Events
May 19, 6 PM - May 23, 12 AM
Calling all developers, creators, and AI innovators to join us in Seattle @Microsoft Build May 19-22.
Register todayThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
With copilots in the Copilot Studio app in Teams or Classic chatbots in the Copilot Studio web app, you can enable extra features that improve the core AI.
Agents include next-generation AI features that supersede or replace the features listed in this article.
You can use these AI features for backwards compatibility with older chatbots and support some scenarios. In most cases, you should create or convert your agents with the unified authoring canvas to get the best implementation of multiple AI technologies.
Important
Generative AI features, such as generative answers and natural language understanding, are only available if you create or convert a chatbot using the unified authoring canvas in the Copilot Studio web app.
You can use the AI features if:
Copilot Studio hosts multiple AI models and AI capabilities on a single service. The core feature is a transformer-based natural language understanding (NLU) model.
Traditionally, intent triggering—how an AI model determines the intent of a question by using NLU—is formalized as a multi-class classification problem. The model is highly associated with known categories. But any change in these categories means you need to build a new AI model.
Copilot Studio, however, employs a language understanding model that uses an example-based approach, powered by a deep neural model. This type of large-scale model only needs to be trained once, with large amounts of data, using AI supercomputing. The AI is then used with a few examples without further training.
This model is part of the AI at Scale initiative by Microsoft. The way AI is developed and used is changing. In Copilot Studio, this model allows for an intuitive way for chatbot makers to create content confidently, without having to involve AI experts.
With the Copilot Studio model, you provide a few examples when you craft trigger phrases for a topic. The examples for a single topic are usually 5 to 10 phrases.
Shorter trigger phrases are better, and you should aim for 2 to 10 words per phrase. Trigger phrases should be semantically different. For example, changing a single verb or noun could be enough to expand a topic's coverage.
Other changes or additions between phrases can be:
Plurals don't improve the triggering because contractions are already accounted for in the AI model.
Entities used in related topics automatically identify in user intents when matched with their trigger phrases. For example, the user intent "I want to book a ticket to Boston" matches with the trigger phrase "I want to book a ticket to Paris."
Topic overlap detection helps improve topic triggering accuracy by finding overlaps between topics. Resolving topic overlaps reduces the copilot's need to ask clarifying questions before triggering a topic.
Tip
Topic overlap detection is in general availability and supports all languages supported in Copilot Studio.
After you enable advanced AI capabilities, you can view a list of overlapped topics. In the navigation menu, select Analytics, then select the Topic triggering tab.
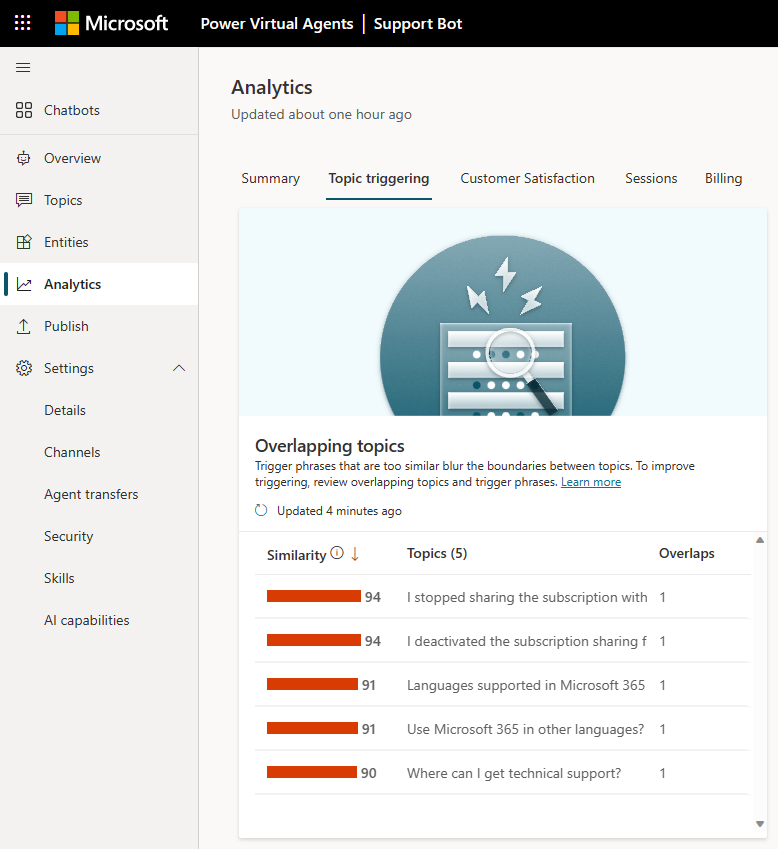
The list shows each overlapping topic along with a similarity score. This score represents the overall overlapped status for a topic and the number of topics that overlap with the listed one. The AI determines the similarity score as it evaluates how semantically similar the overlapping trigger phrases are to each other. A higher score means a topic has one or more trigger phrases close to another topic's trigger phrases.
You can sort the list by its similarity score, topic name, or number of trigger phrase overlaps.
If you select an item in the list, the Topic overlap details pane opens.
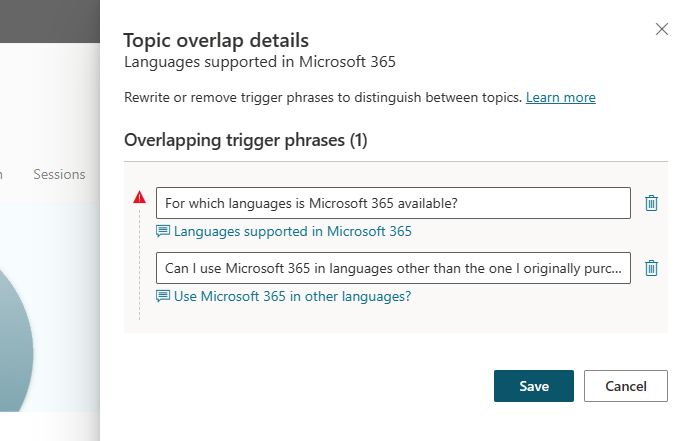
In this example, there's one trigger phrase in the "Languages supported in Microsoft 365" topic (For which languages is Microsoft 365 available?) that semantically overlaps with a trigger phrase in the "Use Microsoft 365 in other languages?" topic (Can I use Microsoft 365 in languages other than the one I originally purchased?). Here, the AI determines that both trigger phrases are semantically similar. The phrases have similar sentence structure, words, and grammar.
Using semantically similar trigger phrases for two different topics can lead to confusion. The copilot might not know which topic to open and asks follow-up questions to the copilot user.
Identifying semantically similar trigger phrases can also help you consolidate topics if they're too similar. You can edit the topics to make them more distinct.
On the Topic overlap details pane, you can select the link to go directly to a topic. You can also make changes to the trigger phrase or delete it. Select Save to apply any changes.
After you save your changes, the overlapping status automatically refreshes. You can manually refresh the topic overlap status, using the refresh icon in the Overlapping topics section.
This feature analyzes sessions between your agent and users and gives suggestions based on unmatched user input.
Once enabled, go to Analytics > Topic triggering (preview). A list of potential topics are shown with the number of times a query about this topic was made by users of the agent. The top 200 suggestions are shown.

The topic suggestion analyzer automatically runs once every one to two hours. The analyzer scans all new queries made since the analyzer last ran. The analyzer groups together queries that don't match an existing topic and shows them in the list. Your agent needs at least 100 new conversations from the last time any suggestion was generated to trigger the process. Suggestions with more than three user sessions are shown.
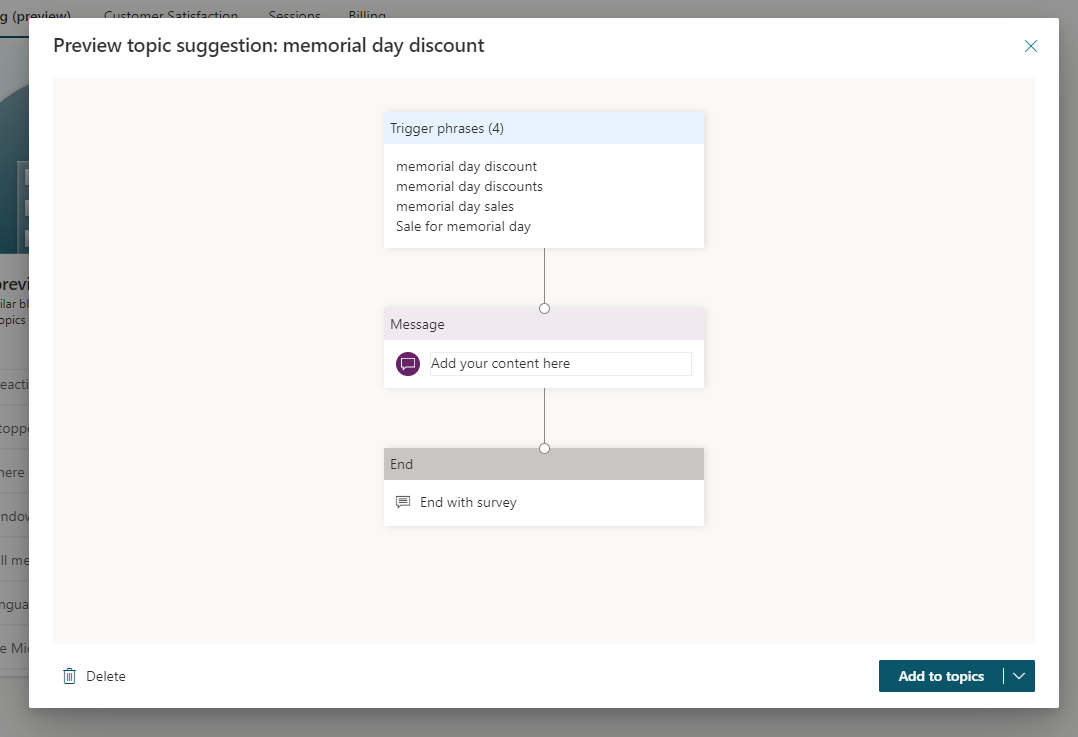
When you select an item in the suggestion list, a topic suggestion window appears, showing the topic with some suggested trigger phrases. The suggested trigger phrases are based on queries made by agent users that aren't matched to an existing topic.
You can choose to delete the entire suggested topic, for example if the topic is irrelevant to the agent, or add it to your list of topics by selecting Add to topics.
Important
You can't enable these features for agents not marked Classic. This includes any agent created (or converted) in the web app after May 23, 2023, or any agents that aren't created with the unified authoring canvas.
The unified authoring canvas includes improvements to the types of AI used by Copilot Studio. We recommend you create and convert your agents with the unified authoring canvas.
To enable these older AI capabilities in Copilot Studio:
Events
May 19, 6 PM - May 23, 12 AM
Calling all developers, creators, and AI innovators to join us in Seattle @Microsoft Build May 19-22.
Register todayTraining
Learning path
Introduction to generative AI for trainers - Training
Discover the world of generative AI, including basic concepts, the different applications in various fields, and the skills necessary to use generative AI tools within training environments. Gain knowledge of large language models (LLMs), AI-powered image generators, and Microsoft Copilot. Explore prompt engineering, navigate the limitations of content created by generative AI models, and learn to utilize generative AI models into your trainings critically and responsibly.
Certification
Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Engineer Associate - Certifications
Design and implement an Azure AI solution using Azure AI services, Azure AI Search, and Azure Open AI.