APPLIES TO:  Power BI Report Builder
Power BI Report Builder  Power BI Desktop
Power BI Desktop
This article explains how to configure Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) data sources in the Power BI gateway, and how to use ODBC data sources in Power BI Report Builder.
Data Source Name (DSN) and driver connection strings are both supported.
Note
Power BI Report Builder is now 64-bit, and will no longer work with 32-bit drivers. Both Power BI Report Builder and The Power BI Gateway require the 64-bit version.
Before you install the Power BI gateway
You need a Power BI gateway version February 2021 or later. We recommend installing the gateway on a separate computer from Power BI Report Builder or Power BI Desktop. There are some scenarios where using the same computer might cause problems.
The latest version of Power BI Report Builder already contains the ODBC data extension.
- Install the latest version of Power BI Report Builder.
- Install the 64-bit ODBC driver that you plan to use with Power BI Report Builder.
Follow these steps to set up the Power BI gateway for ODBC data sources.
Download the latest Power BI gateway.
Note
Personal gateways aren't supported for paginated reports, because they require DirectQuery support.
Refer to the article What is an on-premises data gateway? for information on setting it up.
Install the 64-bit ODBC driver that you plan to use on the gateway computer.
Note
File DSNs aren't supported. If you'd like to use a DSN, create a 64-bit System DSN on the gateway computer.
To configure an ODBC data source in the Power BI service, select Manage connections and gateways under Settings:
Select New at the top of the ribbon to add a new data source. Then choose Add data source > ODBC Data Source Type:
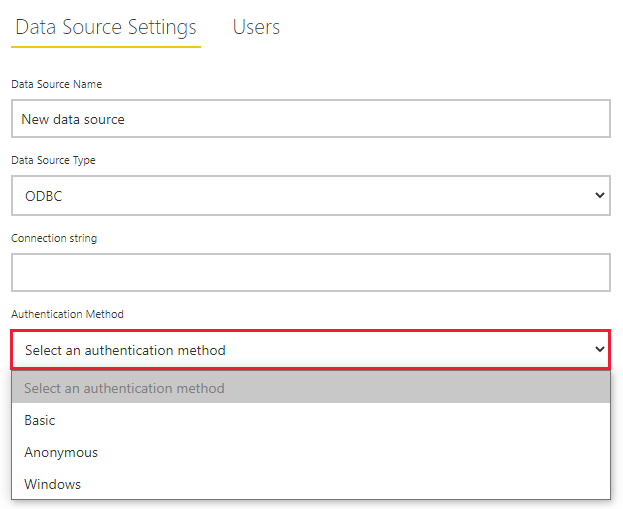
Paste in the connection string (System DSN or driver) and select an authentication method. For ODBC data sources, the following authentication methods are supported:
When you select the Add button, the Power BI service connects to the ODBC data source using the supplied connection string and credentials to validate that the gateway is able to connect.
ODBC connection string examples
Here are some ODBC connection string examples for a System DSN, as well as various ODBC drivers:
- "dsn=Northwind"
- "driver={Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb, *.accdb)};dbq=c:\Data\Northwind.mdb"
- "driver={SnowflakeDSIIDriver};warehouse=DEMO_WH;server=org.snowflakecomputing.com"
- "driver={Amazon Redshift (x64)};server=org.us-west-2.redshift.amazonaws.com;database=dev"
Certain drivers and configurations might not support all authentication methods.
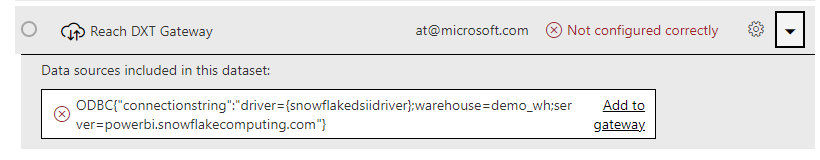
In addition to creating ODBC data sources in the gateway up front, you can create ODBC data sources on demand when you upload a paginated report. If an ODBC data source doesn’t exist, the upload process prompts you to create one:
Limitations and considerations
In general, all the limitations that apply to using the ODBC data extension in Power BI Report Builder apply to using the ODBC data extensions in the Power BI gateway as well.
Here are some of the limitations:
For most ODBC drivers, DateTime parameters require changes to the Command text in the RDL dataset to cast a DateTime parameter value to the appropriate format for a given ODBC data source.
Example query:
SELECT * FROM DEMO_DB.PUBLIC.DATES WHERE DATE < DATE(?)
Note
Some data sources might require specific formatting. You can use an expression to format the parameter in the preceding example. For example, =Format(Parameters!Date.Value, "yyyy-MM-dd").
For some ODBC drivers, there's a behavior difference between the gateway and Power BI Report Builder. This may apply to all, some, or just one driver. One example is that the Simba-BigQuery query requires casting of the parameter if it's not a string type.
Example error string: "A data source used by this report returned an error. An exception encountered while accessing the target data source ERROR [42000] [Simba][BigQuery] (70) Invalid query: No matching signature for operator = for argument types: INT64, STRING. Supported signature: ANY = ANY at [2:7]"
Example query with proper cast for an INT64 column:
SELECT * FROM 'teamplz.Sample.SampleTable' WHERE DataID=CAST(? as INT64)
Any special data types exposed by a given ODBC driver or backend that aren't simply mapped to an ADO.Net data type aren't supported. One example is the Snowflake Array data type.
Scenarios where ODBC drivers use stored procedures without parameters are generally not supported. However, the Amazon Redshift driver has in/out parameters that are supported.


