ทําความเข้าใจการแมปมุมมองข้อมูลในวิชวล Power BI
บทความนี้อธิบายถึงการแมปมุมมองข้อมูลและอธิบายวิธีการใช้บทบาทข้อมูลเพื่อสร้างวิชวลชนิดต่าง ๆ ซึ่งอธิบายวิธีการระบุข้อกําหนดเงื่อนไขสําหรับบทบาทข้อมูลและชนิดที่แตกต่างกันdataMappings
การแมปที่ถูกต้องแต่ละครั้งจะสร้างมุมมองข้อมูล คุณสามารถให้การแมปข้อมูลได้หลายรายการภายใต้เงื่อนไขบางประการ ตัวเลือกการแมปที่สนับสนุนคือ:
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"conditions": [ ... ],
"categorical": { ... },
"single": { ... },
"table": { ... },
"matrix": { ... }
}
]
Power BI สร้างการแมปไปยังมุมมองข้อมูลเฉพาะเมื่อมีการกําหนดการแมปที่ถูกต้องใน dataViewMappingsด้วย
กล่าวอีกนัย categorical หนึ่งคือ อาจกําหนดใน dataViewMappings แต่การแมปอื่นๆ เช่น table หรือ singleอาจไม่เป็นเช่นนั้น ในกรณีดังกล่าว Power BI สร้างมุมมองข้อมูลด้วยการแมปเดียว categorical ในขณะที่ table การทําแผนที่อื่น ๆ ยังคงไม่ได้ถูกกําหนด ตัวอย่างเช่น:
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"categorical": {
"categories": [ ... ],
"values": [ ... ]
},
"metadata": { ... }
}
]
เงื่อนไข
ส่วน conditions สร้างกฎสําหรับการแมปข้อมูลที่เฉพาะเจาะจง ถ้าข้อมูลตรงกับชุดของเงื่อนไขที่อธิบายวิชวลจะยอมรับข้อมูลได้ถูกต้อง
สําหรับแต่ละเขตข้อมูล คุณสามารถระบุค่าต่ําสุดและสูงสุดได้ ค่า แสดงถึงจํานวนของเขตข้อมูลที่สามารถผูกกับบทบาทข้อมูลนั้นได้
หมายเหตุ
ถ้ามีการเว้นบทบาทข้อมูลไว้ในเงื่อนไข อาจมีเขตข้อมูลจํานวนเท่ากับจํานวนหนึ่ง
ในตัวอย่าง category ต่อไปนี้ จะจํากัดอยู่เพียงหนึ่งเขตข้อมูล และ measure ถูกจํากัดไว้ที่เขตข้อมูลสองเขต
"conditions": [
{ "category": { "max": 1 }, "measure": { "max": 2 } },
]
คุณยังสามารถตั้งค่าเงื่อนไขหลายเงื่อนไขสําหรับบทบาทข้อมูลได้ ในกรณีดังกล่าว ข้อมูลจะถูกต้องหากเป็นไปตามเงื่อนไขอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่ง
"conditions": [
{ "category": { "min": 1, "max": 1 }, "measure": { "min": 2, "max": 2 } },
{ "category": { "min": 2, "max": 2 }, "measure": { "min": 1, "max": 1 } }
]
ในตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ จําเป็นต้องใช้หนึ่งในสองเงื่อนไขต่อไปนี้:
- เขตข้อมูลประเภทหนึ่งรายการอย่างแน่นอนและหน่วยวัดสองรายการอย่างแน่นอน
- สองประเภทอย่างแน่นอนและหนึ่งหน่วยวัดอย่างแน่นอน
การแมปข้อมูลเดียว
การแมปข้อมูลเดี่ยวเป็นรูปแบบที่ง่ายที่สุดของการแมปข้อมูล ซึ่งเป็นการยอมรับเขตข้อมูลหน่วยวัดเดียวและส่งกลับผลรวม ถ้าเขตข้อมูลเป็นตัวเลข จะส่งกลับผลรวม มิฉะนั้นจะส่งกลับจํานวนของค่าที่ไม่ซ้ํากัน
หากต้องการใช้การแมปข้อมูลเดี่ยว ให้กําหนดชื่อของบทบาทข้อมูลที่คุณต้องการแมป การแมปนี้จะทํางานกับเขตข้อมูลหน่วยวัดเดียวเท่านั้น ถ้ามีการกําหนดเขตข้อมูลที่สอง จะไม่มีการสร้างมุมมองข้อมูล ดังนั้นจึงเป็นแนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่จะรวมเงื่อนไขที่จํากัดข้อมูลไว้ในเขตข้อมูลเดียว
หมายเหตุ
การแมปข้อมูลนี้ไม่สามารถใช้ร่วมกับการแมปข้อมูลอื่น ๆ ได้ ซึ่งหมายถึงการลดข้อมูลให้เป็นค่าตัวเลขเดียว
ตัวอย่างเช่น:
{
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Y",
"name": "Y",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"conditions": [
{
"Y": {
"max": 1
}
}
],
"single": {
"role": "Y"
}
}
]
}
มุมมองข้อมูลที่เกิดขึ้นยังคงสามารถมีการแมปชนิดอื่น ๆ ได้ เช่น ตารางหรือตามประเภท แต่การแมปแต่ละครั้งจะมีเพียงค่าเดียวเท่านั้น แนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดคือ เข้าถึงค่าเฉพาะในการแมปเดียวเท่านั้น
{
"dataView": [
{
"metadata": null,
"categorical": null,
"matrix": null,
"table": null,
"tree": null,
"single": {
"value": 94163140.3560001
}
}
]
}
ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้ประมวลผลการแมปมุมมองข้อมูลแบบง่าย:
"use strict";
import powerbi from "powerbi-visuals-api";
import DataView = powerbi.DataView;
import DataViewSingle = powerbi.DataViewSingle;
// standard imports
// ...
export class Visual implements IVisual {
private target: HTMLElement;
private host: IVisualHost;
private valueText: HTMLParagraphElement;
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
// constructor body
this.target = options.element;
this.host = options.host;
this.valueText = document.createElement("p");
this.target.appendChild(this.valueText);
// ...
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
const dataView: DataView = options.dataViews[0];
const singleDataView: DataViewSingle = dataView.single;
if (!singleDataView ||
!singleDataView.value ) {
return
}
this.valueText.innerText = singleDataView.value.toString();
}
}
ตัวอย่างโค้ดก่อนหน้านี้ส่งผลให้เกิดการแสดงค่าเดียวจาก Power BI:
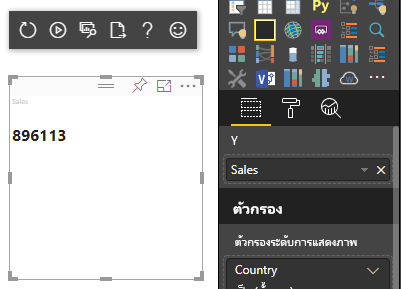
การแมปข้อมูลจัดกลุ่ม
การแมปข้อมูลจัดกลุ่มถูกใช้เพื่อให้ได้มาซึ่งการจัดกลุ่มหรือประเภทของข้อมูลอิสระ ประเภทยังสามารถจัดกลุ่มเข้าด้วยกันโดยใช้ "จัดกลุ่มตาม" ในการแมปข้อมูล
การแมปข้อมูลจัดกลุ่มพื้นฐาน
พิจารณาบทบาทข้อมูลต่อไปนี้และการแมป:
"dataRoles":[
{
"displayName": "Category",
"name": "category",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Y Axis",
"name": "measure",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"dataViewMappings": {
"categorical": {
"categories": {
"for": { "in": "category" }
},
"values": {
"select": [
{ "bind": { "to": "measure" } }
]
}
}
}
ตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้อ่าน "แมปบทบาทข้อมูลของฉันcategoryเพื่อให้สําหรับทุกเขตข้อมูลที่ฉันลากลงใน categoryข้อมูลจะถูกแมปไปยังcategorical.categories นอกจากนี้ยังแมปบทบาทข้อมูลของฉัน measure ไปยัง categorical.valuesอีกด้วย"
- สำหรับ ใน: รวม รายการทั้งหมดใน บทบาทข้อมูลนี้ในคิวรีข้อมูล
- ผูก ไปยัง: สร้างผลลัพธ์เดียวกับสําหรับ... ใน แต่คาดว่าจะมีบทบาทข้อมูลที่มีเงื่อนไขที่จํากัดให้อยู่ในเขตข้อมูลเดียว
จัดกลุ่มข้อมูลจัดกลุ่ม
ตัวอย่างถัดไปใช้บทบาทข้อมูลสองบทบาทเดียวกันกับตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ และเพิ่มบทบาทข้อมูลอีกสองบทบาทที่ชื่อว่า grouping และmeasure2
"dataRole":[
{
"displayName": "Category",
"name": "category",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Y Axis",
"name": "measure",
"kind": "Measure"
},
{
"displayName": "Grouping with",
"name": "grouping",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "X Axis",
"name": "measure2",
"kind": "Grouping"
}
],
"dataViewMappings":{
"categorical": {
"categories": {
"for": { "in": "category" }
},
"values": {
"group": {
"by": "grouping",
"select":[
{ "bind": { "to": "measure" } },
{ "bind": { "to": "measure2" } }
]
}
}
}
}
ความแตกต่างระหว่างการแมปนี้กับการแมปพื้นฐานคือวิธีการ categorical.values แมป เมื่อคุณแมป measure บทบาทข้อมูล และ measure2 ไปยังบทบาท groupingข้อมูล แกน x และแกน y สามารถปรับมาตราส่วนได้อย่างเหมาะสม
จัดกลุ่มข้อมูลแบบลําดับชั้น
ในตัวอย่างถัดไป ข้อมูลจัดกลุ่มถูกใช้เพื่อสร้างลําดับชั้น ซึ่งสามารถใช้เพื่อสนับสนุน การดําเนินการดูรายละเอียด แนวลึก
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงบทบาทข้อมูลและการแมป:
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Categories",
"name": "category",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Measures",
"name": "measure",
"kind": "Measure"
},
{
"displayName": "Series",
"name": "series",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"categorical": {
"categories": {
"for": {
"in": "category"
}
},
"values": {
"group": {
"by": "series",
"select": [{
"for": {
"in": "measure"
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
]
พิจารณาข้อมูลตามประเภทต่อไปนี้:
| ประเทศ/ภูมิภาค | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | X | X | 650 | 350 |
| แคนาดา | X | 630 | 490 | X |
| เม็กซิโก | 645 | X | x | X |
| สหราชอาณาจักร | X | X | 831 | X |
Power BI สร้างมุมมองข้อมูลแบบจัดกลุ่มด้วยชุดประเภทต่อไปนี้
{
"categorical": {
"categories": [
{
"source": {...},
"values": [
"Canada",
"USA",
"UK",
"Mexico"
],
"identity": [...],
"identityFields": [...],
}
]
}
}
แต่ละcategoryแมปไปยังชุดของvalues valuesแต่ละรายการเหล่านี้จะถูกจัดกลุ่มตาม seriesซึ่งแสดงเป็นปี
ตัวอย่างเช่น อาร์เรย์ แต่ละ values ตัวแสดงถึงหนึ่งปี
นอกจากนี้ อาร์เรย์ แต่ละรายการ values ยังมีค่าสี่ค่า: Canada, USA, UK และ Mexico
{
"values": [
// Values for year 2013
{
"source": {...},
"values": [
null, // Value for `Canada` category
null, // Value for `USA` category
null, // Value for `UK` category
645 // Value for `Mexico` category
],
"identity": [...],
},
// Values for year 2014
{
"source": {...},
"values": [
630, // Value for `Canada` category
null, // Value for `USA` category
null, // Value for `UK` category
null // Value for `Mexico` category
],
"identity": [...],
},
// Values for year 2015
{
"source": {...},
"values": [
490, // Value for `Canada` category
650, // Value for `USA` category
831, // Value for `UK` category
null // Value for `Mexico` category
],
"identity": [...],
},
// Values for year 2016
{
"source": {...},
"values": [
null, // Value for `Canada` category
350, // Value for `USA` category
null, // Value for `UK` category
null // Value for `Mexico` category
],
"identity": [...],
}
]
}
ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้มีไว้สําหรับการประมวลผลการแมปมุมมองข้อมูลแบบจัดกลุ่ม ตัวอย่างนี้สร้างโครงสร้างแบบลําดับชั้น ค่าปี>ของประเทศ/ภูมิภาค>
"use strict";
import powerbi from "powerbi-visuals-api";
import DataView = powerbi.DataView;
import DataViewCategorical = powerbi.DataViewCategorical;
import DataViewValueColumnGroup = powerbi.DataViewValueColumnGroup;
import PrimitiveValue = powerbi.PrimitiveValue;
// standard imports
// ...
export class Visual implements IVisual {
private target: HTMLElement;
private host: IVisualHost;
private categories: HTMLElement;
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
// constructor body
this.target = options.element;
this.host = options.host;
this.categories = document.createElement("pre");
this.target.appendChild(this.categories);
// ...
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
const dataView: DataView = options.dataViews[0];
const categoricalDataView: DataViewCategorical = dataView.categorical;
if (!categoricalDataView ||
!categoricalDataView.categories ||
!categoricalDataView.categories[0] ||
!categoricalDataView.values) {
return;
}
// Categories have only one column in data buckets
// To support several columns of categories data bucket, iterate categoricalDataView.categories array.
const categoryFieldIndex = 0;
// Measure has only one column in data buckets.
// To support several columns on data bucket, iterate years.values array in map function
const measureFieldIndex = 0;
let categories: PrimitiveValue[] = categoricalDataView.categories[categoryFieldIndex].values;
let values: DataViewValueColumnGroup[] = categoricalDataView.values.grouped();
let data = {};
// iterate categories/countries-regions
categories.map((category: PrimitiveValue, categoryIndex: number) => {
data[category.toString()] = {};
// iterate series/years
values.map((years: DataViewValueColumnGroup) => {
if (!data[category.toString()][years.name] && years.values[measureFieldIndex].values[categoryIndex]) {
data[category.toString()][years.name] = []
}
if (years.values[0].values[categoryIndex]) {
data[category.toString()][years.name].push(years.values[measureFieldIndex].values[categoryIndex]);
}
});
});
this.categories.innerText = JSON.stringify(data, null, 6);
console.log(data);
}
}
นี่คือวิชวลผลลัพธ์:

การแมปตาราง
มุมมอง ข้อมูลตาราง เป็นรายการของจุดข้อมูลที่สามารถรวมจุดข้อมูลตัวเลขได้เป็นหลัก
ตัวอย่างเช่น ใช้ ข้อมูลเดียวกันในส่วนก่อนหน้า แต่ด้วยความสามารถต่อไปนี้:
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Column",
"name": "column",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Value",
"name": "value",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"table": {
"rows": {
"select": [
{
"for": {
"in": "column"
}
},
{
"for": {
"in": "value"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
แสดงภาพมุมมองข้อมูลตารางดังตัวอย่างนี้:
| ประเทศ/ภูมิภาค | Year | การขาย |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 2016 | 100 |
| USA | 2015 | 50 |
| แคนาดา | 2015 | 200 |
| แคนาดา | 2015 | 50 |
| เม็กซิโก | 2013 | 300 |
| สหราชอาณาจักร | 2014 | 150 |
| USA | 2015 | 75 |
การผูกข้อมูล:

Power BI จะแสดงข้อมูลของคุณเป็นมุมมองข้อมูลตาราง อย่าสันนิษฐานว่ามีการสั่งซื้อข้อมูลแล้ว
{
"table" : {
"columns": [...],
"rows": [
[
"Canada",
2014,
630
],
[
"Canada",
2015,
490
],
[
"Mexico",
2013,
645
],
[
"UK",
2014,
831
],
[
"USA",
2015,
650
],
[
"USA",
2016,
350
]
]
}
}
เมื่อต้องการรวมข้อมูล ให้เลือกเขตข้อมูลที่ต้องการ จากนั้นเลือกผลรวม
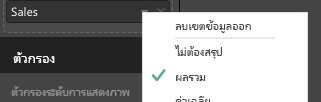
ตัวอย่างโค้ดเพื่อประมวลผลการแมปมุมมองข้อมูลแบบตาราง
"use strict";
import "./../style/visual.less";
import powerbi from "powerbi-visuals-api";
// ...
import DataViewMetadataColumn = powerbi.DataViewMetadataColumn;
import DataViewTable = powerbi.DataViewTable;
import DataViewTableRow = powerbi.DataViewTableRow;
import PrimitiveValue = powerbi.PrimitiveValue;
// standard imports
// ...
export class Visual implements IVisual {
private target: HTMLElement;
private host: IVisualHost;
private table: HTMLParagraphElement;
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
// constructor body
this.target = options.element;
this.host = options.host;
this.table = document.createElement("table");
this.target.appendChild(this.table);
// ...
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
const dataView: DataView = options.dataViews[0];
const tableDataView: DataViewTable = dataView.table;
if (!tableDataView) {
return
}
while(this.table.firstChild) {
this.table.removeChild(this.table.firstChild);
}
//draw header
const tableHeader = document.createElement("th");
tableDataView.columns.forEach((column: DataViewMetadataColumn) => {
const tableHeaderColumn = document.createElement("td");
tableHeaderColumn.innerText = column.displayName
tableHeader.appendChild(tableHeaderColumn);
});
this.table.appendChild(tableHeader);
//draw rows
tableDataView.rows.forEach((row: DataViewTableRow) => {
const tableRow = document.createElement("tr");
row.forEach((columnValue: PrimitiveValue) => {
const cell = document.createElement("td");
cell.innerText = columnValue.toString();
tableRow.appendChild(cell);
})
this.table.appendChild(tableRow);
});
}
}
ไฟล์ style/visual.less สไตล์ของวิชวลประกอบด้วยเค้าโครงสําหรับตาราง:
table {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
tr, th {
display: flex;
flex: 1;
}
td {
flex: 1;
border: 1px solid black;
}
วิชวลผลลัพธ์จะมีลักษณะดังนี้:
การแมปข้อมูลเมทริกซ์
การแมปข้อมูลเมทริกซ์ คล้ายกับการแมปข้อมูลตาราง แต่มีการแสดงแถวแบบลําดับชั้น ค่าบทบาทข้อมูลใด ๆ สามารถใช้เป็นค่าส่วนหัวคอลัมน์ได้
{
"dataRoles": [
{
"name": "Category",
"displayName": "Category",
"displayNameKey": "Visual_Category",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"name": "Column",
"displayName": "Column",
"displayNameKey": "Visual_Column",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"name": "Measure",
"displayName": "Measure",
"displayNameKey": "Visual_Values",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"matrix": {
"rows": {
"for": {
"in": "Category"
}
},
"columns": {
"for": {
"in": "Column"
}
},
"values": {
"select": [
{
"for": {
"in": "Measure"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
โครงสร้างแบบลําดับชั้นของข้อมูลเมทริกซ์
Power BI สร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลแบบลําดับชั้น รากของลําดับชั้นต้นไม้ประกอบด้วยข้อมูลจาก คอลัมน์ โหนดแม่ ของ Category บทบาทข้อมูลที่มีโหนดลูกจาก คอลัมน์ โหนดลูก ของตารางบทบาทข้อมูล
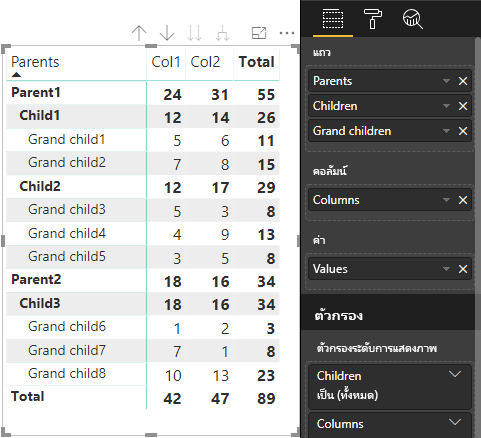
แบบจําลองแสดงความหมาย:
| ผู้ปกครอง | รายการรอง | หลานชาย | คอลัมน์ | ค่า |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parent1 | Child1 | Grand child1 | Col1 | 5 |
| Parent1 | Child1 | Grand child1 | Col2 | 6 |
| Parent1 | Child1 | Grand child2 | Col1 | 7 |
| Parent1 | Child1 | Grand child2 | Col2 | 8 |
| Parent1 | Child2 | Grand child3 | Col1 | 5 |
| Parent1 | Child2 | Grand child3 | Col2 | 3 |
| Parent1 | Child2 | Grand child4 | Col1 | 4 |
| Parent1 | Child2 | Grand child4 | Col2 | 9 |
| Parent1 | Child2 | Grand child5 | Col1 | 3 |
| Parent1 | Child2 | Grand child5 | Col2 | 5 |
| Parent2 | Child3 | Grand child6 | Col1 | 1 |
| Parent2 | Child3 | Grand child6 | Col2 | 2 |
| Parent2 | Child3 | Grand child7 | Col1 | 7 |
| Parent2 | Child3 | Grand child7 | Col2 | 1 |
| Parent2 | Child3 | Grand child8 | Col1 | 10 |
| Parent2 | Child3 | Grand child8 | Col2 | 13 |
วิชวลเมทริกซ์หลักของ Power BI แสดงข้อมูลเป็นตาราง
วิชวลได้รับโครงสร้างข้อมูลตามที่อธิบายไว้ในโค้ดต่อไปนี้ (แสดงเฉพาะสองแถวแรกของตารางเท่านั้น):
{
"metadata": {...},
"matrix": {
"rows": {
"levels": [...],
"root": {
"childIdentityFields": [...],
"children": [
{
"level": 0,
"levelValues": [...],
"value": "Parent1",
"identity": {...},
"childIdentityFields": [...],
"children": [
{
"level": 1,
"levelValues": [...],
"value": "Child1",
"identity": {...},
"childIdentityFields": [...],
"children": [
{
"level": 2,
"levelValues": [...],
"value": "Grand child1",
"identity": {...},
"values": {
"0": {
"value": 5 // value for Col1
},
"1": {
"value": 6 // value for Col2
}
}
},
...
]
},
...
]
},
...
]
}
},
"columns": {
"levels": [...],
"root": {
"childIdentityFields": [...],
"children": [
{
"level": 0,
"levelValues": [...],
"value": "Col1",
"identity": {...}
},
{
"level": 0,
"levelValues": [...],
"value": "Col2",
"identity": {...}
},
...
]
}
},
"valueSources": [...]
}
}
ขยายและยุบส่วนหัวของแถว
สําหรับ API 4.1.0 หรือใหม่กว่า ข้อมูลเมทริกซ์สนับสนุน การขยายและการยุบส่วนหัวของแถว จาก API 4.2 คุณสามารถขยาย/ยุบทั้งระดับโดยทางโปรแกรมได้ คุณลักษณะขยายและยุบจะปรับให้เหมาะสมในการดึงข้อมูลไปยัง dataView โดยอนุญาตให้ผู้ใช้ขยายหรือยุบแถวโดยไม่ต้องดึงข้อมูลทั้งหมดสําหรับระดับถัดไป ซึ่งจะดึงข้อมูลสําหรับแถวที่เลือกเท่านั้น สถานะการขยายของส่วนหัวของแถวยังคงสอดคล้องกันระหว่างบุ๊กมาร์กและแม้กระทั่งในรายงานที่บันทึกไว้ ซึ่งไม่ได้เฉพาะเจาะจงสําหรับวิชวลแต่ละภาพ
สามารถเพิ่มคําสั่งขยายและยุบไปยังเมนูบริบทได้โดยการจัดหา dataRoles พารามิเตอร์ไปยัง showContextMenu เมธอด
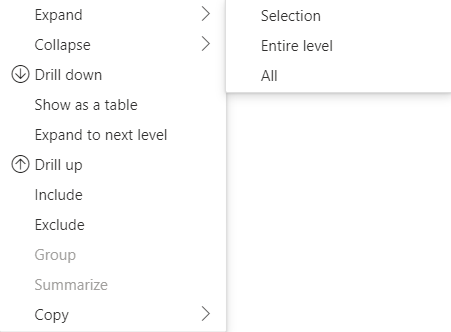
หากต้องการขยายจํานวนมากของจุดข้อมูล ให้ใช้ API ดึงข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมด้วย API แบบขยาย/ยุบ
คุณลักษณะ API
องค์ประกอบต่อไปนี้ถูกเพิ่มไปยัง API เวอร์ชัน 4.1.0 เพื่อเปิดใช้งานการขยายและการยุบส่วนหัวของแถว:
ค่า
isCollapsedสถานะในDataViewTreeNode:interface DataViewTreeNode { //... /** * TRUE if the node is Collapsed * FALSE if it is Expanded * Undefined if it cannot be Expanded (e.g. subtotal) */ isCollapsed?: boolean; }toggleExpandCollapseวิธีการในISelectionMangerอินเทอร์เฟซ:interface ISelectionManager { //... showContextMenu(selectionId: ISelectionId, position: IPoint, dataRoles?: string): IPromise<{}>; // dataRoles is the name of the role of the selected data point toggleExpandCollapse(selectionId: ISelectionId, entireLevel?: boolean): IPromise<{}>; // Expand/Collapse an entire level will be available from API 4.2.0 //... }ค่า
canBeExpandedสถานะใน DataViewHierarchyLevel:interface DataViewHierarchyLevel { //... /** If TRUE, this level can be expanded/collapsed */ canBeExpanded?: boolean; }
ข้อกําหนดของวิชวล
เมื่อต้องการเปิดใช้งานคุณลักษณะขยายการยุบบนวิชวลโดยใช้มุมมองข้อมูลเมทริกซ์:
เพิ่มโค้ดต่อไปนี้ลงในไฟล์ capabilities.json:
"expandCollapse": { "roles": ["Rows"], //”Rows” is the name of rows data role "addDataViewFlags": { "defaultValue": true //indicates if the DataViewTreeNode will get the isCollapsed flag by default } },ยืนยันว่าบทบาทสามารถเจาะได้:
"drilldown": { "roles": ["Rows"] },สําหรับแต่ละโหนด ให้สร้างอินสแตนซ์ของตัวสร้างการเลือกโดยการ
withMatrixNodeเรียกใช้วิธีการ ในระดับลําดับชั้นโหนดที่เลือกและสร้างselectionIdตัวอย่างเช่น:let nodeSelectionBuilder: ISelectionIdBuilder = visualHost.createSelectionIdBuilder(); // parantNodes is a list of the parents of the selected node. // node is the current node which the selectionId is created for. parentNodes.push(node); for (let i = 0; i < parentNodes.length; i++) { nodeSelectionBuilder = nodeSelectionBuilder.withMatrixNode(parentNodes[i], levels); } const nodeSelectionId: ISelectionId = nodeSelectionBuilder.createSelectionId();สร้างอินสแตนซ์ของตัวจัดการการเลือก และใช้
selectionManager.toggleExpandCollapse()วิธีการ ด้วยพารามิเตอร์ของselectionIdที่คุณสร้างขึ้นสําหรับโหนดที่เลือก ตัวอย่างเช่น:// handle click events to apply expand\collapse action for the selected node button.addEventListener("click", () => { this.selectionManager.toggleExpandCollapse(nodeSelectionId); });
หมายเหตุ
- ถ้าโหนดที่เลือกไม่ใช่โหนดแถว PowerBI จะละเว้นการเรียกขยายและยุบ และคําสั่งขยายและยุบจะถูกลบออกจากเมนูบริบท
- พารามิเตอร์
dataRolesจําเป็นสําหรับshowContextMenuเมธอด เฉพาะเมื่อวิชวลdrilldownรองรับหรือexpandCollapseคุณลักษณะ หากวิชวลรองรับคุณลักษณะเหล่านี้ แต่ไม่มี dataRoles ให้ ข้อผิดพลาดจะแสดงผลไปยังคอนโซลเมื่อใช้วิชวลของนักพัฒนาหรือหากดีบักวิชวลสาธารณะด้วยการเปิดใช้งานโหมดดีบัก
ข้อควรพิจารณาและข้อจำกัด
- หลังจากที่คุณขยายโหนด ขีดจํากัดข้อมูลใหม่จะถูกนําไปใช้กับ DataView DataView ใหม่อาจไม่มีโหนดบางโหนดที่แสดงใน DataView ก่อนหน้านี้
- เมื่อใช้การขยายหรือยุบ จะมีการเพิ่มผลรวมแม้ว่าวิชวลไม่ได้ร้องขอ
- ไม่สนับสนุนการขยายและการยุบคอลัมน์
เก็บคอลัมน์เมตาดาต้าทั้งหมด
สําหรับ API 5.1.0 หรือใหม่กว่า การทําให้คอลัมน์เมตาดาต้าทั้งหมดได้รับการสนับสนุน คุณลักษณะนี้ช่วยให้วิชวลได้รับเมตาดาต้าสําหรับคอลัมน์ทั้งหมดไม่ว่าการฉายภาพที่ใช้งานอยู่คืออะไร
เพิ่มบรรทัดต่อไปนี้ลงในไฟล์ capabilities.json ของคุณ:
"keepAllMetadataColumns": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Indicates that visual is going to receive all metadata columns, no matter what the active projections are"
}
การตั้งค่าคุณสมบัติ true นี้จะส่งผลให้ได้รับเมตาดาต้าทั้งหมด รวมถึงจากคอลัมน์ที่ยุบ การตั้งค่าไป false หรือปล่อยไว้โดยไม่ได้กําหนดไว้จะส่งผลให้ได้รับเมตาดาต้าเฉพาะในคอลัมน์ที่มีโปรเจคชันที่ใช้งานอยู่เท่านั้น (ตัวอย่างเช่น ขยาย)
อัลกอริทึมในการลดข้อมูล
อัลกอริทึมการลดข้อมูลจะควบคุมว่าข้อมูลใดและจะได้รับข้อมูลเท่าใดในมุมมองข้อมูล
จํานวนถูกตั้งค่าเป็นจํานวนสูงสุดของค่าที่มุมมองข้อมูลสามารถยอมรับได้ ถ้ามีค่าจํานวนมากกว่า อัลกอริทึมการลดมิติข้อมูลจะกําหนดค่าที่ควรได้รับ
ประเภทของอัลกอริทึมในการลดข้อมูล
มีการตั้งค่าอัลกอริธึมการลดข้อมูลสี่ประเภท:
top: ค่าจํานวนแรกจะถูกนํามาจากแบบจําลองความหมายbottom: ค่าจํานวนสุดท้ายจะถูกนํามาจากแบบจําลองความหมายsample: มีการรวมรายการแรกและสุดท้าย และ นับ จํานวนหน่วยข้อมูลที่มีช่วงที่เท่ากันระหว่างกัน ตัวอย่างเช่น ถ้าคุณมีแบบจําลองความหมาย [0, 1, 2, ... 100] และ count เป็น 9 คุณจะได้รับค่า [0, 10, 20 ... 100].window: โหลดหน้าต่างของจุดข้อมูลหนึ่งรายการในช่วงเวลาที่มีองค์ประกอบ count ในปัจจุบันtopและwindowเทียบเท่ากัน ในอนาคต การตั้งค่าหน้าต่างจะรองรับอย่างสมบูรณ์
ตามค่าเริ่มต้น วิชวล Power BI ทั้งหมดมีอัลกอริทึมการลดข้อมูลสูงสุดที่ใช้กับ count ซึ่งตั้งค่าเป็นจุดข้อมูล 1,000 จุด ค่าเริ่มต้นนี้จะเทียบเท่ากับการตั้งค่าคุณสมบัติต่อไปนี้ใน ไฟล์ capabilities.json :
"dataReductionAlgorithm": {
"top": {
"count": 1000
}
}
คุณสามารถปรับเปลี่ยน ค่า count เป็นค่าจํานวนเต็มใดก็ตามได้สูงถึง 30000 วิชวล Power BI ที่ใช้ภาษา R สามารถรองรับได้ถึง 150000 แถว
การใช้งานอัลกอริทึมในการลดข้อมูล
อัลกอริธึมการลดมิติข้อมูลสามารถใช้ในการแมปมุมมองข้อมูลจัดกลุ่ม ตาราง หรือเมทริกซ์ได้
ในการแมปข้อมูลจัดกลุ่ม คุณสามารถเพิ่มอัลกอริทึมไปยังส่วน "ประเภท" และ/หรือ "กลุ่ม" ของ values สําหรับการแมปข้อมูลแบบจัดกลุ่มได้
"dataViewMappings": {
"categorical": {
"categories": {
"for": { "in": "category" },
"dataReductionAlgorithm": {
"window": {
"count": 300
}
}
},
"values": {
"group": {
"by": "series",
"select": [{
"for": {
"in": "measure"
}
}
],
"dataReductionAlgorithm": {
"top": {
"count": 100
}
}
}
}
}
}
ในการแมปมุมมองข้อมูลแบบตาราง ใช้อัลกอริทึมการลดมิติข้อมูลกับ rows ส่วน ของตารางการแมปมุมมองข้อมูล
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"table": {
"rows": {
"for": {
"in": "values"
},
"dataReductionAlgorithm": {
"top": {
"count": 2000
}
}
}
}
}
]
คุณสามารถใช้อัลกอริธึมการลดมิติข้อมูลกับ rows ส่วน และ columns ของเมทริกซ์การแมปมุมมองข้อมูล
เนื้อหาที่เกี่ยวข้อง
คำติชม
เร็วๆ นี้: ตลอดปี 2024 เราจะขจัดปัญหา GitHub เพื่อเป็นกลไกคำติชมสำหรับเนื้อหา และแทนที่ด้วยระบบคำติชมใหม่ สำหรับข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม ให้ดู: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback
ส่งและดูข้อคิดเห็นสำหรับ