Azure Monitor Agent overview
Azure Monitor Agent (AMA) collects monitoring data from the guest operating system of Azure and hybrid virtual machines and delivers it to Azure Monitor for use by features, insights, and other services, such as Microsoft Sentinel and Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Azure Monitor Agent replaces Azure Monitor's legacy monitoring agents (MMA/OMS). This article provides an overview of Azure Monitor Agent's capabilities and supported use cases.
Here's a short introduction to Azure Monitor agent video, which includes a quick demo of how to set up the agent from the Azure portal: ITOps Talk: Azure Monitor Agent
Benefits
Using Azure Monitor agent, you get immediate benefits as shown below:
- Cost savings by using data collection rules:
- Enables targeted and granular data collection for a machine or subset(s) of machines, as compared to the "all or nothing" approach of legacy agents.
- Allows filtering rules and data transformations to reduce the overall data volume being uploaded, thus lowering ingestion and storage costs significantly.
- Security and Performance
- Enhanced security through Managed Identity and Microsoft Entra tokens (for clients).
- Higher event throughput that is 25% better than the legacy Log Analytics (MMA/OMS) agents.
- Simpler management including efficient troubleshooting:
- Supports data uploads to multiple destinations (multiple Log Analytics workspaces, i.e. multihoming on Windows and Linux) including cross-region and cross-tenant data collection (using Azure LightHouse).
- Centralized agent configuration "in the cloud" for enterprise scale throughout the data collection lifecycle, from onboarding to deployment to updates and changes over time.
- Any change in configuration is rolled out to all agents automatically, without requiring a client side deployment.
- Greater transparency and control of more capabilities and services, such as Microsoft Sentinel, Defender for Cloud, and VM Insights.
- A single agent that serves all data collection needs across supported servers and client devices. A single agent is the goal, although Azure Monitor Agent is currently converging with the Log Analytics agents.
Consolidating legacy agents
Azure Monitor Agent replaces the Legacy Agent, which sends data to a Log Analytics workspace and supports monitoring solutions.
The Log Analytics agent is on a deprecation path and won't be supported after August 31, 2024. Any new data centers brought online after January 1 2024 will not support the Log Analytics agent. If you use the Log Analytics agent to ingest data to Azure Monitor, migrate to the new Azure Monitor agent prior to that date.
Install the agent and configure data collection
Azure Monitor Agent uses data collection rules, where you define which data you want each agent to collect. Data collection rules let you manage data collection settings at scale and define unique, scoped configurations for subsets of machines. You can define a rule to send data from multiple machines to multiple destinations across regions and tenants.
Note
To send data across tenants, you must first enable Azure Lighthouse. Cloning a machine with Azure Monitor Agent installed is not supported. The best practice for these situations is to use Azure Policy or an Infrastructure as a code tool to deploy AMA at scale.
To collect data using Azure Monitor Agent:
Install the agent on the resource.
Resource type Installation method More information Virtual machines and VM scale sets Virtual machine extension Installs the agent by using Azure extension framework. On-premises Arc-enabled servers Virtual machine extension (after installing the Azure Arc agent) Installs the agent by using Azure extension framework, provided for on-premises by first installing Azure Arc agent. Windows 10, 11 Client Operating Systems Client installer Installs the agent by using a Windows MSI installer. The installer works on laptops, but the agent isn't optimized yet for battery or network consumption. Define a data collection rule and associate the resource to the rule.
The table below lists the types of data you can currently collect with the Azure Monitor Agent and where you can send that data.
Data source Destinations Description Performance - Azure Monitor Metrics (Public preview):
- For Windows - Virtual Machine Guest namespace
- For Linux1 - azure.vm.linux.guestmetrics namespace
- Log Analytics workspace - Perf table
Numerical values measuring performance of different aspects of operating system and workloads Windows event logs (including sysmon events) Log Analytics workspace - Event table Information sent to the Windows event logging system Syslog Log Analytics workspace - Syslog2 table Information sent to the Linux event logging system. Collect syslog with Azure Monitor Agent Text and JSON logs Log Analytics workspace - custom table(s) created manually Collect text logs with Azure Monitor Agent Windows IIS logs Internet Information Service (IIS) logs from to the local disk of Windows machines [Collect IIS Logs with Azure Monitor Agent].(data-collection-iis.md) Windows Firewall logs Firewall logs from the local disk of a Windows Machine 1 On Linux, using Azure Monitor Metrics as the only destination is supported in v1.10.9.0 or higher.
2 Azure Monitor Linux Agent versions 1.15.2 and higher support syslog RFC formats including Cisco Meraki, Cisco ASA, Cisco FTD, Sophos XG, Juniper Networks, Corelight Zeek, CipherTrust, NXLog, McAfee, and Common Event Format (CEF).Note
On rsyslog-based systems, Azure Monitor Linux Agent adds forwarding rules to the default ruleset defined in the rsyslog configuration. If multiple rulesets are used, inputs bound to non-default ruleset(s) are not forwarded to Azure Monitor Agent. For more information about multiple rulesets in rsyslog, see the official documentation.
Note
Azure Monitor Agent also supports Azure service SQL Best Practices Assessment which is currently Generally available. For more information, refer Configure best practices assessment using Azure Monitor Agent.
- Azure Monitor Metrics (Public preview):
Supported services and features
For a list of features and services that use Azure Monitor Agent for data collection, see Migrate to Azure Monitor Agent from Log Analytics agent.
Supported regions
Azure Monitor Agent is available in all public regions, Azure Government and China clouds, for generally available features. It's not yet supported in air-gapped clouds. For more information, see Product availability by region.
Costs
There's no cost for the Azure Monitor Agent, but you might incur charges for the data ingested and stored. For information on Log Analytics data collection and retention and for customer metrics, see Azure Monitor pricing.
Compare to legacy agents
The tables below provide a comparison of Azure Monitor Agent with the legacy the Azure Monitor telemetry agents for Windows and Linux.
Windows agents
| Category | Area | Azure Monitor Agent | Legacy Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environments supported | |||
| Azure | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Other cloud (Azure Arc) | ✓ | ✓ | |
| On-premises (Azure Arc) | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Windows Client OS | ✓ | ||
| Data collected | |||
| Event Logs | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Performance | ✓ | ✓ | |
| File based logs | ✓ | ✓ | |
| IIS logs | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Data sent to | |||
| Azure Monitor Logs | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Services and features supported | |||
| Microsoft Sentinel | ✓ (View scope) | ✓ | |
| VM Insights | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Microsoft Defender for Cloud - Only uses MDE agent | |||
| Automation Update Management - Moved to Azure Update Manager | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Azure Stack HCI | ✓ | ||
| Update Manager - no longer uses agents | |||
| Change Tracking | ✓ | ✓ | |
| SQL Best Practices Assessment | ✓ |
Linux agents
| Category | Area | Azure Monitor Agent | Legacy Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environments supported | |||
| Azure | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Other cloud (Azure Arc) | ✓ | ✓ | |
| On-premises (Azure Arc) | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Data collected | |||
| Syslog | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Performance | ✓ | ✓ | |
| File based logs | ✓ | ||
| Data sent to | |||
| Azure Monitor Logs | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Services and features supported | |||
| Microsoft Sentinel | ✓ (View scope) | ✓ | |
| VM Insights | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Microsoft Defender for Cloud - Only use MDE agent | |||
| Automation Update Management - Moved to Azure Update Manager | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Update Manager - no longer uses agents | |||
| Change Tracking | ✓ | ✓ |
Supported operating systems
The following tables list the operating systems that Azure Monitor Agent and the legacy agents support. All operating systems are assumed to be x64. x86 isn't supported for any operating system. View supported operating systems for Azure Arc Connected Machine agent, which is a prerequisite to run Azure Monitor agent on physical servers and virtual machines hosted outside of Azure (that is, on-premises) or in other clouds.
Windows
| Operating system | Azure Monitor agent | Legacy agent |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2022 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Windows Server 2022 Core | ✓ | |
| Windows Server 2019 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Windows Server 2019 Core | ✓ | |
| Windows Server 2016 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Windows Server 2016 Core | ✓ | |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Windows Server 2012 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Windows 11 Client and Pro | ✓1, 2 | |
| Windows 11 Enterprise (including multi-session) |
✓ | |
| Windows 10 1803 (RS4) and higher | ✓1 | |
| Windows 10 Enterprise (including multi-session) and Pro (Server scenarios only) |
✓ | ✓ |
| Azure Stack HCI | ✓ | ✓ |
| Windows IoT Enterprise | ✓ |
1 Using the Azure Monitor agent client installer.
2 Also supported on Arm64-based machines.
Linux
Caution
This article references CentOS, a Linux distribution that is nearing End Of Life (EOL) status. Please consider your use and planning accordingly. For more information, see the CentOS End Of Life guidance.
| Operating system | Azure Monitor agent 1 | Legacy Agent 1 |
|---|---|---|
| AlmaLinux 9 | ✓2 | ✓ |
| AlmaLinux 8 | ✓2 | ✓ |
| Amazon Linux 2017.09 | ✓ | |
| Amazon Linux 2 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Azure Linux | ✓ | |
| CentOS Linux 8 | ✓ | ✓ |
| CentOS Linux 7 | ✓2 | ✓ |
| CBL-Mariner 2.0 | ✓2,3 | |
| Debian 11 | ✓2 | ✓ |
| Debian 10 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Debian 9 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Debian 8 | ✓ | |
| OpenSUSE 15 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Oracle Linux 9 | ✓ | |
| Oracle Linux 8 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Oracle Linux 7 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Oracle Linux 6.4+ | ||
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 9+ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 8.6+ | ✓2 | ✓ |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 8.0-8.5 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 7 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 6.7+ | ||
| Rocky Linux 9 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Rocky Linux 8 | ✓ | ✓ |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP4 | ✓2 | ✓ |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP3 | ✓ | ✓ |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP2 | ✓ | ✓ |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 | ✓ | ✓ |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 | ✓ | ✓ |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 | ✓ | ✓ |
| Ubuntu 22.04 LTS | ✓ | ✓ |
| Ubuntu 20.04 LTS | ✓2 | ✓ |
| Ubuntu 18.04 LTS | ✓2 | ✓ |
| Ubuntu 16.04 LTS | ✓ | ✓ |
| Ubuntu 14.04 LTS | ✓ |
1 Requires Python (2 or 3) to be installed on the machine.
2 Also supported on Arm64-based machines.
3 Requires at least 4GB of disk space allocated (not provided by default).
Note
Machines and appliances that run heavily customized or stripped-down versions of the above distributions and hosted solutions that disallow customization by the user are not supported. Azure Monitor and legacy agents rely on various packages and other baseline functionality that is often removed from such systems, and their installation may require some environmental modifications considered to be disallowed by the appliance vendor. For instance, GitHub Enterprise Server is not supported due to heavy customization as well as documented, license-level disallowance of operating system modification.
Note
CBL-Mariner 2.0's disk size is by default around 1GB to provide storage savings, compared to other Azure VMs that are around 30GB. However, the Azure Monitor Agent requires at least 4GB disk size in order to install and run successfully. Please check out CBL-Mariner's documentation for more information and instructions on how to increase disk size before installing the agent.
Linux Hardening Standards
The Azure Monitoring Agent for Linux now officially supports various hardening standards for Linux operating systems and distros. Every release of the agent is tested and certified against the supported hardening standards. We test against the images that are publicly available on the Azure Marketplace and published by CIS and only support the settings and hardening that are applied to those images. If you apply additional customizations on your own golden images, and those settings are not covered by the CIS images, it will be considered a non-supported scenario.
Only the Azure Monitoring Agent for Linux will support these hardening standards. There are no plans to support this in the Log Analytics Agent (legacy) or the Diagnostics Extension
Currently supported hardening standards:
- SELinux
- CIS Lvl 1 and 21
- STIG
- FIPs
- FedRamp
| Operating system | Azure Monitor agent 1 | Legacy Agent1 |
|---|---|---|
| CentOS Linux 7 | ✓ | |
| Debian 10 | ✓ | |
| Ubuntu 18 | ✓ | |
| Ubuntu 20 | ✓ | |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 7 | ✓ | |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 8 | ✓ |
1 Supports only the above distros and version
Frequently asked questions
This section provides answers to common questions.
Does Azure Monitor require an agent?
An agent is only required to collect data from the operating system and workloads in virtual machines. The virtual machines can be located in Azure, another cloud environment, or on-premises. See Azure Monitor Agent overview.
Does Azure Monitor Agent support data collection for the various Log Analytics solutions and Azure services like Microsoft Defender for Cloud and Microsoft Sentinel?
For a list of features and services that use Azure Monitor Agent for data collection, see Migrate to Azure Monitor Agent from Log Analytics agent.
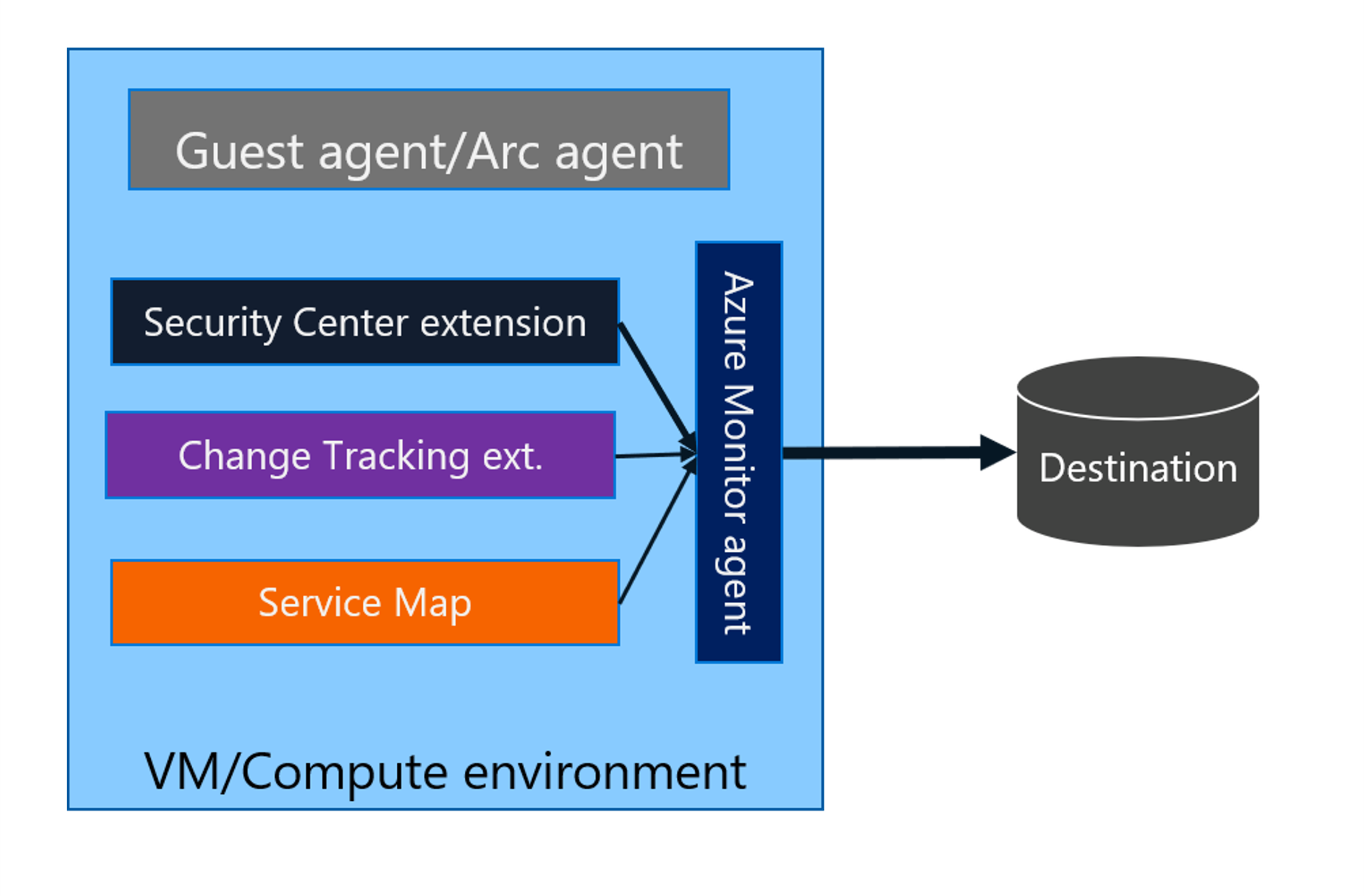
Some services might install other extensions to collect more data or to transforms or process data, and then use Azure Monitor Agent to route the final data to Azure Monitor.
The following diagram explains the new extensibility architecture.
Does Azure Monitor Agent support non-Azure environments like other clouds or on-premises?
Both on-premises machines and machines connected to other clouds are supported for servers today, after you have the Azure Arc agent installed. For purposes of running Azure Monitor Agent and data collection rules, the Azure Arc requirement comes at no extra cost or resource consumption. The Azure Arc agent is only used as an installation mechanism. You don't need to enable the paid management features if you don't want to use them.
Does Azure Monitor Agent support auditd logs on Linux or AUOMS?
Yes, but you need to onboard to Defender for Cloud (previously Azure Security Center). It's available as an extension to Azure Monitor Agent, which collects Linux auditd logs via AUOMS.
Why do I need to install the Azure Arc Connected Machine agent to use Azure Monitor Agent?
Azure Monitor Agent authenticates to your workspace via managed identity, which is created when you install the Connected Machine agent. Managed Identity is a more secure and manageable authentication solution from Azure. The legacy Log Analytics agent authenticated by using the workspace ID and key instead, so it didn't need Azure Arc.
Next steps
- Install the Azure Monitor Agent on Windows and Linux virtual machines.
- Create a data collection rule to collect data from the agent and send it to Azure Monitor.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for