In this article, you learn how to access and manage your Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) resources using the Azure portal.
To view Kubernetes resources in the Azure portal, you need an AKS cluster. Any cluster is supported, but if you're using Microsoft Entra integration, your cluster must use AKS-managed Microsoft Entra integration. If your cluster uses legacy Microsoft Entra ID, you can upgrade your cluster in the portal or with the Azure CLI. You can also use the Azure portal to create a new AKS cluster.
View Kubernetes resources
In the Azure portal, navigate to your AKS cluster resource.
From the service menu, select Kubernetes resources. The Kubernetes resources list displays the following categories:
- Namespaces shows information about the namespaces of your cluster.
- Workloads shows information about deployments, pods, replica sets, stateful sets, daemon sets, jobs, and cron jobs deployed to your cluster.
- Services and ingresses shows all of your cluster's service and ingress resources.
- Storage shows your Azure storage classes and persistent volume information.
- Configuration shows your cluster's config maps and secrets.
- Custom resources shows any custom resources deployed to your cluster.
- Events shows all events related to your cluster.
- Run command allows you to remotely invoke commands, like
kubectl and helm, on your cluster through the Azure API without directly connecting to the cluster.

Deploy a sample application
In this section, we deploy the Azure Store application from the AKS quickstart.
To deploy the Azure Store application, you need to connect to your AKS cluster. Follow these steps to connect to your cluster using the Azure portal:
- From the Overview page of your AKS cluster, select Connect.
- Follow the instructions to connect to your cluster using Cloud Shell, Azure CLI, or Run command.
Deploy the Azure Store application
From the Kubernetes resources list, select Services and ingresses.
Select Create > Apply a YAML.
Copy and paste the following YAML into the editor:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: rabbitmq
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: rabbitmq
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: rabbitmq
spec:
nodeSelector:
"kubernetes.io/os": linux
containers:
- name: rabbitmq
image: mcr.microsoft.com/mirror/docker/library/rabbitmq:3.10-management-alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 5672
name: rabbitmq-amqp
- containerPort: 15672
name: rabbitmq-http
env:
- name: RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER
value: "username"
- name: RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS
value: "password"
resources:
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 250m
memory: 256Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins
mountPath: /etc/rabbitmq/enabled_plugins
subPath: enabled_plugins
volumes:
- name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins
configMap:
name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins
items:
- key: rabbitmq_enabled_plugins
path: enabled_plugins
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
rabbitmq_enabled_plugins: |
[rabbitmq_management,rabbitmq_prometheus,rabbitmq_amqp1_0].
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: rabbitmq
spec:
selector:
app: rabbitmq
ports:
- name: rabbitmq-amqp
port: 5672
targetPort: 5672
- name: rabbitmq-http
port: 15672
targetPort: 15672
type: ClusterIP
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: order-service
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: order-service
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: order-service
spec:
nodeSelector:
"kubernetes.io/os": linux
containers:
- name: order-service
image: ghcr.io/azure-samples/aks-store-demo/order-service:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
env:
- name: ORDER_QUEUE_HOSTNAME
value: "rabbitmq"
- name: ORDER_QUEUE_PORT
value: "5672"
- name: ORDER_QUEUE_USERNAME
value: "username"
- name: ORDER_QUEUE_PASSWORD
value: "password"
- name: ORDER_QUEUE_NAME
value: "orders"
- name: FASTIFY_ADDRESS
value: "0.0.0.0"
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1m
memory: 50Mi
limits:
cpu: 75m
memory: 128Mi
initContainers:
- name: wait-for-rabbitmq
image: busybox
command: ['sh', '-c', 'until nc -zv rabbitmq 5672; do echo waiting for rabbitmq; sleep 2; done;']
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1m
memory: 50Mi
limits:
cpu: 75m
memory: 128Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: order-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- name: http
port: 3000
targetPort: 3000
selector:
app: order-service
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: product-service
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: product-service
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: product-service
spec:
nodeSelector:
"kubernetes.io/os": linux
containers:
- name: product-service
image: ghcr.io/azure-samples/aks-store-demo/product-service:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 3002
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1m
memory: 1Mi
limits:
cpu: 1m
memory: 7Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: product-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- name: http
port: 3002
targetPort: 3002
selector:
app: product-service
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: store-front
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: store-front
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: store-front
spec:
nodeSelector:
"kubernetes.io/os": linux
containers:
- name: store-front
image: ghcr.io/azure-samples/aks-store-demo/store-front:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
name: store-front
env:
- name: VUE_APP_ORDER_SERVICE_URL
value: "http://order-service:3000/"
- name: VUE_APP_PRODUCT_SERVICE_URL
value: "http://product-service:3002/"
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1m
memory: 200Mi
limits:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 512Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: store-front
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app: store-front
type: LoadBalancer
Select Add.
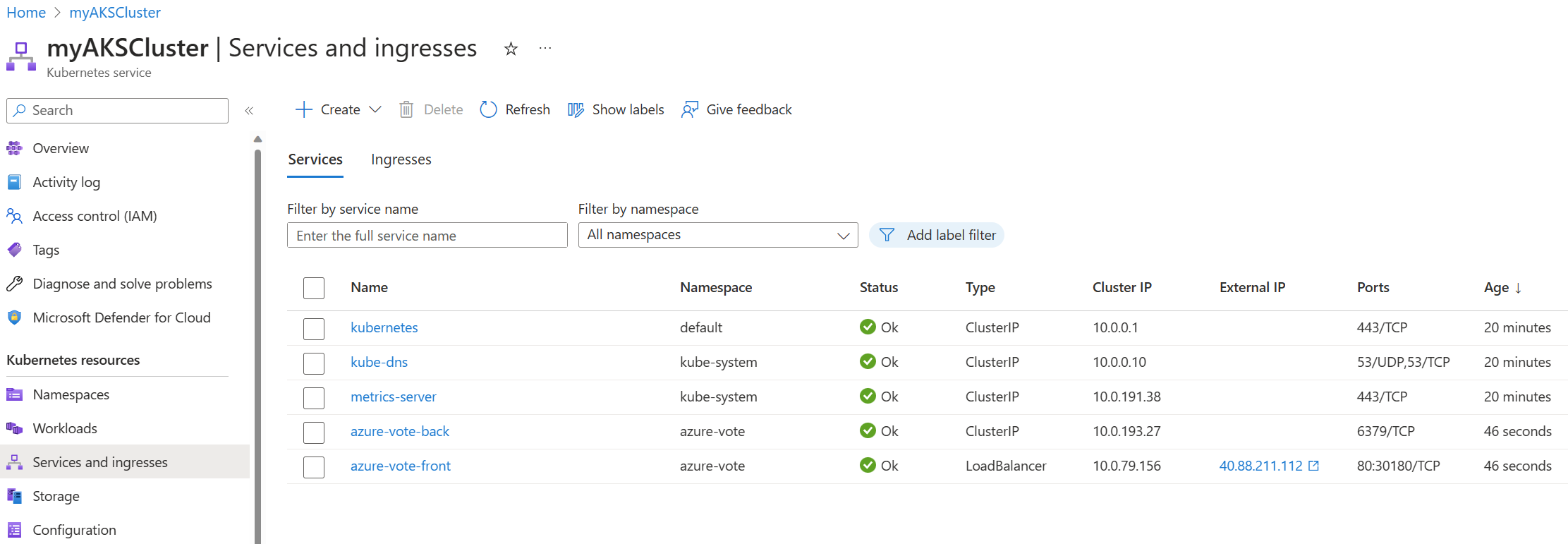
Once the application finishes deploying, you see the following services in the Services list:
- order-service
- product-service
- rabbitmq
- store-front
Monitor deployment insights
Enable the monitoring add-on on your AKS cluster
AKS clusters with Container Insights enabled can access various deployment insights in the Azure portal. If you don't have monitoring enabled on your cluster, you can enable it using the following steps:
From the service menu of your AKS cluster resource, select Monitoring > Insights > Configure monitoring.
On the Configure Container Insights page, select Configure.
It might take a few minutes for the monitoring solution to deploy and begin collecting data.
- From the service menu of your AKS cluster resource, select Workloads.
- Select a deployment from the list to view deployment insights, such as CPU and memory usage.
Note
You can also select Monitoring > Insights to view more in-depth information about specific nodes and containers.
If you no longer need the Azure Store application, you can delete the services to avoid incurring Azure costs.
- From the Kubernetes resources list, select Services and ingresses.
- Select the services you want to delete, and then select Delete.
To access the Kubernetes resources, you need access to the AKS cluster, Kubernetes API, and Kubernetes objects. Make sure you're either a cluster administrator or a user with the appropriate permissions to access the AKS cluster. For more information, see Access and identity options for AKS.
You might need to enable the Kubernetes resource view for existing clusters.
Tip
You can add the AKS feature for API server authorized IP ranges to limit API server access to only the firewall's public endpoint. Another option is to update the --api-server-authorized-ip-ranges/-ApiServerAccessAuthorizedIpRange to include access for a local client computer or the IP address range from which you're browsing the Azure portal. To allow this access, you need the computer's public IPv4 address. You can find this address using the following Azure CLI or Azure PowerShell commands, or you can search "what is my IP address" in your browser.
Retrieve your IP address using the following command:
CURRENT_IP=$(dig +short myip.opendns.com @resolver1.opendns.com)
Add your IP address to the AKS approved list using the az aks update command with the --api-server-authorized-ip-ranges parameter.
az aks update --resource-group <resource-group-name> --name <aks-cluster-name> --api-server-authorized-ip-ranges $CURRENT_IP/32
Retrieve your IP address using the following command:
$CURRENT_IP = (Invoke-RestMethod -Uri http://ipinfo.io/json).ip
Add your IP address to the AKS approved list using the Set-AzAksCluster command with the -ApiServerAccessAuthorizedIpRange parameter.
Set-AzAksCluster -ResourceGroupName <resource-group-name> -Name <aks-cluster-name> -ApiServerAccessAuthorizedIpRange $CURRENT_IP/32
This article showed you how to access Kubernetes resources from the Azure portal. For more information about AKS, Core concepts for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).


