Ask Learn
PreviewPlease sign in to use this experience.
Sign inThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
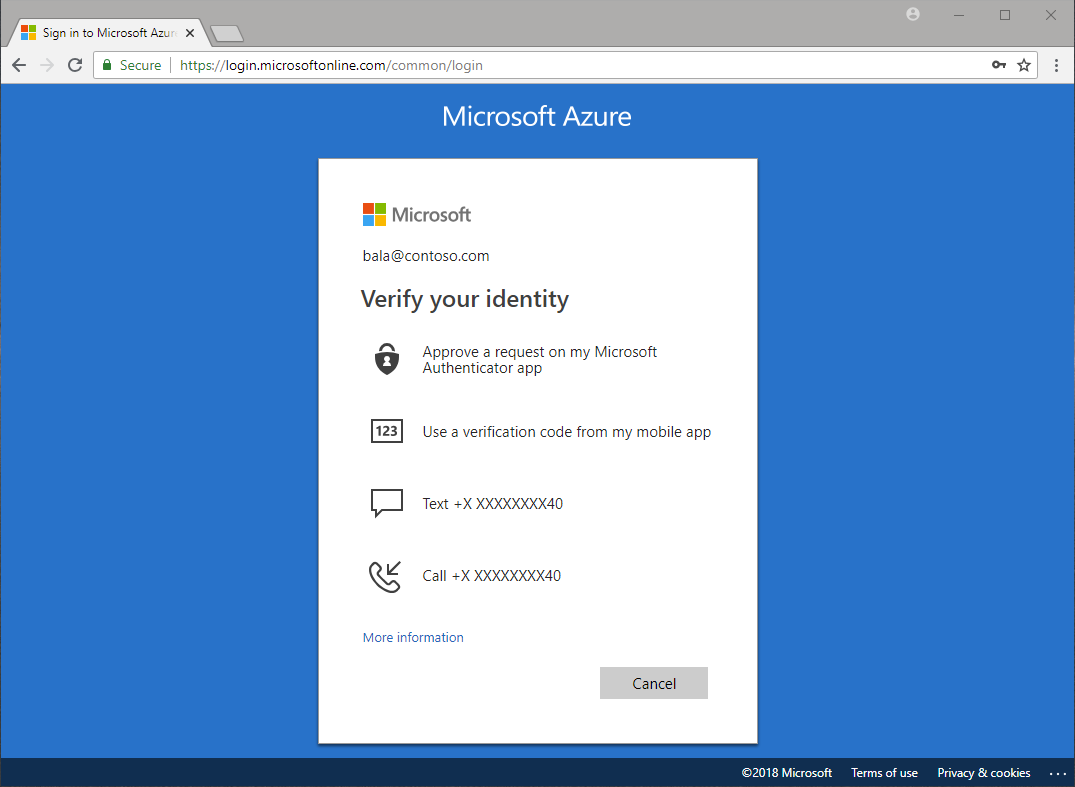
Multifactor authentication is a process in which users are prompted during the sign-in process for an additional form of identification, such as a code on their cellphone or a fingerprint scan.
Multifactor authentication dramatically improves the security of an identity, while still being simple for users. The extra authentication factor must be something that's difficult for an attacker to obtain or duplicate.
Microsoft Entra multifactor authentication works by requiring:
Multifactor authentication verification prompts are configured to be part of the Microsoft Entra sign-in event. Microsoft Entra ID automatically requests and processes multifactor authentication, without you making any changes to your applications or services. When a user signs in, they receive a multifactor authentication prompt, and can choose from one of the additional verification forms that they've registered.
An administrator can require certain verification methods, or the user can access their MyAccount to edit or add verification methods.
The following additional forms of verification, described in the previous unit, can be used with Microsoft Entra multifactor authentication:
Security defaults are a set of basic identity security mechanisms recommended by Microsoft. When enabled, these recommendations are automatically enforced in your organization. The goal is to ensure that all organizations have a basic level of security enabled at no extra cost. These defaults enable some of the most common security features and controls, including:
Security defaults are a great option for organizations that want to increase their security posture but don’t know where to start, or for organizations using the free tier of Microsoft Entra ID licensing. Security defaults may not be appropriate for organizations with Microsoft Entra ID P1 or P2 licenses or more complex security requirements. To learn more, visit What are security defaults?
Please sign in to use this experience.
Sign in