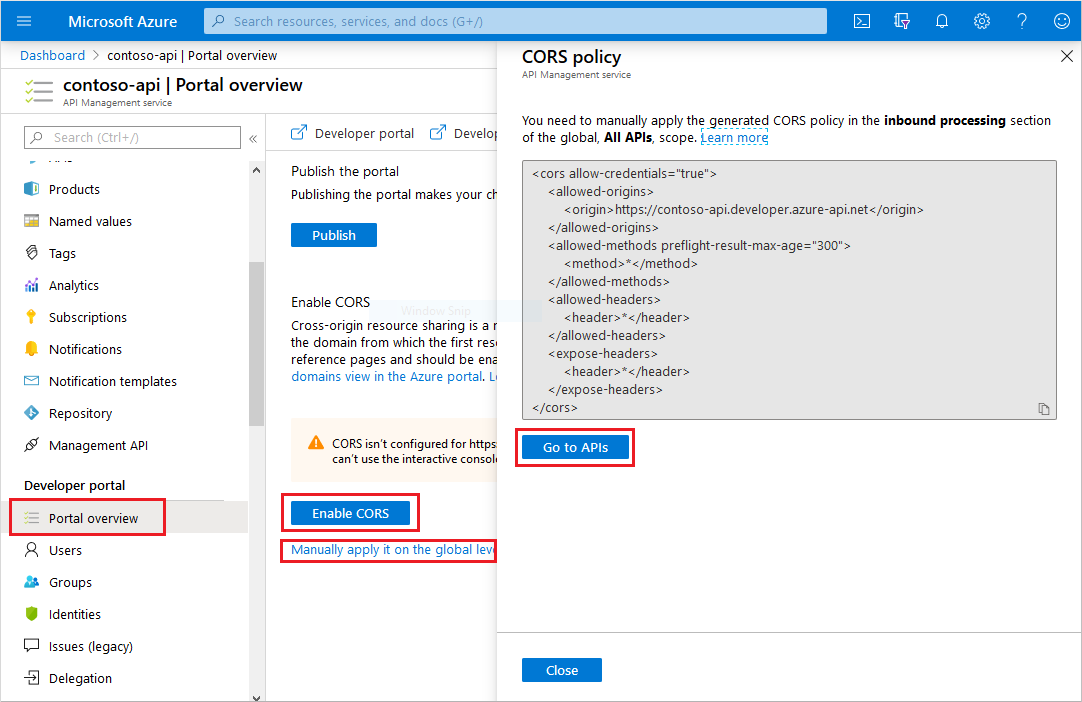
- In the left menu of your API Management instance, under Developer portal, select Portal overview.
- Under Enable CORS, the status of CORS policy configuration is displayed. A warning box indicates an absent or misconfigured policy.
- To enable CORS from the developer portal for all APIs, select Enable CORS.
Enable CORS policy manually
- Select the Manually apply it on the global level link to see the generated policy code.
- Navigate to All APIs in the APIs section of your API Management instance.
- Select the </> icon in the Inbound processing section.
- In the policy editor, insert the policy in the <inbound> section of the XML file. Make sure the <origin> value matches your developer portal's domain.
Note
If you apply the CORS policy in the Product scope, instead of the API(s) scope, and your API uses subscription key authentication through a header, your console won't work.
The browser automatically issues an OPTIONS HTTP request, which doesn't contain a header with the subscription key. Because of the missing subscription key, API Management can't associate the OPTIONS call with a Product, so it can't apply the CORS policy.
As a workaround, you can pass the subscription key in a query parameter.
CORS proxy option
For some scenarios (for example, if the API Management gateway is network isolated), you can choose to configure the developer portal as a CORS proxy itself, instead of enabling a CORS policy for your APIs. The CORS proxy routes the interactive console's API calls through the portal's backend in your API Management instance.
Note
If the APIs are exposed through a self-hosted gateway or your service is in a virtual network, the connectivity from the API Management developer portal's backend service to the gateway is required.
To configure the CORS proxy, access the developer portal as an administrator:
- On the Overview page of your API Management instance, select Developer portal. The developer portal opens in a new browser tab.
- In the left menu of the administrative interface, select Pages > APIs > Details.
- On the APIs: Details page, select the Operation: Details widget, and select Edit widget.
- Select Use CORS proxy.
- Save changes to the portal, and republish the portal.
CORS configuration for self-hosted developer portal
If you self-host the developer portal, the following configuration is needed to enable CORS:
Specify the portal's backend endpoint using the
backendUrloption in the configuration files. Otherwise, the self-hosted portal isn't aware of the location of the backend service.Add Origin domain values to the self-hosted portal configuration specifying the environments where the self-hosted portal is hosted. Learn more
Related content
- For more information about configuring a policy, see Set or edit policies.
- For details about the CORS policy, see the cors policy reference.
Tilbakemeldinger
Kommer snart: Gjennom 2024 faser vi ut GitHub Issues som tilbakemeldingsmekanisme for innhold, og erstatter det med et nytt system for tilbakemeldinger. Hvis du vil ha mer informasjon, kan du se: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Send inn og vis tilbakemelding for