Korzystanie z modeli analizy dokumentów
Ta zawartość dotyczy:v4.0 (wersja zapoznawcza) | Poprzednie wersje:![]()
![]() v3.1 (GA)v3.0 (GA)
v3.1 (GA)v3.0 (GA)![]()
![]() v2.1 (GA)
v2.1 (GA)
Ta zawartość dotyczy:v3.1 (GA)Najnowsza wersja:![]()
![]() v4.0 (wersja zapoznawcza) | | Poprzednie wersje:
v4.0 (wersja zapoznawcza) | | Poprzednie wersje:![]() v3.0
v3.0![]() v2.1
v2.1
Ta zawartość dotyczy:v3.0 (GA) | Najnowsze wersje:![]()
![]() v4.0 (wersja zapoznawcza)
v4.0 (wersja zapoznawcza)![]() v3.1 | Poprzednia wersja:
v3.1 | Poprzednia wersja:![]() v2.1
v2.1
Ta zawartość dotyczy:v2.1 Najnowsza wersja:![]()
![]() v4.0 (wersja zapoznawcza) |
v4.0 (wersja zapoznawcza) |
Z tego przewodnika dowiesz się, jak dodawać modele analizy dokumentów do aplikacji i przepływów pracy. Użyj wybranego zestawu SDK języka programowania lub interfejsu API REST.
Azure AI Document Intelligence to oparta na chmurze usługa Azure AI, która używa uczenia maszynowego do wyodrębniania kluczowych elementów tekstu i struktury z dokumentów. Zalecamy korzystanie z bezpłatnej usługi podczas uczenia się technologii. Pamiętaj, że liczba bezpłatnych stron jest ograniczona do 500 miesięcznie.
Wybierz spośród następujących modeli analizy dokumentów i analizuj i wyodrębnij dane oraz wartości z formularzy i dokumentów:
Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
readmodelu jako podstawy do wyodrębniania tekstów z dokumentów.Wstępnie utworzony model układu wyodrębnia lokalizacje tekstu i tekstu, tabele, znaczniki zaznaczenia i informacje o strukturze z dokumentów i obrazów. Pary klucz/wartość można wyodrębnić przy użyciu modelu układu z włączonym opcjonalnym parametrem
features=keyValuePairsciągu zapytania.Wstępnie utworzony model kontraktu wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z umów umownych.
Model prebuilt-healthInsuranceCard.us wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z amerykańskich kart ubezpieczenia zdrowotnego.
Wstępnie utworzony model dokumentów podatkowych wyodrębnia informacje zgłaszane na temat formularzy podatkowych w USA.
Wstępnie utworzony model faktury wyodrębnia pola kluczy i elementy wiersza z faktur sprzedaży w różnych formatach i jakości. Pola obejmują obrazy przechwycone przez telefon, zeskanowane dokumenty i cyfrowe pliki PDF.
Wstępnie utworzony model paragonu wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z drukowanych i odręcznych paragonów sprzedaży.
Wstępnie utworzony model idDocument wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z amerykańskich licencji kierowców, międzynarodowych stron biograficznych paszportów, identyfikatorów stanów USA, kart ubezpieczenia społecznego i stałych kart rezydentów.
- Wstępnie utworzony model businessCard wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje i dane kontaktowe z obrazów wizytówek.
Dokumentacja interfejsu API referencyjna zestawu SDK biblioteki | klienta — pakiet referencyjny | | (NuGet) | Przykłady | obsługiwane wersje interfejsu API REST
Dokumentacja zestawu SDK biblioteki | klienta — dokumentacja | | | interfejsu API REST — przykłady przykładów |obsługiwanych wersji interfejsu API REST
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Środowisko IDE programu Visual Studio.
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
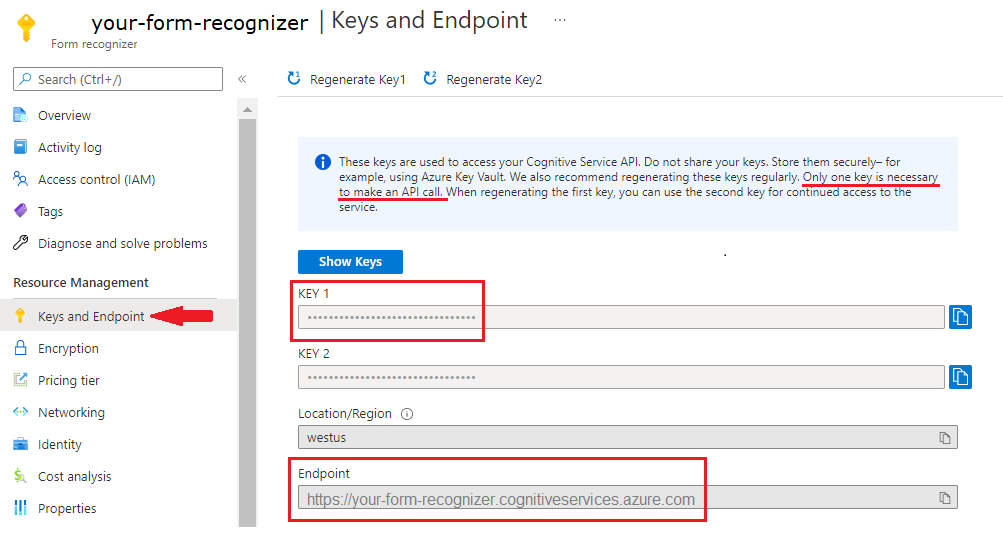
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.
Plik dokumentu w lokalizacji adresu URL. W tym projekcie można użyć przykładowych formularzy podanych w poniższej tabeli dla każdej funkcji:
Funkcja modelID document-url Odczyt modelu odczyt wstępnie utworzony Broszura przykładowa Model układu wstępnie utworzony układ Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej Model formularza W-2 prebuilt-tax.us.w2 Przykładowy formularz W-2 Model faktury wstępnie utworzona faktura Przykładowa faktura Model paragonu wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie Przykładowe potwierdzenie Model dokumentu identyfikatora prebuilt-idDocument Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze Model wizytówek wstępnie utworzona karta biznesowa Przykładowa wizytówka
Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Uruchom program Visual Studio.
Na stronie początkowej wybierz pozycję Utwórz nowy projekt.
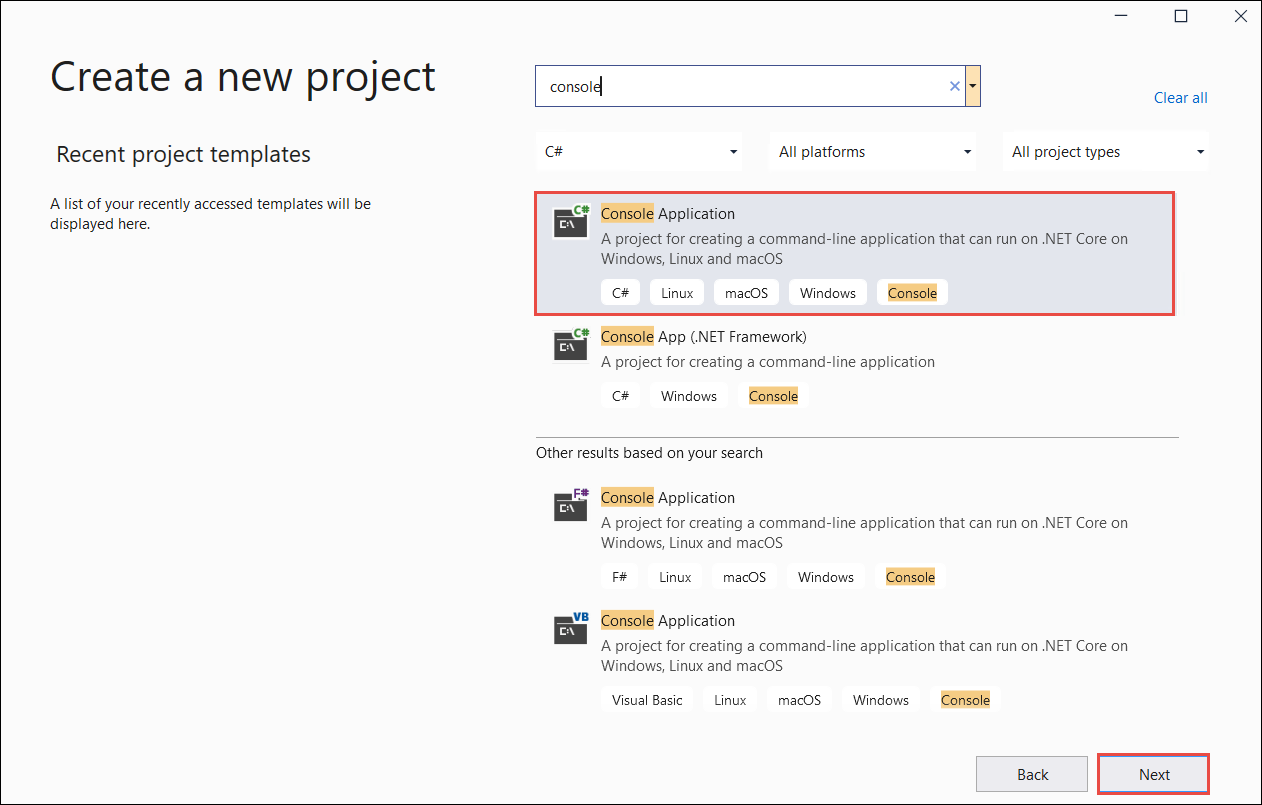
Na stronie Tworzenie nowego projektu wprowadź konsolę w polu wyszukiwania. Wybierz szablon Aplikacja konsolowa, a następnie wybierz pozycję Dalej.
Na stronie Konfigurowanie nowego projektu w obszarze Nazwa projektu wprowadź docIntelligence_app. Następnie kliknij przycisk Dalej.

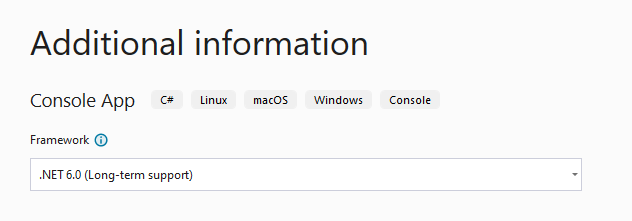
Na stronie Dodatkowe informacje wybierz pozycję .NET 8.0 (obsługa długoterminowa), a następnie wybierz pozycję Utwórz.
Instalowanie biblioteki klienta za pomocą narzędzia NuGet
Kliknij prawym przyciskiem myszy projekt docIntelligence_app i wybierz polecenie Zarządzaj pakietami NuGet... .

Wybierz kartę Przeglądaj i wpisz Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.

Wybierz wersję z menu rozwijanego i zainstaluj pakiet w projekcie.
Kompilowanie aplikacji
Uwaga
Począwszy od platformy .NET 6, nowe projekty korzystające z console szablonu generują nowy styl programu, który różni się od poprzednich wersji. Nowe dane wyjściowe korzystają z ostatnich funkcji języka C#, które upraszczają pisanie kodu.
W przypadku korzystania z nowszej wersji wystarczy napisać treść Main metody. Nie trzeba dołączać instrukcji najwyższego poziomu, globalnych dyrektyw using ani niejawnych dyrektyw using. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Szablon aplikacji konsolowej języka C# generuje instrukcje najwyższego poziomu.
Otwórz plik Program.cs.
Usuń istniejący kod, w tym wiersz
Console.Writeline("Hello World!").Wybierz jeden z następujących przykładów kodu i skopiuj/wklej do pliku Program.cs aplikacji:
Po dodaniu przykładowego kodu do aplikacji wybierz zielony przycisk Start obok nazwy projektu, aby skompilować i uruchomić program, lub naciśnij klawisz F5.

Korzystanie z modelu odczytu
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
//sample document
Uri fileUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-read", fileUri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
foreach (DocumentPage page in result.Pages)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document Page {page.PageNumber} has {page.Lines.Count} line(s), {page.Words.Count} word(s),");
Console.WriteLine($"and {page.SelectionMarks.Count} selection mark(s).");
for (int i = 0; i < page.Lines.Count; i++)
{
DocumentLine line = page.Lines[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Line {i} has content: '{line.Content}'.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < line.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
}
foreach (DocumentStyle style in result.Styles)
{
// Check the style and style confidence to see if text is handwritten.
// Note that value '0.8' is used as an example.
bool isHandwritten = style.IsHandwritten.HasValue && style.IsHandwritten == true;
if (isHandwritten && style.Confidence > 0.8)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Handwritten content found:");
foreach (DocumentSpan span in style.Spans)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Content: {result.Content.Substring(span.Index, span.Length)}");
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Detected languages:");
foreach (DocumentLanguage language in result.Languages)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Found language with locale'{language.Locale}' with confidence {language.Confidence}.");
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl read dane wyjściowe modelu.
Korzystanie z modelu układu
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri fileUri = new Uri ("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-layout", fileUri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
foreach (DocumentPage page in result.Pages)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document Page {page.PageNumber} has {page.Lines.Count} line(s), {page.Words.Count} word(s),");
Console.WriteLine($"and {page.SelectionMarks.Count} selection mark(s).");
for (int i = 0; i < page.Lines.Count; i++)
{
DocumentLine line = page.Lines[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Line {i} has content: '{line.Content}'.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < line.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < page.SelectionMarks.Count; i++)
{
DocumentSelectionMark selectionMark = page.SelectionMarks[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Selection Mark {i} is {selectionMark.State}.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < selectionMark.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {selectionMark.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {selectionMark.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Paragraphs:");
foreach (DocumentParagraph paragraph in result.Paragraphs)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Paragraph content: {paragraph.Content}");
if (paragraph.Role != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Role: {paragraph.Role}");
}
}
foreach (DocumentStyle style in result.Styles)
{
// Check the style and style confidence to see if text is handwritten.
// Note that value '0.8' is used as an example.
bool isHandwritten = style.IsHandwritten.HasValue && style.IsHandwritten == true;
if (isHandwritten && style.Confidence > 0.8)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Handwritten content found:");
foreach (DocumentSpan span in style.Spans)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Content: {result.Content.Substring(span.Index, span.Length)}");
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("The following tables were extracted:");
for (int i = 0; i < result.Tables.Count; i++)
{
DocumentTable table = result.Tables[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Table {i} has {table.RowCount} rows and {table.ColumnCount} columns.");
foreach (DocumentTableCell cell in table.Cells)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Cell ({cell.RowIndex}, {cell.ColumnIndex}) has kind '{cell.Kind}' and content: '{cell.Content}'.");
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu układu.
Korzystanie z ogólnego modelu dokumentów
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri fileUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-layout.pdf");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-document", fileUri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
Console.WriteLine("Detected key-value pairs:");
foreach (DocumentKeyValuePair kvp in result.KeyValuePairs)
{
if (kvp.Value == null)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Found key with no value: '{kvp.Key.Content}'");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($" Found key-value pair: '{kvp.Key.Content}' and '{kvp.Value.Content}'");
}
}
foreach (DocumentPage page in result.Pages)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document Page {page.PageNumber} has {page.Lines.Count} line(s), {page.Words.Count} word(s),");
Console.WriteLine($"and {page.SelectionMarks.Count} selection mark(s).");
for (int i = 0; i < page.Lines.Count; i++)
{
DocumentLine line = page.Lines[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Line {i} has content: '{line.Content}'.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < line.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < page.SelectionMarks.Count; i++)
{
DocumentSelectionMark selectionMark = page.SelectionMarks[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Selection Mark {i} is {selectionMark.State}.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < selectionMark.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {selectionMark.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {selectionMark.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
}
foreach (DocumentStyle style in result.Styles)
{
// Check the style and style confidence to see if text is handwritten.
// Note that value '0.8' is used as an example.
bool isHandwritten = style.IsHandwritten.HasValue && style.IsHandwritten == true;
if (isHandwritten && style.Confidence > 0.8)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Handwritten content found:");
foreach (DocumentSpan span in style.Spans)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Content: {result.Content.Substring(span.Index, span.Length)}");
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("The following tables were extracted:");
for (int i = 0; i < result.Tables.Count; i++)
{
DocumentTable table = result.Tables[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Table {i} has {table.RowCount} rows and {table.ColumnCount} columns.");
foreach (DocumentTableCell cell in table.Cells)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Cell ({cell.RowIndex}, {cell.ColumnIndex}) has kind '{cell.Kind}' and content: '{cell.Content}'.");
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl ogólne dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu.
Korzystanie z modelu podatkowego W-2
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri w2Uri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-tax.us.w2", w2Uri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
for (int i = 0; i < result.Documents.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document {i}:");
AnalyzedDocument document = result.Documents[i];
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("AdditionalInfo", out DocumentField? additionalInfoField))
{
if (additionalInfoField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField infoField in additionalInfoField.Value.AsList())
{
Console.WriteLine("AdditionalInfo:");
if (infoField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> infoFields = infoField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (infoFields.TryGetValue("Amount", out DocumentField? amountField))
{
if (amountField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Double)
{
double amount = amountField.Value.AsDouble();
Console.WriteLine($" Amount: '{amount}', with confidence {amountField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (infoFields.TryGetValue("LetterCode", out DocumentField? letterCodeField))
{
if (letterCodeField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string letterCode = letterCodeField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" LetterCode: '{letterCode}', with confidence {letterCodeField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("AllocatedTips", out DocumentField? allocatedTipsField))
{
if (allocatedTipsField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Double)
{
double allocatedTips = allocatedTipsField.Value.AsDouble();
Console.WriteLine($"Allocated Tips: '{allocatedTips}', with confidence {allocatedTipsField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("Employer", out DocumentField? employerField))
{
if (employerField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> employerFields = employerField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (employerFields.TryGetValue("Name", out DocumentField? employerNameField))
{
if (employerNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string name = employerNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Employer Name: '{name}', with confidence {employerNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (employerFields.TryGetValue("IdNumber", out DocumentField? idNumberField))
{
if (idNumberField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string id = idNumberField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Employer ID Number: '{id}', with confidence {idNumberField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (employerFields.TryGetValue("Address", out DocumentField? addressField))
{
if (addressField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Address)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Employer Address: '{addressField.Content}', with confidence {addressField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2.
Korzystanie z modelu faktury
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri invoiceUri = new Uri("https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/raw/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/invoice.pdf");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-invoice", invoiceUri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
for (int i = 0; i < result.Documents.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document {i}:");
AnalyzedDocument document = result.Documents[i];
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("VendorName", out DocumentField vendorNameField))
{
if (vendorNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string vendorName = vendorNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Vendor Name: '{vendorName}', with confidence {vendorNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("CustomerName", out DocumentField customerNameField))
{
if (customerNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string customerName = customerNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Customer Name: '{customerName}', with confidence {customerNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("Items", out DocumentField itemsField))
{
if (itemsField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField itemField in itemsField.Value.AsList())
{
Console.WriteLine("Item:");
if (itemField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> itemFields = itemField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("Description", out DocumentField itemDescriptionField))
{
if (itemDescriptionField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string itemDescription = itemDescriptionField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" Description: '{itemDescription}', with confidence {itemDescriptionField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("Amount", out DocumentField itemAmountField))
{
if (itemAmountField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Currency)
{
CurrencyValue itemAmount = itemAmountField.Value.AsCurrency();
Console.WriteLine($" Amount: '{itemAmount.Symbol}{itemAmount.Amount}', with confidence {itemAmountField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("SubTotal", out DocumentField subTotalField))
{
if (subTotalField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Currency)
{
CurrencyValue subTotal = subTotalField.Value.AsCurrency();
Console.WriteLine($"Sub Total: '{subTotal.Symbol}{subTotal.Amount}', with confidence {subTotalField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("TotalTax", out DocumentField totalTaxField))
{
if (totalTaxField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Currency)
{
CurrencyValue totalTax = totalTaxField.Value.AsCurrency();
Console.WriteLine($"Total Tax: '{totalTax.Symbol}{totalTax.Amount}', with confidence {totalTaxField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("InvoiceTotal", out DocumentField invoiceTotalField))
{
if (invoiceTotalField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Currency)
{
CurrencyValue invoiceTotal = invoiceTotalField.Value.AsCurrency();
Console.WriteLine($"Invoice Total: '{invoiceTotal.Symbol}{invoiceTotal.Amount}', with confidence {invoiceTotalField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu faktury.
Korzystanie z modelu paragonu
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri receiptUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-receipt", receiptUri);
AnalyzeResult receipts = operation.Value;
foreach (AnalyzedDocument receipt in receipts.Documents)
{
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("MerchantName", out DocumentField merchantNameField))
{
if (merchantNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string merchantName = merchantNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Merchant Name: '{merchantName}', with confidence {merchantNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("TransactionDate", out DocumentField transactionDateField))
{
if (transactionDateField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Date)
{
DateTimeOffset transactionDate = transactionDateField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($"Transaction Date: '{transactionDate}', with confidence {transactionDateField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("Items", out DocumentField itemsField))
{
if (itemsField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField itemField in itemsField.Value.AsList())
{
Console.WriteLine("Item:");
if (itemField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> itemFields = itemField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("Description", out DocumentField itemDescriptionField))
{
if (itemDescriptionField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string itemDescription = itemDescriptionField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" Description: '{itemDescription}', with confidence {itemDescriptionField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("TotalPrice", out DocumentField itemTotalPriceField))
{
if (itemTotalPriceField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Double)
{
double itemTotalPrice = itemTotalPriceField.Value.AsDouble();
Console.WriteLine($" Total Price: '{itemTotalPrice}', with confidence {itemTotalPriceField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("Total", out DocumentField totalField))
{
if (totalField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Double)
{
double total = totalField.Value.AsDouble();
Console.WriteLine($"Total: '{total}', with confidence '{totalField.Confidence}'");
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu.
Model dokumentu identyfikatora
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri idDocumentUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-idDocument", idDocumentUri);
AnalyzeResult identityDocuments = operation.Value;
AnalyzedDocument identityDocument = identityDocuments.Documents.Single();
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("Address", out DocumentField addressField))
{
if (addressField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string address = addressField.Value. AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Address: '{address}', with confidence {addressField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("CountryRegion", out DocumentField countryRegionField))
{
if (countryRegionField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.CountryRegion)
{
string countryRegion = countryRegionField.Value.AsCountryRegion();
Console.WriteLine($"CountryRegion: '{countryRegion}', with confidence {countryRegionField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DateOfBirth", out DocumentField dateOfBirthField))
{
if (dateOfBirthField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Date)
{
DateTimeOffset dateOfBirth = dateOfBirthField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($"Date Of Birth: '{dateOfBirth}', with confidence {dateOfBirthField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DateOfExpiration", out DocumentField dateOfExpirationField))
{
if (dateOfExpirationField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Date)
{
DateTimeOffset dateOfExpiration = dateOfExpirationField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($"Date Of Expiration: '{dateOfExpiration}', with confidence {dateOfExpirationField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DocumentNumber", out DocumentField documentNumberField))
{
if (documentNumberField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string documentNumber = documentNumberField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Document Number: '{documentNumber}', with confidence {documentNumberField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("FirstName", out DocumentField firstNameField))
{
if (firstNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string firstName = firstNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"First Name: '{firstName}', with confidence {firstNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("LastName", out DocumentField lastNameField))
{
if (lastNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string lastName = lastNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Last Name: '{lastName}', with confidence {lastNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("Region", out DocumentField regionfield))
{
if (regionfield.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string region = regionfield.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Region: '{region}', with confidence {regionfield.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("Sex", out DocumentField sexfield))
{
if (sexfield.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string sex = sexfield.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Sex: '{sex}', with confidence {sexfield.Confidence}");
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu id-document.
Korzystanie z modelu wizytówek
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri businessCardUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/business-card-english.jpg");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-businessCard", businessCardUri);
AnalyzeResult businessCards = operation.Value;
foreach (AnalyzedDocument businessCard in businessCards.Documents)
{
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("ContactNames", out DocumentField ContactNamesField))
{
if (ContactNamesField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField contactNameField in ContactNamesField.Value.AsList())
{
Console.WriteLine("Contact Name: ");
if (contactNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> contactNameFields = contactNameField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (contactNameFields.TryGetValue("FirstName", out DocumentField firstNameField))
{
if (firstNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string firstName = firstNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" First Name: '{firstName}', with confidence {firstNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (contactNameFields.TryGetValue("LastName", out DocumentField lastNameField))
{
if (lastNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string lastName = lastNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" Last Name: '{lastName}', with confidence {lastNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("JobTitles", out DocumentField jobTitlesFields))
{
if (jobTitlesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField jobTitleField in jobTitlesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (jobTitleField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string jobTitle = jobTitleField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Job Title: '{jobTitle}', with confidence {jobTitleField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Departments", out DocumentField departmentFields))
{
if (departmentFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField departmentField in departmentFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (departmentField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string department = departmentField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Department: '{department}', with confidence {departmentField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Emails", out DocumentField emailFields))
{
if (emailFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField emailField in emailFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (emailField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string email = emailField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Email: '{email}', with confidence {emailField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Websites", out DocumentField websiteFields))
{
if (websiteFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField websiteField in websiteFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (websiteField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string website = websiteField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Website: '{website}', with confidence {websiteField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("MobilePhones", out DocumentField mobilePhonesFields))
{
if (mobilePhonesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField mobilePhoneField in mobilePhonesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (mobilePhoneField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.PhoneNumber)
{
string mobilePhone = mobilePhoneField.Value.AsPhoneNumber();
Console.WriteLine($"Mobile phone number: '{mobilePhone}', with confidence {mobilePhoneField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("WorkPhones", out DocumentField workPhonesFields))
{
if (workPhonesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField workPhoneField in workPhonesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (workPhoneField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.PhoneNumber)
{
string workPhone = workPhoneField.Value.AsPhoneNumber();
Console.WriteLine($"Work phone number: '{workPhone}', with confidence {workPhoneField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Faxes", out DocumentField faxesFields))
{
if (faxesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField faxField in faxesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (faxField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.PhoneNumber)
{
string fax = faxField.Value.AsPhoneNumber();
Console.WriteLine($"Fax phone number: '{fax}', with confidence {faxField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Addresses", out DocumentField addressesFields))
{
if (addressesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField addressField in addressesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (addressField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string address = addressField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Address: '{address}', with confidence {addressField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("CompanyNames", out DocumentField companyNamesFields))
{
if (companyNamesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField companyNameField in companyNamesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (companyNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string companyName = companyNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Company name: '{companyName}', with confidence {companyNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu wizytówek.
Dokumentacja interfejsu API referencyjna zestawu SDK biblioteki | klienta — pakiet referencyjny | | (NuGet) | Przykłady | obsługiwane wersje interfejsu API REST
Dokumentacja zestawu SDK biblioteki | klienta — dokumentacja | | | interfejsu API REST — przykłady przykładów |obsługiwanych wersji interfejsu API REST
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Środowisko IDE programu Visual Studio.
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Plik dokumentu w lokalizacji adresu URL. W tym projekcie można użyć przykładowych formularzy podanych w poniższej tabeli dla każdej funkcji:
Funkcja modelID document-url Odczyt modelu odczyt wstępnie utworzony Broszura przykładowa Model układu wstępnie utworzony układ Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej Model formularza W-2 prebuilt-tax.us.w2 Przykładowy formularz W-2 Model faktury wstępnie utworzona faktura Przykładowa faktura Model paragonu wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie Przykładowe potwierdzenie Model dokumentu identyfikatora prebuilt-idDocument Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze Model wizytówek wstępnie utworzona karta biznesowa Przykładowa wizytówka
Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Uruchom program Visual Studio.
Na stronie początkowej wybierz pozycję Utwórz nowy projekt.

Na stronie Tworzenie nowego projektu wprowadź konsolę w polu wyszukiwania. Wybierz szablon Aplikacja konsolowa, a następnie wybierz pozycję Dalej.

Na stronie Konfigurowanie nowego projektu w obszarze Nazwa projektu wprowadź docIntelligence_app. Następnie kliknij przycisk Dalej.

Na stronie Dodatkowe informacje wybierz pozycję .NET 8.0 (obsługa długoterminowa), a następnie wybierz pozycję Utwórz.

Instalowanie biblioteki klienta za pomocą narzędzia NuGet
Kliknij prawym przyciskiem myszy projekt docIntelligence_app i wybierz polecenie Zarządzaj pakietami NuGet... .

Wybierz kartę Przeglądaj i wpisz Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.

Wybierz wersję z menu rozwijanego i zainstaluj pakiet w projekcie.
Kompilowanie aplikacji
Uwaga
Począwszy od platformy .NET 6, nowe projekty korzystające z console szablonu generują nowy styl programu, który różni się od poprzednich wersji. Nowe dane wyjściowe korzystają z ostatnich funkcji języka C#, które upraszczają pisanie kodu.
W przypadku korzystania z nowszej wersji wystarczy napisać treść Main metody. Nie trzeba dołączać instrukcji najwyższego poziomu, globalnych dyrektyw using ani niejawnych dyrektyw using. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Szablon aplikacji konsolowej języka C# generuje instrukcje najwyższego poziomu.
Otwórz plik Program.cs.
Usuń istniejący kod, w tym wiersz
Console.Writeline("Hello World!").Wybierz jeden z następujących przykładów kodu i skopiuj/wklej do pliku Program.cs aplikacji:
Po dodaniu przykładowego kodu do aplikacji wybierz zielony przycisk Start obok nazwy projektu, aby skompilować i uruchomić program, lub naciśnij klawisz F5.

Korzystanie z modelu odczytu
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
//sample document
Uri fileUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-read", fileUri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
foreach (DocumentPage page in result.Pages)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document Page {page.PageNumber} has {page.Lines.Count} line(s), {page.Words.Count} word(s),");
Console.WriteLine($"and {page.SelectionMarks.Count} selection mark(s).");
for (int i = 0; i < page.Lines.Count; i++)
{
DocumentLine line = page.Lines[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Line {i} has content: '{line.Content}'.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < line.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
}
foreach (DocumentStyle style in result.Styles)
{
// Check the style and style confidence to see if text is handwritten.
// Note that value '0.8' is used as an example.
bool isHandwritten = style.IsHandwritten.HasValue && style.IsHandwritten == true;
if (isHandwritten && style.Confidence > 0.8)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Handwritten content found:");
foreach (DocumentSpan span in style.Spans)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Content: {result.Content.Substring(span.Index, span.Length)}");
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Detected languages:");
foreach (DocumentLanguage language in result.Languages)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Found language with locale'{language.Locale}' with confidence {language.Confidence}.");
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl read dane wyjściowe modelu.
Korzystanie z modelu układu
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri fileUri = new Uri ("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-layout", fileUri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
foreach (DocumentPage page in result.Pages)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document Page {page.PageNumber} has {page.Lines.Count} line(s), {page.Words.Count} word(s),");
Console.WriteLine($"and {page.SelectionMarks.Count} selection mark(s).");
for (int i = 0; i < page.Lines.Count; i++)
{
DocumentLine line = page.Lines[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Line {i} has content: '{line.Content}'.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < line.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < page.SelectionMarks.Count; i++)
{
DocumentSelectionMark selectionMark = page.SelectionMarks[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Selection Mark {i} is {selectionMark.State}.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < selectionMark.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {selectionMark.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {selectionMark.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Paragraphs:");
foreach (DocumentParagraph paragraph in result.Paragraphs)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Paragraph content: {paragraph.Content}");
if (paragraph.Role != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Role: {paragraph.Role}");
}
}
foreach (DocumentStyle style in result.Styles)
{
// Check the style and style confidence to see if text is handwritten.
// Note that value '0.8' is used as an example.
bool isHandwritten = style.IsHandwritten.HasValue && style.IsHandwritten == true;
if (isHandwritten && style.Confidence > 0.8)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Handwritten content found:");
foreach (DocumentSpan span in style.Spans)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Content: {result.Content.Substring(span.Index, span.Length)}");
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("The following tables were extracted:");
for (int i = 0; i < result.Tables.Count; i++)
{
DocumentTable table = result.Tables[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Table {i} has {table.RowCount} rows and {table.ColumnCount} columns.");
foreach (DocumentTableCell cell in table.Cells)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Cell ({cell.RowIndex}, {cell.ColumnIndex}) has kind '{cell.Kind}' and content: '{cell.Content}'.");
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu układu.
Korzystanie z ogólnego modelu dokumentów
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri fileUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-layout.pdf");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-document", fileUri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
Console.WriteLine("Detected key-value pairs:");
foreach (DocumentKeyValuePair kvp in result.KeyValuePairs)
{
if (kvp.Value == null)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Found key with no value: '{kvp.Key.Content}'");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($" Found key-value pair: '{kvp.Key.Content}' and '{kvp.Value.Content}'");
}
}
foreach (DocumentPage page in result.Pages)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document Page {page.PageNumber} has {page.Lines.Count} line(s), {page.Words.Count} word(s),");
Console.WriteLine($"and {page.SelectionMarks.Count} selection mark(s).");
for (int i = 0; i < page.Lines.Count; i++)
{
DocumentLine line = page.Lines[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Line {i} has content: '{line.Content}'.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < line.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {line.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < page.SelectionMarks.Count; i++)
{
DocumentSelectionMark selectionMark = page.SelectionMarks[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Selection Mark {i} is {selectionMark.State}.");
Console.WriteLine($" Its bounding polygon (points ordered clockwise):");
for (int j = 0; j < selectionMark.BoundingPolygon.Count; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Point {j} => X: {selectionMark.BoundingPolygon[j].X}, Y: {selectionMark.BoundingPolygon[j].Y}");
}
}
}
foreach (DocumentStyle style in result.Styles)
{
// Check the style and style confidence to see if text is handwritten.
// Note that value '0.8' is used as an example.
bool isHandwritten = style.IsHandwritten.HasValue && style.IsHandwritten == true;
if (isHandwritten && style.Confidence > 0.8)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Handwritten content found:");
foreach (DocumentSpan span in style.Spans)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Content: {result.Content.Substring(span.Index, span.Length)}");
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("The following tables were extracted:");
for (int i = 0; i < result.Tables.Count; i++)
{
DocumentTable table = result.Tables[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Table {i} has {table.RowCount} rows and {table.ColumnCount} columns.");
foreach (DocumentTableCell cell in table.Cells)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Cell ({cell.RowIndex}, {cell.ColumnIndex}) has kind '{cell.Kind}' and content: '{cell.Content}'.");
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl ogólne dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu.
Korzystanie z modelu podatkowego W-2
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri w2Uri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-tax.us.w2", w2Uri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
for (int i = 0; i < result.Documents.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document {i}:");
AnalyzedDocument document = result.Documents[i];
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("AdditionalInfo", out DocumentField? additionalInfoField))
{
if (additionalInfoField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField infoField in additionalInfoField.Value.AsList())
{
Console.WriteLine("AdditionalInfo:");
if (infoField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> infoFields = infoField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (infoFields.TryGetValue("Amount", out DocumentField? amountField))
{
if (amountField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Double)
{
double amount = amountField.Value.AsDouble();
Console.WriteLine($" Amount: '{amount}', with confidence {amountField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (infoFields.TryGetValue("LetterCode", out DocumentField? letterCodeField))
{
if (letterCodeField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string letterCode = letterCodeField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" LetterCode: '{letterCode}', with confidence {letterCodeField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("AllocatedTips", out DocumentField? allocatedTipsField))
{
if (allocatedTipsField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Double)
{
double allocatedTips = allocatedTipsField.Value.AsDouble();
Console.WriteLine($"Allocated Tips: '{allocatedTips}', with confidence {allocatedTipsField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("Employer", out DocumentField? employerField))
{
if (employerField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> employerFields = employerField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (employerFields.TryGetValue("Name", out DocumentField? employerNameField))
{
if (employerNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string name = employerNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Employer Name: '{name}', with confidence {employerNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (employerFields.TryGetValue("IdNumber", out DocumentField? idNumberField))
{
if (idNumberField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string id = idNumberField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Employer ID Number: '{id}', with confidence {idNumberField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (employerFields.TryGetValue("Address", out DocumentField? addressField))
{
if (addressField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Address)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Employer Address: '{addressField.Content}', with confidence {addressField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2.
Korzystanie z modelu faktury
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri invoiceUri = new Uri("https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/raw/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/invoice.pdf");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-invoice", invoiceUri);
AnalyzeResult result = operation.Value;
for (int i = 0; i < result.Documents.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Document {i}:");
AnalyzedDocument document = result.Documents[i];
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("VendorName", out DocumentField vendorNameField))
{
if (vendorNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string vendorName = vendorNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Vendor Name: '{vendorName}', with confidence {vendorNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("CustomerName", out DocumentField customerNameField))
{
if (customerNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string customerName = customerNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Customer Name: '{customerName}', with confidence {customerNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("Items", out DocumentField itemsField))
{
if (itemsField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField itemField in itemsField.Value.AsList())
{
Console.WriteLine("Item:");
if (itemField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> itemFields = itemField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("Description", out DocumentField itemDescriptionField))
{
if (itemDescriptionField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string itemDescription = itemDescriptionField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" Description: '{itemDescription}', with confidence {itemDescriptionField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("Amount", out DocumentField itemAmountField))
{
if (itemAmountField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Currency)
{
CurrencyValue itemAmount = itemAmountField.Value.AsCurrency();
Console.WriteLine($" Amount: '{itemAmount.Symbol}{itemAmount.Amount}', with confidence {itemAmountField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("SubTotal", out DocumentField subTotalField))
{
if (subTotalField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Currency)
{
CurrencyValue subTotal = subTotalField.Value.AsCurrency();
Console.WriteLine($"Sub Total: '{subTotal.Symbol}{subTotal.Amount}', with confidence {subTotalField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("TotalTax", out DocumentField totalTaxField))
{
if (totalTaxField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Currency)
{
CurrencyValue totalTax = totalTaxField.Value.AsCurrency();
Console.WriteLine($"Total Tax: '{totalTax.Symbol}{totalTax.Amount}', with confidence {totalTaxField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (document.Fields.TryGetValue("InvoiceTotal", out DocumentField invoiceTotalField))
{
if (invoiceTotalField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Currency)
{
CurrencyValue invoiceTotal = invoiceTotalField.Value.AsCurrency();
Console.WriteLine($"Invoice Total: '{invoiceTotal.Symbol}{invoiceTotal.Amount}', with confidence {invoiceTotalField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu faktury.
Korzystanie z modelu paragonu
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri receiptUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-receipt", receiptUri);
AnalyzeResult receipts = operation.Value;
foreach (AnalyzedDocument receipt in receipts.Documents)
{
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("MerchantName", out DocumentField merchantNameField))
{
if (merchantNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string merchantName = merchantNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Merchant Name: '{merchantName}', with confidence {merchantNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("TransactionDate", out DocumentField transactionDateField))
{
if (transactionDateField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Date)
{
DateTimeOffset transactionDate = transactionDateField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($"Transaction Date: '{transactionDate}', with confidence {transactionDateField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("Items", out DocumentField itemsField))
{
if (itemsField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField itemField in itemsField.Value.AsList())
{
Console.WriteLine("Item:");
if (itemField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> itemFields = itemField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("Description", out DocumentField itemDescriptionField))
{
if (itemDescriptionField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string itemDescription = itemDescriptionField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" Description: '{itemDescription}', with confidence {itemDescriptionField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("TotalPrice", out DocumentField itemTotalPriceField))
{
if (itemTotalPriceField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Double)
{
double itemTotalPrice = itemTotalPriceField.Value.AsDouble();
Console.WriteLine($" Total Price: '{itemTotalPrice}', with confidence {itemTotalPriceField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("Total", out DocumentField totalField))
{
if (totalField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Double)
{
double total = totalField.Value.AsDouble();
Console.WriteLine($"Total: '{total}', with confidence '{totalField.Confidence}'");
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu.
Model dokumentu identyfikatora
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri idDocumentUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-idDocument", idDocumentUri);
AnalyzeResult identityDocuments = operation.Value;
AnalyzedDocument identityDocument = identityDocuments.Documents.Single();
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("Address", out DocumentField addressField))
{
if (addressField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string address = addressField.Value. AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Address: '{address}', with confidence {addressField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("CountryRegion", out DocumentField countryRegionField))
{
if (countryRegionField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.CountryRegion)
{
string countryRegion = countryRegionField.Value.AsCountryRegion();
Console.WriteLine($"CountryRegion: '{countryRegion}', with confidence {countryRegionField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DateOfBirth", out DocumentField dateOfBirthField))
{
if (dateOfBirthField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Date)
{
DateTimeOffset dateOfBirth = dateOfBirthField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($"Date Of Birth: '{dateOfBirth}', with confidence {dateOfBirthField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DateOfExpiration", out DocumentField dateOfExpirationField))
{
if (dateOfExpirationField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Date)
{
DateTimeOffset dateOfExpiration = dateOfExpirationField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($"Date Of Expiration: '{dateOfExpiration}', with confidence {dateOfExpirationField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DocumentNumber", out DocumentField documentNumberField))
{
if (documentNumberField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string documentNumber = documentNumberField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Document Number: '{documentNumber}', with confidence {documentNumberField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("FirstName", out DocumentField firstNameField))
{
if (firstNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string firstName = firstNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"First Name: '{firstName}', with confidence {firstNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("LastName", out DocumentField lastNameField))
{
if (lastNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string lastName = lastNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Last Name: '{lastName}', with confidence {lastNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("Region", out DocumentField regionfield))
{
if (regionfield.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string region = regionfield.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Region: '{region}', with confidence {regionfield.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("Sex", out DocumentField sexfield))
{
if (sexfield.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string sex = sexfield.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Sex: '{sex}', with confidence {sexfield.Confidence}");
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu id-document.
Korzystanie z modelu wizytówek
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.DocumentAnalysis;
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables to create your `AzureKeyCredential` and `DocumentAnalysisClient` instances
string key = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_KEY");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("DI_ENDPOINT");
AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
// sample document document
Uri businessCardUri = new Uri("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/business-card-english.jpg");
AnalyzeDocumentOperation operation = await client.AnalyzeDocumentFromUriAsync(WaitUntil.Completed, "prebuilt-businessCard", businessCardUri);
AnalyzeResult businessCards = operation.Value;
foreach (AnalyzedDocument businessCard in businessCards.Documents)
{
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("ContactNames", out DocumentField ContactNamesField))
{
if (ContactNamesField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField contactNameField in ContactNamesField.Value.AsList())
{
Console.WriteLine("Contact Name: ");
if (contactNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, DocumentField> contactNameFields = contactNameField.Value.AsDictionary();
if (contactNameFields.TryGetValue("FirstName", out DocumentField firstNameField))
{
if (firstNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string firstName = firstNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" First Name: '{firstName}', with confidence {firstNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (contactNameFields.TryGetValue("LastName", out DocumentField lastNameField))
{
if (lastNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string lastName = lastNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" Last Name: '{lastName}', with confidence {lastNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("JobTitles", out DocumentField jobTitlesFields))
{
if (jobTitlesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField jobTitleField in jobTitlesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (jobTitleField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string jobTitle = jobTitleField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Job Title: '{jobTitle}', with confidence {jobTitleField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Departments", out DocumentField departmentFields))
{
if (departmentFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField departmentField in departmentFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (departmentField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string department = departmentField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Department: '{department}', with confidence {departmentField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Emails", out DocumentField emailFields))
{
if (emailFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField emailField in emailFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (emailField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string email = emailField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Email: '{email}', with confidence {emailField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Websites", out DocumentField websiteFields))
{
if (websiteFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField websiteField in websiteFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (websiteField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string website = websiteField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Website: '{website}', with confidence {websiteField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("MobilePhones", out DocumentField mobilePhonesFields))
{
if (mobilePhonesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField mobilePhoneField in mobilePhonesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (mobilePhoneField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.PhoneNumber)
{
string mobilePhone = mobilePhoneField.Value.AsPhoneNumber();
Console.WriteLine($"Mobile phone number: '{mobilePhone}', with confidence {mobilePhoneField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("WorkPhones", out DocumentField workPhonesFields))
{
if (workPhonesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField workPhoneField in workPhonesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (workPhoneField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.PhoneNumber)
{
string workPhone = workPhoneField.Value.AsPhoneNumber();
Console.WriteLine($"Work phone number: '{workPhone}', with confidence {workPhoneField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Faxes", out DocumentField faxesFields))
{
if (faxesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField faxField in faxesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (faxField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.PhoneNumber)
{
string fax = faxField.Value.AsPhoneNumber();
Console.WriteLine($"Fax phone number: '{fax}', with confidence {faxField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Addresses", out DocumentField addressesFields))
{
if (addressesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField addressField in addressesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (addressField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string address = addressField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Address: '{address}', with confidence {addressField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("CompanyNames", out DocumentField companyNamesFields))
{
if (companyNamesFields.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.List)
{
foreach (DocumentField companyNameField in companyNamesFields.Value.AsList())
{
if (companyNameField.FieldType == DocumentFieldType.String)
{
string companyName = companyNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Company name: '{companyName}', with confidence {companyNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu wizytówek.
Dokumentacja interfejsu API REST ( | Maven) | Przykłady |obsługiwanej wersji interfejsu API REST biblioteki klienta | |
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Najnowsza wersja programu Visual Studio Code lub preferowanego środowiska IDE. Zobacz Java w programie Visual Studio Code.
- Program Visual Studio Code oferuje pakiet kodowania dla języka Java dla systemów Windows i macOS. Pakiet kodowania jest pakietem
VSkodu, zestawu Java Development Kit (JDK) i kolekcją sugerowanych rozszerzeń firmy Microsoft. Pakiet kodowania może również służyć do naprawiania istniejącego środowiska programistycznego. - Jeśli używasz kodu i pakietu kodowania dla języka
VSJava, zainstaluj rozszerzenie Gradle dla języka Java.
Jeśli nie używasz programu Visual Studio Code, upewnij się, że w środowisku projektowym zainstalowano następujące elementy:
- Zestaw Java Development Kit (JDK) w wersji 8 lub nowszej. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Microsoft Build of OpenJDK (Microsoft Build of OpenJDK).
- Gradle, wersja 6.8 lub nowsza.
- Program Visual Studio Code oferuje pakiet kodowania dla języka Java dla systemów Windows i macOS. Pakiet kodowania jest pakietem
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Napiwek
Utwórz zasób usług Azure AI, jeśli planujesz uzyskać dostęp do wielu usług azure AI przy użyciu jednego punktu końcowego i klucza. W przypadku dostępu tylko do analizy dokumentów utwórz zasób analizy dokumentów. Jeśli zamierzasz używać uwierzytelniania Firmy Microsoft Entra, potrzebujesz zasobu z jedną usługą.
Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Plik dokumentu pod adresem URL. W tym projekcie można użyć przykładowych formularzy podanych w poniższej tabeli dla każdej funkcji:
Funkcja modelID document-url Odczyt modelu odczyt wstępnie utworzony Broszura przykładowa Model układu wstępnie utworzony układ Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej Model formularza W-2 prebuilt-tax.us.w2 Przykładowy formularz W-2 Model faktury wstępnie utworzona faktura Przykładowa faktura Model paragonu wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie Przykładowe potwierdzenie Model dokumentu identyfikatora prebuilt-idDocument Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze
Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Aby skonfigurować środowisko programowania, utwórz projekt Gradle i zainstaluj bibliotekę klienta.
Tworzenie projektu Gradle
W oknie konsoli utwórz katalog dla aplikacji o nazwie doc-intelligence-app i przejdź do niego.
mkdir doc-intelligence-app cd doc-intelligence-appgradle initUruchom polecenie z katalogu roboczego. To polecenie tworzy podstawowe pliki kompilacji dla narzędzia Gradle, w tym build.gradle.kts, które są używane w czasie wykonywania do tworzenia i konfigurowania aplikacji.gradle init --type basicPo wyświetleniu monitu wybierz pozycję Język DSL, a następnie Kotlin.
Wybierz klawisz Enter , aby zaakceptować domyślną nazwę projektu, doc-intelligence-app.
Instalowanie biblioteki klienta
W tym artykule jest używany menedżer zależności narzędzia Gradle. Bibliotekę klienta i informacje dotyczące innych menedżerów zależności można znaleźć w repozytorium centralnym programu Maven.
Otwórz plik build.gradle.kts projektu w środowisku IDE. Skopiuj i wklej następujący kod, aby dołączyć bibliotekę klienta jako instrukcję
implementationwraz z wymaganymi wtyczkami i ustawieniami.plugins { java application } application { mainClass.set("DocIntelligence") } repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { implementation group: 'com.azure', name: 'azure-ai-documentintelligence', version: '1.0.0-beta.2' }
Tworzenie aplikacji Java
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, utwórz wystąpienie DocumentIntelligenceClient klasy . W tym celu należy utworzyć element za AzureKeyCredentialkey pomocą witryny Azure Portal i DocumentIntelligenceClient wystąpienia za pomocą narzędzia AzureKeyCredential i analizy endpointdokumentów.
W katalogu doc-intelligence-app uruchom następujące polecenie:
mkdir -p src/main/java
To polecenie tworzy następującą strukturę katalogów:
Przejdź do
javakatalogu i utwórz plik o nazwie DocIntelligence.java.Napiwek
Nowy plik można utworzyć przy użyciu programu PowerShell. Otwórz okno programu PowerShell w katalogu projektu, trzymając wciśnięty klawisz Shift i klikając prawym przyciskiem myszy folder, a następnie wpisz następujące polecenie: New-Item DocIntelligence.java.
Otwórz plik DocIntelligence.java i wybierz jeden z następujących przykładów kodu ORAZ skopiuj/wklej do aplikacji:
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
readmodelu jako podstawy do wyodrębniania tekstów z dokumentów. - Wstępnie utworzony model układu wyodrębnia lokalizacje tekstu i tekstu, tabele, znaczniki zaznaczenia i informacje o strukturze z dokumentów i obrazów.
- Wstępnie utworzony model tax.us.w2 wyodrębnia informacje zgłaszane na formularzach podatkowych us Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Wstępnie utworzony model faktury wyodrębnia pola kluczy i elementy wiersza z faktur sprzedaży w różnych formatach.
- Wstępnie utworzony model paragonu wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z drukowanych i odręcznych paragonów sprzedaży.
- Wstępnie utworzony model idDocument wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z amerykańskich licencji kierowców; międzynarodowe strony biograficzne paszportu; Identyfikatory stanów USA; karty ubezpieczenia społecznego; i stałe karty zamieszkania.
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
Wpisz następujące polecenia:
gradle build gradle run
Korzystanie z modelu odczytu
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeDocumentRequest;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResult;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResultOperation;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.Document;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentField;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentFieldType;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DocIntelligence {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentIntelligenceClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentIntelligenceClient client = new DocumentIntelligenceClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
//sample document
String documentUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-read";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeLayoutResultPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocument(modelId, invoiceUrl);;
AnalyzeResult analyzeLayoutResult = analyzeLayoutResultPoller.getFinalResult().getAnalyzeResult();
// pages
analyzeLayoutResult.getPages().forEach(documentPage -> {
System.out.printf("Page has width: %.2f and height: %.2f, measured with unit: %s%n",
documentPage.getWidth(),
documentPage.getHeight(),
documentPage.getUnit());
// lines
documentPage.getLines().forEach(documentLine ->
System.out.printf("Line %s is within a bounding polygon %s.%n",
documentLine.getContent(),
documentLine.getBoundingPolygon().toString()));
// words
documentPage.getWords().forEach(documentWord ->
System.out.printf("Word '%s' has a confidence score of %.2f.%n",
documentWord.getContent(),
documentWord.getConfidence()));
});
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl read dane wyjściowe modelu.
Korzystanie z modelu układu
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeDocumentRequest;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResult;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResultOperation;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.Document;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentField;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentFieldType;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DocIntelligence {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentIntelligenceClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentIntelligenceClient client = new DocumentIntelligenceClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
//sample document
String layoutDocumentUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-layout";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeLayoutResultPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocument(modelId, layoutDocumentUrl);
AnalyzeResult analyzeLayoutResult = analyzeLayoutResultPoller.getFinalResult().getAnalyzeResult();
// pages
analyzeLayoutResult.getPages().forEach(documentPage -> {
System.out.printf("Page has width: %.2f and height: %.2f, measured with unit: %s%n",
documentPage.getWidth(),
documentPage.getHeight(),
documentPage.getUnit());
// lines
documentPage.getLines().forEach(documentLine ->
System.out.printf("Line %s is within a bounding polygon %s.%n",
documentLine.getContent(),
documentLine.getBoundingPolygon().toString()));
// words
documentPage.getWords().forEach(documentWord ->
System.out.printf("Word '%s' has a confidence score of %.2f%n",
documentWord.getContent(),
documentWord.getConfidence()));
// selection marks
documentPage.getSelectionMarks().forEach(documentSelectionMark ->
System.out.printf("Selection mark is '%s' and is within a bounding polygon %s with confidence %.2f.%n",
documentSelectionMark.getSelectionMarkState().toString(),
getBoundingCoordinates(documentSelectionMark.getBoundingPolygon()),
documentSelectionMark.getConfidence()));
});
// tables
List < DocumentTable > tables = analyzeLayoutResult.getTables();
for (int i = 0; i < tables.size(); i++) {
DocumentTable documentTables = tables.get(i);
System.out.printf("Table %d has %d rows and %d columns.%n", i, documentTables.getRowCount(),
documentTables.getColumnCount());
documentTables.getCells().forEach(documentTableCell -> {
System.out.printf("Cell '%s', has row index %d and column index %d.%n", documentTableCell.getContent(),
documentTableCell.getRowIndex(), documentTableCell.getColumnIndex());
});
System.out.println();
}
}
// Utility function to get the bounding polygon coordinates.
private static String getBoundingCoordinates(List < Point > boundingPolygon) {
return boundingPolygon.stream().map(point -> String.format("[%.2f, %.2f]", point.getX(),
point.getY())).collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu układu.
Korzystanie z ogólnego modelu dokumentów
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeDocumentRequest;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResult;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResultOperation;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.Document;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentField;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentFieldType;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DocIntelligence {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentIntelligenceClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentIntelligenceClient client = new DocumentIntelligenceClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
//sample document
String generalDocumentUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-layout.pdf";
String modelId = "prebuilt-document";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeDocumentPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocument(modelId, generalDocumentUrl);
AnalyzeResult analyzeResult = analyzeDocumentPoller.getFinalResult().getAnalyzeResult();;
// pages
analyzeResult.getPages().forEach(documentPage -> {
System.out.printf("Page has width: %.2f and height: %.2f, measured with unit: %s%n",
documentPage.getWidth(),
documentPage.getHeight(),
documentPage.getUnit());
// lines
documentPage.getLines().forEach(documentLine ->
System.out.printf("Line %s is within a bounding polygon %s.%n",
documentLine.getContent(),
documentLine.getBoundingPolygon().toString()));
// words
documentPage.getWords().forEach(documentWord ->
System.out.printf("Word %s has a confidence score of %.2f%n.",
documentWord.getContent(),
documentWord.getConfidence()));
});
// tables
List < DocumentTable > tab_les = analyzeResult.getTables();
for (int i = 0; i < tab_les.size(); i++) {
DocumentTable documentTable = tab_les.get(i);
System.out.printf("Table %d has %d rows and %d columns.%n", i, documentTable.getRowCount(),
documentTable.getColumnCount());
documentTable.getCells().forEach(documentTableCell -> {
System.out.printf("Cell '%s', has row index %d and column index %d.%n",
documentTableCell.getContent(),
documentTableCell.getRowIndex(), documentTableCell.getColumnIndex());
});
System.out.println();
}
// Key-value pairs
analyzeResult.getKeyValuePairs().forEach(documentKeyValuePair -> {
System.out.printf("Key content: %s%n", documentKeyValuePair.getKey().getContent());
System.out.printf("Key content bounding region: %s%n",
documentKeyValuePair.getKey().getBoundingRegions().toString());
if (documentKeyValuePair.getValue() != null) {
System.out.printf("Value content: %s%n", documentKeyValuePair.getValue().getContent());
System.out.printf("Value content bounding region: %s%n", documentKeyValuePair.getValue().getBoundingRegions().toString());
}
});
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl ogólne dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu.
Korzystanie z modelu podatkowego W-2
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeDocumentRequest;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResult;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResultOperation;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.Document;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentField;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentFieldType;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DocIntelligence {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentIntelligenceClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentIntelligenceClient client = new DocumentIntelligenceClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
// sample document
String w2Url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-tax.us.w2";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeW2Poller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocument(modelId, w2Url);
AnalyzeResult analyzeTaxResult = analyzeW2Poller.getFinalResult().getAnalyzeResult();
for (int i = 0; i < analyzeTaxResult.getDocuments().size(); i++) {
AnalyzedDocument analyzedTaxDocument = analyzeTaxResult.getDocuments().get(i);
Map < String, DocumentField > taxFields = analyzedTaxDocument.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Analyzing Document %d -----------%n", i);
DocumentField w2FormVariantField = taxFields.get("W2FormVariant");
if (w2FormVariantField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == w2FormVariantField.getType()) {
String merchantName = w2FormVariantField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Form variant: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantName, w2FormVariantField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField employeeField = taxFields.get("Employee");
if (employeeField != null) {
System.out.println("Employee Data: ");
if (DocumentFieldType.MAP == employeeField.getType()) {
Map < String, DocumentField > employeeDataFieldMap = employeeField.getValueAsMap();
DocumentField employeeName = employeeDataFieldMap.get("Name");
if (employeeName != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == employeeName.getType()) {
String employeesName = employeeName.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Employee Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
employeesName, employeeName.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField employeeAddrField = employeeDataFieldMap.get("Address");
if (employeeAddrField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == employeeAddrField.getType()) {
String employeeAddress = employeeAddrField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Employee Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
employeeAddress, employeeAddrField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
}
DocumentField employerField = taxFields.get("Employer");
if (employerField != null) {
System.out.println("Employer Data: ");
if (DocumentFieldType.MAP == employerField.getType()) {
Map < String, DocumentField > employerDataFieldMap = employerField.getValueAsMap();
DocumentField employerNameField = employerDataFieldMap.get("Name");
if (employerNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == employerNameField.getType()) {
String employerName = employerNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Employer Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
employerName, employerNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField employerIDNumberField = employerDataFieldMap.get("IdNumber");
if (employerIDNumberField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == employerIDNumberField.getType()) {
String employerIdNumber = employerIDNumberField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Employee ID Number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
employerIdNumber, employerIDNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
}
DocumentField taxYearField = taxFields.get("TaxYear");
if (taxYearField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == taxYearField.getType()) {
String taxYear = taxYearField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Tax year: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
taxYear, taxYearField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField taxDateField = taxFields.get("TaxDate");
if (taxDateField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == taxDateField.getType()) {
LocalDate taxDate = taxDateField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Tax Date: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
taxDate, taxDateField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField socialSecurityTaxField = taxFields.get("SocialSecurityTaxWithheld");
if (socialSecurityTaxField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == socialSecurityTaxField.getType()) {
Double socialSecurityTax = socialSecurityTaxField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Social Security Tax withheld: %.2f, confidence: %.2f%n",
socialSecurityTax, socialSecurityTaxField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2.
Korzystanie z modelu faktury
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeDocumentRequest;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResult;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResultOperation;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.Document;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentField;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentFieldType;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DocIntelligence {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentIntelligenceClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentIntelligenceClient client = new DocumentIntelligenceClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
// sample document
String invoiceUrl = "https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/raw/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/invoice.pdf";
String modelId = "prebuilt-invoice";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeInvoicesPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocument(modelId, invoiceUrl);
AnalyzeResult analyzeInvoiceResult = analyzeInvoicesPoller.getFinalResult().getAnalyzeResult();
for (int i = 0; i < analyzeInvoiceResult.getDocuments().size(); i++) {
AnalyzedDocument analyzedInvoice = analyzeInvoiceResult.getDocuments().get(i);
Map < String, DocumentField > invoiceFields = analyzedInvoice.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Analyzing invoice %d -----------%n", i);
DocumentField vendorNameField = invoiceFields.get("VendorName");
if (vendorNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == vendorNameField.getType()) {
String merchantName = vendorNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Vendor Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantName, vendorNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField vendorAddressField = invoiceFields.get("VendorAddress");
if (vendorAddressField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == vendorAddressField.getType()) {
String merchantAddress = vendorAddressField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Vendor address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantAddress, vendorAddressField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField customerNameField = invoiceFields.get("CustomerName");
if (customerNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == customerNameField.getType()) {
String merchantAddress = customerNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Customer Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantAddress, customerNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField customerAddressRecipientField = invoiceFields.get("CustomerAddressRecipient");
if (customerAddressRecipientField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == customerAddressRecipientField.getType()) {
String customerAddr = customerAddressRecipientField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Customer Address Recipient: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
customerAddr, customerAddressRecipientField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField invoiceIdField = invoiceFields.get("InvoiceId");
if (invoiceIdField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == invoiceIdField.getType()) {
String invoiceId = invoiceIdField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Invoice ID: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
invoiceId, invoiceIdField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField invoiceDateField = invoiceFields.get("InvoiceDate");
if (customerNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == invoiceDateField.getType()) {
LocalDate invoiceDate = invoiceDateField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Invoice Date: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
invoiceDate, invoiceDateField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField invoiceTotalField = invoiceFields.get("InvoiceTotal");
if (customerAddressRecipientField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == invoiceTotalField.getType()) {
Double invoiceTotal = invoiceTotalField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Invoice Total: %.2f, confidence: %.2f%n",
invoiceTotal, invoiceTotalField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField invoiceItemsField = invoiceFields.get("Items");
if (invoiceItemsField != null) {
System.out.printf("Invoice Items: %n");
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == invoiceItemsField.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > invoiceItems = invoiceItemsField.getValueAsList();
invoiceItems.stream()
.filter(invoiceItem -> DocumentFieldType.MAP == invoiceItem.getType())
.map(documentField -> documentField.getValueAsMap())
.forEach(documentFieldMap -> documentFieldMap.forEach((key, documentField) -> {
if ("Description".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == documentField.getType()) {
String name = documentField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Description: %s, confidence: %.2fs%n",
name, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("Quantity".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double quantity = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Quantity: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
quantity, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("UnitPrice".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double unitPrice = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Unit Price: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
unitPrice, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("ProductCode".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double productCode = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Product Code: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
productCode, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
}));
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu faktury.
Korzystanie z modelu paragonów
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeDocumentRequest;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResult;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResultOperation;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.Document;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentField;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentFieldType;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DocIntelligence {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentIntelligenceClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentIntelligenceClient client = new DocumentIntelligenceClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
String receiptUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-receipt";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeReceiptPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocument(modelId, receiptUrl);
AnalyzeResult receiptResults = analyzeReceiptPoller.getFinalResult().getAnalyzeResult();
for (int i = 0; i < receiptResults.getDocuments().size(); i++) {
AnalyzedDocument analyzedReceipt = receiptResults.getDocuments().get(i);
Map < String, DocumentField > receiptFields = analyzedReceipt.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Analyzing receipt info %d -----------%n", i);
DocumentField merchantNameField = receiptFields.get("MerchantName");
if (merchantNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == merchantNameField.getType()) {
String merchantName = merchantNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Merchant Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantName, merchantNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField merchantPhoneNumberField = receiptFields.get("MerchantPhoneNumber");
if (merchantPhoneNumberField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.PHONE_NUMBER == merchantPhoneNumberField.getType()) {
String merchantAddress = merchantPhoneNumberField.getValueAsPhoneNumber();
System.out.printf("Merchant Phone number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantAddress, merchantPhoneNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField merchantAddressField = receiptFields.get("MerchantAddress");
if (merchantAddressField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == merchantAddressField.getType()) {
String merchantAddress = merchantAddressField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Merchant Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantAddress, merchantAddressField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField transactionDateField = receiptFields.get("TransactionDate");
if (transactionDateField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == transactionDateField.getType()) {
LocalDate transactionDate = transactionDateField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Transaction Date: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
transactionDate, transactionDateField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField receiptItemsField = receiptFields.get("Items");
if (receiptItemsField != null) {
System.out.printf("Receipt Items: %n");
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == receiptItemsField.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > receiptItems = receiptItemsField.getValueAsList();
receiptItems.stream()
.filter(receiptItem -> DocumentFieldType.MAP == receiptItem.getType())
.map(documentField -> documentField.getValueAsMap())
.forEach(documentFieldMap -> documentFieldMap.forEach((key, documentField) -> {
if ("Name".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == documentField.getType()) {
String name = documentField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Name: %s, confidence: %.2fs%n",
name, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("Quantity".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double quantity = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Quantity: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
quantity, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("Price".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double price = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Price: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
price, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("TotalPrice".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double totalPrice = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Total Price: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
totalPrice, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
}));
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu.
Korzystanie z modelu dokumentów identyfikatorów
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeDocumentRequest;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResult;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.AnalyzeResultOperation;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.Document;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentField;
import com.azure.ai.documentintelligence.models.DocumentFieldType;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DocIntelligence {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentIntelligenceClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentIntelligenceClient client = new DocumentIntelligenceClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
//sample document
String licenseUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-idDocument";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeIdentityDocumentPoller = client.beginAnalyzeDocument(modelId, licenseUrl);
AnalyzeResult identityDocumentResults = analyzeIdentityDocumentPoller.getFinalResult().getAnalyzeResult();
for (int i = 0; i < identityDocumentResults.getDocuments().size(); i++) {
AnalyzedDocument analyzedIDDocument = identityDocumentResults.getDocuments().get(i);
Map < String, DocumentField > licenseFields = analyzedIDDocument.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Analyzed license info for page %d -----------%n", i);
DocumentField addressField = licenseFields.get("Address");
if (addressField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == addressField.getType()) {
String address = addressField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
address, addressField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField countryRegionDocumentField = licenseFields.get("CountryRegion");
if (countryRegionDocumentField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == countryRegionDocumentField.getType()) {
String countryRegion = countryRegionDocumentField.getValueAsCountry();
System.out.printf("Country or region: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
countryRegion, countryRegionDocumentField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField dateOfBirthField = licenseFields.get("DateOfBirth");
if (dateOfBirthField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == dateOfBirthField.getType()) {
LocalDate dateOfBirth = dateOfBirthField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Date of Birth: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
dateOfBirth, dateOfBirthField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField dateOfExpirationField = licenseFields.get("DateOfExpiration");
if (dateOfExpirationField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == dateOfExpirationField.getType()) {
LocalDate expirationDate = dateOfExpirationField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Document date of expiration: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
expirationDate, dateOfExpirationField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField documentNumberField = licenseFields.get("DocumentNumber");
if (documentNumberField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == documentNumberField.getType()) {
String documentNumber = documentNumberField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Document number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
documentNumber, documentNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField firstNameField = licenseFields.get("FirstName");
if (firstNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == firstNameField.getType()) {
String firstName = firstNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("First Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
firstName, documentNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField lastNameField = licenseFields.get("LastName");
if (lastNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == lastNameField.getType()) {
String lastName = lastNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Last name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
lastName, lastNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField regionField = licenseFields.get("Region");
if (regionField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == regionField.getType()) {
String region = regionField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Region: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
region, regionField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu identyfikatora.
Dokumentacja interfejsu API REST ( | Maven) | Przykłady| obsługiwanych wersji interfejsu API REST biblioteki klienta | |
Dokumentacja interfejsu API REST ( | Maven) | Przykłady|obsługiwanych wersji interfejsu API REST biblioteki klienta | |
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Najnowsza wersja programu Visual Studio Code lub preferowanego środowiska IDE. Zobacz Java w programie Visual Studio Code.
- Program Visual Studio Code oferuje pakiet kodowania dla języka Java dla systemów Windows i macOS. Pakiet kodu jest pakietem
VS Code, zestawem Java Development Kit (JDK) i kolekcją sugerowanych rozszerzeń firmy Microsoft. Pakiet kodowania może również służyć do naprawiania istniejącego środowiska programistycznego. - Jeśli używasz pakietu programistycznego dla języka
VS CodeJava, zainstaluj rozszerzenie Gradle for Java .
Jeśli nie używasz programu Visual Studio Code, upewnij się, że w środowisku projektowym zainstalowano następujące elementy:
- Zestaw Java Development Kit (JDK) w wersji 8 lub nowszej. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Microsoft Build of OpenJDK (Microsoft Build of OpenJDK).
- Gradle, wersja 6.8 lub nowsza.
- Program Visual Studio Code oferuje pakiet kodowania dla języka Java dla systemów Windows i macOS. Pakiet kodu jest pakietem
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Napiwek
Utwórz zasób usług Azure AI, jeśli planujesz uzyskać dostęp do wielu usług azure AI przy użyciu jednego punktu końcowego i klucza. W przypadku dostępu tylko do analizy dokumentów utwórz zasób analizy dokumentów. Jeśli zamierzasz używać uwierzytelniania Firmy Microsoft Entra, potrzebujesz zasobu z jedną usługą.
Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Plik dokumentu pod adresem URL. W tym projekcie można użyć przykładowych formularzy podanych w poniższej tabeli dla każdej funkcji:
Funkcja modelID document-url Odczyt modelu odczyt wstępnie utworzony Broszura przykładowa Model układu wstępnie utworzony układ Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej Model formularza W-2 prebuilt-tax.us.w2 Przykładowy formularz W-2 Model faktury wstępnie utworzona faktura Przykładowa faktura Model paragonu wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie Przykładowe potwierdzenie Model dokumentu identyfikatora prebuilt-idDocument Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze Model wizytówek wstępnie utworzona karta biznesowa Przykładowa wizytówka
Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Aby skonfigurować środowisko programowania, utwórz projekt Gradle i zainstaluj bibliotekę klienta.
Tworzenie projektu Gradle
W oknie konsoli utwórz katalog dla aplikacji o nazwie form-recognizer-app i przejdź do niego.
mkdir form-recognizer-app cd form-recognizer-appgradle initUruchom polecenie z katalogu roboczego. To polecenie tworzy podstawowe pliki kompilacji dla narzędzia Gradle, w tym build.gradle.kts, które są używane w czasie wykonywania do tworzenia i konfigurowania aplikacji.gradle init --type basicPo wyświetleniu monitu wybierz pozycję Język DSL, a następnie Kotlin.
Wybierz klawisz Enter , aby zaakceptować domyślną nazwę projektu, form-recognizer-app.
Instalowanie biblioteki klienta
W tym artykule jest używany menedżer zależności narzędzia Gradle. Bibliotekę klienta i informacje dotyczące innych menedżerów zależności można znaleźć w repozytorium centralnym programu Maven.
Otwórz plik build.gradle.kts projektu w środowisku IDE. Skopiuj i wklej następujący kod, aby dołączyć bibliotekę klienta jako instrukcję
implementationwraz z wymaganymi wtyczkami i ustawieniami.plugins { java application } application { mainClass.set("FormRecognizer") } repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { implementation(group = "com.azure", name = "azure-ai-formrecognizer", version = "4.0.0") }
Tworzenie aplikacji Java
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, utwórz wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu należy utworzyć element za AzureKeyCredentialkey pomocą witryny Azure Portal i DocumentAnalysisClient wystąpienia za pomocą narzędzia AzureKeyCredential i analizy endpointdokumentów.
W katalogu form-recognizer-app uruchom następujące polecenie:
mkdir -p src/main/javaUtworzysz następującą strukturę katalogów:
Przejdź do
javakatalogu i utwórz plik o nazwie FormRecognizer.java.Napiwek
Nowy plik można utworzyć przy użyciu programu PowerShell. Otwórz okno programu PowerShell w katalogu projektu, trzymając wciśnięty klawisz Shift i klikając prawym przyciskiem myszy folder, a następnie wpisz następujące polecenie: New-Item FormRecognizer.java.
Otwórz plik FormRecognizer.java i wybierz jeden z następujących przykładów kodu i skopiuj/wklej do aplikacji:
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
readmodelu jako podstawy do wyodrębniania tekstów z dokumentów. - Wstępnie utworzony model układu wyodrębnia lokalizacje tekstu i tekstu, tabele, znaczniki zaznaczenia i informacje o strukturze z dokumentów i obrazów.
- Wstępnie utworzony model tax.us.w2 wyodrębnia informacje zgłaszane na formularzach podatkowych us Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Wstępnie utworzony model faktury wyodrębnia pola kluczy i elementy wiersza z faktur sprzedaży w różnych formatach.
- Wstępnie utworzony model paragonu wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z drukowanych i odręcznych paragonów sprzedaży.
- Wstępnie utworzony model idDocument wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z amerykańskich licencji kierowców; międzynarodowe strony biograficzne paszportu; Identyfikatory stanów USA; karty ubezpieczenia społecznego; i stałe karty zamieszkania.
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
Wpisz następujące polecenia:
gradle build gradle -PmainClass=FormRecognizer run
Korzystanie z modelu odczytu
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.models.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClient;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FormRecognizer {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
//sample document
String documentUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-read";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeLayoutResultPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl(modelId, documentUrl);
AnalyzeResult analyzeLayoutResult = analyzeLayoutResultPoller.getFinalResult();
// pages
analyzeLayoutResult.getPages().forEach(documentPage -> {
System.out.printf("Page has width: %.2f and height: %.2f, measured with unit: %s%n",
documentPage.getWidth(),
documentPage.getHeight(),
documentPage.getUnit());
// lines
documentPage.getLines().forEach(documentLine ->
System.out.printf("Line %s is within a bounding polygon %s.%n",
documentLine.getContent(),
documentLine.getBoundingPolygon().toString()));
// words
documentPage.getWords().forEach(documentWord ->
System.out.printf("Word '%s' has a confidence score of %.2f.%n",
documentWord.getContent(),
documentWord.getConfidence()));
});
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl read dane wyjściowe modelu.
Korzystanie z modelu układu
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.models.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClient;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FormRecognizer {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
//sample document
String layoutDocumentUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-layout";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeLayoutResultPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl(modelId, layoutDocumentUrl);
AnalyzeResult analyzeLayoutResult = analyzeLayoutResultPoller.getFinalResult();
// pages
analyzeLayoutResult.getPages().forEach(documentPage -> {
System.out.printf("Page has width: %.2f and height: %.2f, measured with unit: %s%n",
documentPage.getWidth(),
documentPage.getHeight(),
documentPage.getUnit());
// lines
documentPage.getLines().forEach(documentLine ->
System.out.printf("Line %s is within a bounding polygon %s.%n",
documentLine.getContent(),
documentLine.getBoundingPolygon().toString()));
// words
documentPage.getWords().forEach(documentWord ->
System.out.printf("Word '%s' has a confidence score of %.2f%n",
documentWord.getContent(),
documentWord.getConfidence()));
// selection marks
documentPage.getSelectionMarks().forEach(documentSelectionMark ->
System.out.printf("Selection mark is '%s' and is within a bounding polygon %s with confidence %.2f.%n",
documentSelectionMark.getSelectionMarkState().toString(),
getBoundingCoordinates(documentSelectionMark.getBoundingPolygon()),
documentSelectionMark.getConfidence()));
});
// tables
List < DocumentTable > tables = analyzeLayoutResult.getTables();
for (int i = 0; i < tables.size(); i++) {
DocumentTable documentTables = tables.get(i);
System.out.printf("Table %d has %d rows and %d columns.%n", i, documentTables.getRowCount(),
documentTables.getColumnCount());
documentTables.getCells().forEach(documentTableCell -> {
System.out.printf("Cell '%s', has row index %d and column index %d.%n", documentTableCell.getContent(),
documentTableCell.getRowIndex(), documentTableCell.getColumnIndex());
});
System.out.println();
}
}
// Utility function to get the bounding polygon coordinates.
private static String getBoundingCoordinates(List < Point > boundingPolygon) {
return boundingPolygon.stream().map(point -> String.format("[%.2f, %.2f]", point.getX(),
point.getY())).collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu układu.
Korzystanie z ogólnego modelu dokumentów
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.models.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClient;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FormRecognizer {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
//sample document
String generalDocumentUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-layout.pdf";
String modelId = "prebuilt-document";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeDocumentPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl(modelId, generalDocumentUrl);
AnalyzeResult analyzeResult = analyzeDocumentPoller.getFinalResult();
// pages
analyzeResult.getPages().forEach(documentPage -> {
System.out.printf("Page has width: %.2f and height: %.2f, measured with unit: %s%n",
documentPage.getWidth(),
documentPage.getHeight(),
documentPage.getUnit());
// lines
documentPage.getLines().forEach(documentLine ->
System.out.printf("Line %s is within a bounding polygon %s.%n",
documentLine.getContent(),
documentLine.getBoundingPolygon().toString()));
// words
documentPage.getWords().forEach(documentWord ->
System.out.printf("Word %s has a confidence score of %.2f%n.",
documentWord.getContent(),
documentWord.getConfidence()));
});
// tables
List < DocumentTable > tab_les = analyzeResult.getTables();
for (int i = 0; i < tab_les.size(); i++) {
DocumentTable documentTable = tab_les.get(i);
System.out.printf("Table %d has %d rows and %d columns.%n", i, documentTable.getRowCount(),
documentTable.getColumnCount());
documentTable.getCells().forEach(documentTableCell -> {
System.out.printf("Cell '%s', has row index %d and column index %d.%n",
documentTableCell.getContent(),
documentTableCell.getRowIndex(), documentTableCell.getColumnIndex());
});
System.out.println();
}
// Key-value pairs
analyzeResult.getKeyValuePairs().forEach(documentKeyValuePair -> {
System.out.printf("Key content: %s%n", documentKeyValuePair.getKey().getContent());
System.out.printf("Key content bounding region: %s%n",
documentKeyValuePair.getKey().getBoundingRegions().toString());
if (documentKeyValuePair.getValue() != null) {
System.out.printf("Value content: %s%n", documentKeyValuePair.getValue().getContent());
System.out.printf("Value content bounding region: %s%n", documentKeyValuePair.getValue().getBoundingRegions().toString());
}
});
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl ogólne dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu.
Korzystanie z modelu podatkowego W-2
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.models.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClient;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FormRecognizer {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
// sample document
String w2Url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-tax.us.w2";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeW2Poller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl(modelId, w2Url);
AnalyzeResult analyzeTaxResult = analyzeW2Poller.getFinalResult();
for (int i = 0; i < analyzeTaxResult.getDocuments().size(); i++) {
AnalyzedDocument analyzedTaxDocument = analyzeTaxResult.getDocuments().get(i);
Map < String, DocumentField > taxFields = analyzedTaxDocument.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Analyzing Document %d -----------%n", i);
DocumentField w2FormVariantField = taxFields.get("W2FormVariant");
if (w2FormVariantField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == w2FormVariantField.getType()) {
String merchantName = w2FormVariantField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Form variant: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantName, w2FormVariantField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField employeeField = taxFields.get("Employee");
if (employeeField != null) {
System.out.println("Employee Data: ");
if (DocumentFieldType.MAP == employeeField.getType()) {
Map < String, DocumentField > employeeDataFieldMap = employeeField.getValueAsMap();
DocumentField employeeName = employeeDataFieldMap.get("Name");
if (employeeName != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == employeeName.getType()) {
String employeesName = employeeName.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Employee Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
employeesName, employeeName.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField employeeAddrField = employeeDataFieldMap.get("Address");
if (employeeAddrField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == employeeAddrField.getType()) {
String employeeAddress = employeeAddrField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Employee Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
employeeAddress, employeeAddrField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
}
DocumentField employerField = taxFields.get("Employer");
if (employerField != null) {
System.out.println("Employer Data: ");
if (DocumentFieldType.MAP == employerField.getType()) {
Map < String, DocumentField > employerDataFieldMap = employerField.getValueAsMap();
DocumentField employerNameField = employerDataFieldMap.get("Name");
if (employerNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == employerNameField.getType()) {
String employerName = employerNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Employer Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
employerName, employerNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField employerIDNumberField = employerDataFieldMap.get("IdNumber");
if (employerIDNumberField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == employerIDNumberField.getType()) {
String employerIdNumber = employerIDNumberField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Employee ID Number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
employerIdNumber, employerIDNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
}
DocumentField taxYearField = taxFields.get("TaxYear");
if (taxYearField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == taxYearField.getType()) {
String taxYear = taxYearField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Tax year: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
taxYear, taxYearField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField taxDateField = taxFields.get("TaxDate");
if (taxDateField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == taxDateField.getType()) {
LocalDate taxDate = taxDateField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Tax Date: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
taxDate, taxDateField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField socialSecurityTaxField = taxFields.get("SocialSecurityTaxWithheld");
if (socialSecurityTaxField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == socialSecurityTaxField.getType()) {
Double socialSecurityTax = socialSecurityTaxField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Social Security Tax withheld: %.2f, confidence: %.2f%n",
socialSecurityTax, socialSecurityTaxField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2.
Korzystanie z modelu faktury
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.models.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClient;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FormRecognizer {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
// sample document
String invoiceUrl = "https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/raw/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/invoice.pdf";
String modelId = "prebuilt-invoice";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeInvoicesPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl(modelId, invoiceUrl);
AnalyzeResult analyzeInvoiceResult = analyzeInvoicesPoller.getFinalResult();
for (int i = 0; i < analyzeInvoiceResult.getDocuments().size(); i++) {
AnalyzedDocument analyzedInvoice = analyzeInvoiceResult.getDocuments().get(i);
Map < String, DocumentField > invoiceFields = analyzedInvoice.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Analyzing invoice %d -----------%n", i);
DocumentField vendorNameField = invoiceFields.get("VendorName");
if (vendorNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == vendorNameField.getType()) {
String merchantName = vendorNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Vendor Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantName, vendorNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField vendorAddressField = invoiceFields.get("VendorAddress");
if (vendorAddressField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == vendorAddressField.getType()) {
String merchantAddress = vendorAddressField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Vendor address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantAddress, vendorAddressField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField customerNameField = invoiceFields.get("CustomerName");
if (customerNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == customerNameField.getType()) {
String merchantAddress = customerNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Customer Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantAddress, customerNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField customerAddressRecipientField = invoiceFields.get("CustomerAddressRecipient");
if (customerAddressRecipientField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == customerAddressRecipientField.getType()) {
String customerAddr = customerAddressRecipientField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Customer Address Recipient: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
customerAddr, customerAddressRecipientField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField invoiceIdField = invoiceFields.get("InvoiceId");
if (invoiceIdField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == invoiceIdField.getType()) {
String invoiceId = invoiceIdField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Invoice ID: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
invoiceId, invoiceIdField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField invoiceDateField = invoiceFields.get("InvoiceDate");
if (customerNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == invoiceDateField.getType()) {
LocalDate invoiceDate = invoiceDateField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Invoice Date: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
invoiceDate, invoiceDateField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField invoiceTotalField = invoiceFields.get("InvoiceTotal");
if (customerAddressRecipientField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == invoiceTotalField.getType()) {
Double invoiceTotal = invoiceTotalField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Invoice Total: %.2f, confidence: %.2f%n",
invoiceTotal, invoiceTotalField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField invoiceItemsField = invoiceFields.get("Items");
if (invoiceItemsField != null) {
System.out.printf("Invoice Items: %n");
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == invoiceItemsField.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > invoiceItems = invoiceItemsField.getValueAsList();
invoiceItems.stream()
.filter(invoiceItem -> DocumentFieldType.MAP == invoiceItem.getType())
.map(documentField -> documentField.getValueAsMap())
.forEach(documentFieldMap -> documentFieldMap.forEach((key, documentField) -> {
if ("Description".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == documentField.getType()) {
String name = documentField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Description: %s, confidence: %.2fs%n",
name, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("Quantity".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double quantity = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Quantity: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
quantity, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("UnitPrice".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double unitPrice = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Unit Price: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
unitPrice, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("ProductCode".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double productCode = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Product Code: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
productCode, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
}));
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu faktury.
Korzystanie z modelu paragonów
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.models.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClient;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FormRecognizer {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
String receiptUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-receipt";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeReceiptPoller =
client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl(modelId, receiptUrl);
AnalyzeResult receiptResults = analyzeReceiptPoller.getFinalResult();
for (int i = 0; i < receiptResults.getDocuments().size(); i++) {
AnalyzedDocument analyzedReceipt = receiptResults.getDocuments().get(i);
Map < String, DocumentField > receiptFields = analyzedReceipt.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Analyzing receipt info %d -----------%n", i);
DocumentField merchantNameField = receiptFields.get("MerchantName");
if (merchantNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == merchantNameField.getType()) {
String merchantName = merchantNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Merchant Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantName, merchantNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField merchantPhoneNumberField = receiptFields.get("MerchantPhoneNumber");
if (merchantPhoneNumberField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.PHONE_NUMBER == merchantPhoneNumberField.getType()) {
String merchantAddress = merchantPhoneNumberField.getValueAsPhoneNumber();
System.out.printf("Merchant Phone number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantAddress, merchantPhoneNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField merchantAddressField = receiptFields.get("MerchantAddress");
if (merchantAddressField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == merchantAddressField.getType()) {
String merchantAddress = merchantAddressField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Merchant Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
merchantAddress, merchantAddressField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField transactionDateField = receiptFields.get("TransactionDate");
if (transactionDateField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == transactionDateField.getType()) {
LocalDate transactionDate = transactionDateField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Transaction Date: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
transactionDate, transactionDateField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField receiptItemsField = receiptFields.get("Items");
if (receiptItemsField != null) {
System.out.printf("Receipt Items: %n");
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == receiptItemsField.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > receiptItems = receiptItemsField.getValueAsList();
receiptItems.stream()
.filter(receiptItem -> DocumentFieldType.MAP == receiptItem.getType())
.map(documentField -> documentField.getValueAsMap())
.forEach(documentFieldMap -> documentFieldMap.forEach((key, documentField) -> {
if ("Name".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == documentField.getType()) {
String name = documentField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Name: %s, confidence: %.2fs%n",
name, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("Quantity".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double quantity = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Quantity: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
quantity, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("Price".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double price = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Price: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
price, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("TotalPrice".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DOUBLE == documentField.getType()) {
Double totalPrice = documentField.getValueAsDouble();
System.out.printf("Total Price: %f, confidence: %.2f%n",
totalPrice, documentField.getConfidence());
}
}
}));
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu.
Korzystanie z modelu dokumentów identyfikatorów
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.models.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClient;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FormRecognizer {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
//sample document
String licenseUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png";
String modelId = "prebuilt-idDocument";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeIdentityDocumentPoller = client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl(modelId, licenseUrl);
AnalyzeResult identityDocumentResults = analyzeIdentityDocumentPoller.getFinalResult();
for (int i = 0; i < identityDocumentResults.getDocuments().size(); i++) {
AnalyzedDocument analyzedIDDocument = identityDocumentResults.getDocuments().get(i);
Map < String, DocumentField > licenseFields = analyzedIDDocument.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Analyzed license info for page %d -----------%n", i);
DocumentField addressField = licenseFields.get("Address");
if (addressField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == addressField.getType()) {
String address = addressField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
address, addressField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField countryRegionDocumentField = licenseFields.get("CountryRegion");
if (countryRegionDocumentField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == countryRegionDocumentField.getType()) {
String countryRegion = countryRegionDocumentField.getValueAsCountry();
System.out.printf("Country or region: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
countryRegion, countryRegionDocumentField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField dateOfBirthField = licenseFields.get("DateOfBirth");
if (dateOfBirthField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == dateOfBirthField.getType()) {
LocalDate dateOfBirth = dateOfBirthField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Date of Birth: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
dateOfBirth, dateOfBirthField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField dateOfExpirationField = licenseFields.get("DateOfExpiration");
if (dateOfExpirationField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.DATE == dateOfExpirationField.getType()) {
LocalDate expirationDate = dateOfExpirationField.getValueAsDate();
System.out.printf("Document date of expiration: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
expirationDate, dateOfExpirationField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField documentNumberField = licenseFields.get("DocumentNumber");
if (documentNumberField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == documentNumberField.getType()) {
String documentNumber = documentNumberField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Document number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
documentNumber, documentNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField firstNameField = licenseFields.get("FirstName");
if (firstNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == firstNameField.getType()) {
String firstName = firstNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("First Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
firstName, documentNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField lastNameField = licenseFields.get("LastName");
if (lastNameField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == lastNameField.getType()) {
String lastName = lastNameField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Last name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
lastName, lastNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
DocumentField regionField = licenseFields.get("Region");
if (regionField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == regionField.getType()) {
String region = regionField.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Region: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
region, regionField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu identyfikatora.
Korzystanie z modelu wizytówek
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.models.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClient;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.documentanalysis.DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FormRecognizer {
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
private static final String key = System.getenv("FR_KEY");
private static final String endpoint = System.getenv("FR_ENDPOINT");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
DocumentAnalysisClient client = new DocumentAnalysisClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint)
.buildClient();
//sample document
String businessCardUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/de5e0d8982ab754823c54de47a47e8e499351523/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/business_card.jpg";
String modelId = "prebuilt-businessCard";
SyncPoller < OperationResult, AnalyzeResult > analyzeBusinessCardPoller = client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl(modelId, businessCardUrl);
AnalyzeResult businessCardPageResults = analyzeBusinessCardPoller.getFinalResult();
for (int i = 0; i < businessCardPageResults.getDocuments().size(); i++) {
System.out.printf("--------Analyzing business card %d -----------%n", i);
AnalyzedDocument analyzedBusinessCard = businessCardPageResults.getDocuments().get(i);
Map < String, DocumentField > businessCardFields = analyzedBusinessCard.getFields();
DocumentField contactNamesDocumentField = businessCardFields.get("ContactNames");
if (contactNamesDocumentField != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == contactNamesDocumentField.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > contactNamesList = contactNamesDocumentField.getValueAsList();
contactNamesList.stream()
.filter(contactName -> DocumentFieldType.MAP == contactName.getType())
.map(contactName -> {
System.out.printf("Contact name: %s%n", contactName.getContent());
return contactName.getValueAsMap();
})
.forEach(contactNamesMap -> contactNamesMap.forEach((key, contactName) -> {
if ("FirstName".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == contactName.getType()) {
String firstName = contactName.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("\tFirst Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
firstName, contactName.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("LastName".equals(key)) {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == contactName.getType()) {
String lastName = contactName.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("\tLast Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
lastName, contactName.getConfidence());
}
}
}));
}
}
DocumentField jobTitles = businessCardFields.get("JobTitles");
if (jobTitles != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == jobTitles.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > jobTitlesItems = jobTitles.getValueAsList();
jobTitlesItems.forEach(jobTitlesItem -> {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == jobTitlesItem.getType()) {
String jobTitle = jobTitlesItem.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Job Title: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
jobTitle, jobTitlesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
DocumentField departments = businessCardFields.get("Departments");
if (departments != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == departments.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > departmentsItems = departments.getValueAsList();
departmentsItems.forEach(departmentsItem -> {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == departmentsItem.getType()) {
String department = departmentsItem.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Department: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
department, departmentsItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
DocumentField emails = businessCardFields.get("Emails");
if (emails != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == emails.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > emailsItems = emails.getValueAsList();
emailsItems.forEach(emailsItem -> {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == emailsItem.getType()) {
String email = emailsItem.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Email: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", email, emailsItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
DocumentField websites = businessCardFields.get("Websites");
if (websites != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == websites.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > websitesItems = websites.getValueAsList();
websitesItems.forEach(websitesItem -> {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == websitesItem.getType()) {
String website = websitesItem.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Web site: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
website, websitesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
DocumentField mobilePhones = businessCardFields.get("MobilePhones");
if (mobilePhones != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == mobilePhones.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > mobilePhonesItems = mobilePhones.getValueAsList();
mobilePhonesItems.forEach(mobilePhonesItem -> {
if (DocumentFieldType.PHONE_NUMBER == mobilePhonesItem.getType()) {
String mobilePhoneNumber = mobilePhonesItem.getValueAsPhoneNumber();
System.out.printf("Mobile phone number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
mobilePhoneNumber, mobilePhonesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
DocumentField otherPhones = businessCardFields.get("OtherPhones");
if (otherPhones != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == otherPhones.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > otherPhonesItems = otherPhones.getValueAsList();
otherPhonesItems.forEach(otherPhonesItem -> {
if (DocumentFieldType.PHONE_NUMBER == otherPhonesItem.getType()) {
String otherPhoneNumber = otherPhonesItem.getValueAsPhoneNumber();
System.out.printf("Other phone number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
otherPhoneNumber, otherPhonesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
DocumentField faxes = businessCardFields.get("Faxes");
if (faxes != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == faxes.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > faxesItems = faxes.getValueAsList();
faxesItems.forEach(faxesItem -> {
if (DocumentFieldType.PHONE_NUMBER == faxesItem.getType()) {
String faxPhoneNumber = faxesItem.getValueAsPhoneNumber();
System.out.printf("Fax phone number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n",
faxPhoneNumber, faxesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
DocumentField addresses = businessCardFields.get("Addresses");
if (addresses != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == addresses.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > addressesItems = addresses.getValueAsList();
addressesItems.forEach(addressesItem -> {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == addressesItem.getType()) {
String address = addressesItem.getValueAsString();
System.out
.printf("Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", address, addressesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
DocumentField companyName = businessCardFields.get("CompanyNames");
if (companyName != null) {
if (DocumentFieldType.LIST == companyName.getType()) {
List < DocumentField > companyNameItems = companyName.getValueAsList();
companyNameItems.forEach(companyNameItem -> {
if (DocumentFieldType.STRING == companyNameItem.getType()) {
String companyNameValue = companyNameItem.getValueAsString();
System.out.printf("Company name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", companyNameValue,
companyNameItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
}
}
}
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu wizytówek.
Pakiet referencyjny | interfejsu API REST biblioteki | klienta (npm) | Przykłady |obsługiwanej wersji interfejsu API REST
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Najnowsza wersja programu Visual Studio Code lub preferowanego środowiska IDE. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Node.js w programie Visual Studio Code.
Najnowsza
LTSwersja Node.js.Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Napiwek
Utwórz zasób usług Azure AI, jeśli planujesz uzyskać dostęp do wielu usług azure AI przy użyciu jednego punktu końcowego i klucza. W przypadku dostępu tylko do analizy dokumentów utwórz zasób analizy dokumentów. Jeśli zamierzasz używać uwierzytelniania Firmy Microsoft Entra, potrzebujesz zasobu z jedną usługą.
Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Plik dokumentu pod adresem URL. W tym projekcie można użyć przykładowych formularzy podanych w poniższej tabeli dla każdej funkcji:
Funkcja modelID document-url Odczyt modelu odczyt wstępnie utworzony Broszura przykładowa Model układu wstępnie utworzony układ Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej Model formularza W-2 prebuilt-tax.us.w2 Przykładowy formularz W-2 Model faktury wstępnie utworzona faktura Przykładowa faktura Model paragonu wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie Przykładowe potwierdzenie Model dokumentu identyfikatora prebuilt-idDocument Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze
Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Utwórz aplikację Node.js Express.
W oknie konsoli utwórz i przejdź do nowego katalogu aplikacji o nazwie
doc-intel-app.mkdir doc-intel-app cd doc-intel-appUruchom polecenie ,
npm initaby zainicjować aplikację i szkielet projektu.npm initOkreśl atrybuty projektu przy użyciu monitów przedstawionych w terminalu.
- Najważniejsze atrybuty to nazwa, numer wersji i punkt wejścia.
- Zalecamy zachowanie
index.jsnazwy punktu wejścia. Opis, polecenie testowe, repozytorium GitHub, słowa kluczowe, autor i informacje o licencji są atrybutami opcjonalnymi. Możesz pominąć je dla tego projektu. - Wybierz klawisz Enter, aby zaakceptować sugestie w nawiasach.
Po zakończeniu monitów polecenie tworzy
package.jsonplik w katalogu doc-intel-app .Zainstaluj bibliotekę
ai-document-intelligenceklienta iazure/identitypakiety npm:npm i @azure-rest/ai-document-intelligence@1.0.0-beta.2 @azure/identity
Plik package.json aplikacji jest aktualizowany przy użyciu zależności.
Utwórz plik o nazwie index.js w katalogu aplikacji.
Napiwek
Nowy plik można utworzyć przy użyciu programu PowerShell. Otwórz okno programu PowerShell w katalogu projektu, trzymając wciśnięty klawisz Shift i klikając prawym przyciskiem myszy folder, a następnie wpisz następujące polecenie: New-Item index.js.
Kompilowanie aplikacji
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentIntelligenceClient klasy . W tym celu utworzysz element AzureKeyCredential z kluczem z witryny Azure Portal i DocumentIntelligenceClient wystąpieniem z AzureKeyCredential punktem końcowym analizy dokumentów i .
index.js Otwórz plik w programie Visual Studio Code lub ulubionym środowisku IDE i wybierz jeden z następujących przykładów kodu i skopiuj/wklej do aplikacji:
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
readmodelu jako podstawy do wyodrębniania tekstów z dokumentów. - Wstępnie utworzony model układu wyodrębnia lokalizacje tekstu i tekstu, tabele, znaczniki zaznaczenia i informacje o strukturze z dokumentów i obrazów.
- Wstępnie utworzony model tax.us.w2 wyodrębnia informacje zgłaszane na formularzach podatkowych us Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Wstępnie utworzony model faktury wyodrębnia informacje zgłoszone w formularzach podatkowych us Internal Revenue Service.
- Wstępnie utworzony model paragonu wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z drukowanych i odręcznych paragonów sprzedaży.
- Wstępnie utworzony model idDocument wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z amerykańskich licencji kierowców; międzynarodowe strony biograficzne paszportu; Identyfikatory stanów USA; karty ubezpieczenia społecznego; i stałe karty zamieszkania.
Korzystanie z modelu odczytu
const { DocumentIntelligenceClient } = require("@azure-rest/ai-document-intelligence");
const { AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/core-auth");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['DI_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['DI_ENDPOINT'];
// sample document
const documentUrlRead = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png"
// helper function
function* getTextOfSpans(content, spans) {
for (const span of spans) {
yield content.slice(span.offset, span.offset + span.length);
}
}
async function main() {
// create your `DocumentIntelligenceClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
const client = DocumentIntelligence(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-read", documentUrlRead);
const {
content,
pages,
languages,
styles
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (pages.length <= 0) {
console.log("No pages were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Pages:");
for (const page of pages) {
console.log("- Page", page.pageNumber, `(unit: ${page.unit})`);
console.log(` ${page.width}x${page.height}, angle: ${page.angle}`);
console.log(` ${page.lines.length} lines, ${page.words.length} words`);
if (page.lines.length > 0) {
console.log(" Lines:");
for (const line of page.lines) {
console.log(` - "${line.content}"`);
// The words of the line can also be iterated independently. The words are computed based on their
// corresponding spans.
for (const word of line.words()) {
console.log(` - "${word.content}"`);
}
}
}
}
}
if (languages.length <= 0) {
console.log("No language spans were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Languages:");
for (const languageEntry of languages) {
console.log(
`- Found language: ${languageEntry.languageCode} (confidence: ${languageEntry.confidence})`
);
for (const text of getTextOfSpans(content, languageEntry.spans)) {
const escapedText = text.replace(/\r?\n/g, "\\n").replace(/"/g, '\\"');
console.log(` - "${escapedText}"`);
}
}
}
if (styles.length <= 0) {
console.log("No text styles were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Styles:");
for (const style of styles) {
console.log(
`- Handwritten: ${style.isHandwritten ? "yes" : "no"} (confidence=${style.confidence})`
);
for (const word of getTextOfSpans(content, style.spans)) {
console.log(` - "${word}"`);
}
}
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl read dane wyjściowe modelu.
Korzystanie z modelu układu
const { DocumentIntelligenceClient } = require("@azure-rest/ai-document-intelligence");
const { AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/core-auth");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['DI_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['DI_ENDPOINT'];
// sample document
const layoutUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png"
async function main() {
const client = DocumentIntelligence(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument(
"prebuilt-layout", layoutUrl);
// Layout extraction produces basic elements such as pages, words, lines, etc. as well as information about the
// appearance (styles) of textual elements.
const { pages, tables } = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (!pages || pages.length <= 0) {
console.log("No pages were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Pages:");
for (const page of pages) {
console.log("- Page", page.pageNumber, `(unit: ${page.unit})`);
console.log(` ${page.width}x${page.height}, angle: ${page.angle}`);
console.log(
` ${page.lines && page.lines.length} lines, ${page.words && page.words.length} words`
);
if (page.lines && page.lines.length > 0) {
console.log(" Lines:");
for (const line of page.lines) {
console.log(` - "${line.content}"`);
// The words of the line can also be iterated independently. The words are computed based on their
// corresponding spans.
for (const word of line.words()) {
console.log(` - "${word.content}"`);
}
}
}
}
}
if (!tables || tables.length <= 0) {
console.log("No tables were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Tables:");
for (const table of tables) {
console.log(
`- Extracted table: ${table.columnCount} columns, ${table.rowCount} rows (${table.cells.length} cells)`
);
}
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu układu.
Korzystanie z ogólnego modelu dokumentów
const { DocumentIntelligenceClient } = require("@azure-rest/ai-document-intelligence");
const { AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/core-auth");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['DI_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['DI_ENDPOINT'];
// sample document
const documentUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-layout.pdf"
async function main() {
const client = DocumentIntelligence(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-document", documentUrl);
const {
keyValuePairs
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (!keyValuePairs || keyValuePairs.length <= 0) {
console.log("No key-value pairs were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Key-Value Pairs:");
for (const {
key,
value,
confidence
} of keyValuePairs) {
console.log("- Key :", `"${key.content}"`);
console.log(" Value:", `"${(value && value.content) || "<undefined>"}" (${confidence})`);
}
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl ogólne dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu.
Korzystanie z modelu podatkowego W-2
const { DocumentIntelligenceClient } = require("@azure-rest/ai-document-intelligence");
const { AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/core-auth");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['DI_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['DI_ENDPOINT'];
const w2DocumentURL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png"
async function main() {
const client = DocumentIntelligence(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-tax.us.w2", w2DocumentURL);
const {
documents: [result]
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (result) {
const { Employee, Employer, ControlNumber, TaxYear, AdditionalInfo } = result.fields;
if (Employee) {
const { Name, Address, SocialSecurityNumber } = Employee.properties;
console.log("Employee:");
console.log(" Name:", Name && Name.content);
console.log(" SSN/TIN:", SocialSecurityNumber && SocialSecurityNumber.content);
if (Address && Address.value) {
const { streetAddress, postalCode } = Address.value;
console.log(" Address:");
console.log(" Street Address:", streetAddress);
console.log(" Postal Code:", postalCode);
}
} else {
console.log("No employee information extracted.");
}
if (Employer) {
const { Name, Address, IdNumber } = Employer.properties;
console.log("Employer:");
console.log(" Name:", Name && Name.content);
console.log(" ID (EIN):", IdNumber && IdNumber.content);
if (Address && Address.value) {
const { streetAddress, postalCode } = Address.value;
console.log(" Address:");
console.log(" Street Address:", streetAddress);
console.log(" Postal Code:", postalCode);
}
} else {
console.log("No employer information extracted.");
}
console.log("Control Number:", ControlNumber && ControlNumber.content);
console.log("Tax Year:", TaxYear && TaxYear.content);
if (AdditionalInfo) {
console.log("Additional Info:");
for (const info of AdditionalInfo.values) {
const { LetterCode, Amount } = info.properties;
console.log(`- ${LetterCode && LetterCode.content}: ${Amount && Amount.content}`);
}
}
} else {
throw new Error("Expected at least one document in the result.");
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2.
Korzystanie z modelu faktury
const { DocumentIntelligenceClient } = require("@azure-rest/ai-document-intelligence");
const { AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/core-auth");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['DI_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['DI_ENDPOINT'];
// sample url
const invoiceUrl = "https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/raw/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/invoice.pdf";
async function main() {
const client = DocumentIntelligence(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-invoice", invoiceUrl);
const {
documents: [result]
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (result) {
const invoice = result.fields;
console.log("Vendor Name:", invoice.VendorName?.content);
console.log("Customer Name:", invoice.CustomerName?.content);
console.log("Invoice Date:", invoice.InvoiceDate?.content);
console.log("Due Date:", invoice.DueDate?.content);
console.log("Items:");
for (const {
properties: item
} of invoice.Items?.values ?? []) {
console.log("-", item.ProductCode?.content ?? "<no product code>");
console.log(" Description:", item.Description?.content);
console.log(" Quantity:", item.Quantity?.content);
console.log(" Date:", item.Date?.content);
console.log(" Unit:", item.Unit?.content);
console.log(" Unit Price:", item.UnitPrice?.content);
console.log(" Tax:", item.Tax?.content);
console.log(" Amount:", item.Amount?.content);
}
console.log("Subtotal:", invoice.SubTotal?.content);
console.log("Previous Unpaid Balance:", invoice.PreviousUnpaidBalance?.content);
console.log("Tax:", invoice.TotalTax?.content);
console.log("Amount Due:", invoice.AmountDue?.content);
} else {
throw new Error("Expected at least one receipt in the result.");
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu faktury.
Korzystanie z modelu paragonu
const { DocumentIntelligenceClient } = require("@azure-rest/ai-document-intelligence");
const { AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/core-auth");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['DI_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['DI_ENDPOINT'];
// sample url
const receiptUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png";
async function main() {
const client = DocumentIntelligence(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-receipt", receiptUrl);
const {
documents: [result]
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (result) {
const {
MerchantName,
Items,
Total
} = result.fields;
console.log("=== Receipt Information ===");
console.log("Type:", result.docType);
console.log("Merchant:", MerchantName && MerchantName.content);
console.log("Items:");
for (const item of (Items && Items.values) || []) {
const {
Description,
TotalPrice
} = item.properties;
console.log("- Description:", Description && Description.content);
console.log(" Total Price:", TotalPrice && TotalPrice.content);
}
console.log("Total:", Total && Total.content);
} else {
throw new Error("Expected at least one receipt in the result.");
}
}
main().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu.
Korzystanie z modelu dokumentów identyfikatorów
const { DocumentIntelligenceClient } = require("@azure-rest/ai-document-intelligence");
const { AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/core-auth");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['DI_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['DI_ENDPOINT'];
// sample document
const idDocumentURL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png"
async function main() {
const client = DocumentIntelligence(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-idDocument", idDocumentURL);
const {
documents: [result]
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (result) {
// The identity document model has multiple document types, so we need to know which document type was actually
extracted.
if (result.docType === "idDocument.driverLicense") {
const { FirstName, LastName, DocumentNumber, DateOfBirth, DateOfExpiration, Height, Weight, EyeColor, Endorsements, Restrictions, VehicleClassifications} = result.fields;
// For the sake of the example, we'll only show a few of the fields that are produced.
console.log("Extracted a Driver License:");
console.log(" Name:", FirstName && FirstName.content, LastName && LastName.content);
console.log(" License No.:", DocumentNumber && DocumentNumber.content);
console.log(" Date of Birth:", DateOfBirth && DateOfBirth.content);
console.log(" Expiration:", DateOfExpiration && DateOfExpiration.content);
console.log(" Height:", Height && Height.content);
console.log(" Weight:", Weight && Weight.content);
console.log(" Eye color:", EyeColor && EyeColor.content);
console.log(" Restrictions:", Restrictions && Restrictions.content);
console.log(" Endorsements:", Endorsements && Endorsements.content);
console.log(" Class:", VehicleClassifications && VehicleClassifications.content);
} else if (result.docType === "idDocument.passport") {
// The passport document type extracts and parses the Passport's machine-readable zone
if (!result.fields.machineReadableZone) {
throw new Error("No Machine Readable Zone extracted from passport.");
}
const {
FirstName,
LastName,
DateOfBirth,
Nationality,
DocumentNumber,
CountryRegion,
DateOfExpiration,
} = result.fields.machineReadableZone.properties;
console.log("Extracted a Passport:");
console.log(" Name:", FirstName && FirstName.content, LastName && LastName.content);
console.log(" Date of Birth:", DateOfBirth && DateOfBirth.content);
console.log(" Nationality:", Nationality && Nationality.content);
console.log(" Passport No.:", DocumentNumber && DocumentNumber.content);
console.log(" Issuer:", CountryRegion && CountryRegion.content);
console.log(" Expiration Date:", DateOfExpiration && DateOfExpiration.content);
} else {
// The only reason this would happen is if the client library's schema for the prebuilt identity document model is
out of date, and a new document type has been introduced.
console.error("Unknown document type in result:", result);
}
} else {
throw new Error("Expected at least one receipt in the result.");
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu identyfikatora.
Dokumentacja zestawu SDK | biblioteki | klienta — dokumentacja pakietu referencyjnego interfejsu API | REST (npm) | Przykłady |obsługiwane wersje interfejsu API REST
Dokumentacja zestawu SDK | biblioteki | klienta — dokumentacja pakietu referencyjnego interfejsu API | REST (npm) | Przykłady |obsługiwane wersje interfejsu API REST
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Najnowsza wersja programu Visual Studio Code lub preferowanego środowiska IDE. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Node.js w programie Visual Studio Code.
Najnowsza
LTSwersja Node.js.Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Napiwek
Utwórz zasób usług Azure AI, jeśli planujesz uzyskać dostęp do wielu usług azure AI przy użyciu jednego punktu końcowego i klucza. W przypadku dostępu tylko do analizy dokumentów utwórz zasób analizy dokumentów. Jeśli zamierzasz używać uwierzytelniania Firmy Microsoft Entra, potrzebujesz zasobu z jedną usługą.
Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Plik dokumentu pod adresem URL. W tym projekcie można użyć przykładowych formularzy podanych w poniższej tabeli dla każdej funkcji:
Funkcja modelID document-url Odczyt modelu odczyt wstępnie utworzony Broszura przykładowa Model układu wstępnie utworzony układ Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej Model formularza W-2 prebuilt-tax.us.w2 Przykładowy formularz W-2 Model faktury wstępnie utworzona faktura Przykładowa faktura Model paragonu wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie Przykładowe potwierdzenie Model dokumentu identyfikatora prebuilt-idDocument Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze Model wizytówek wstępnie utworzona karta biznesowa Przykładowa wizytówka
Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Utwórz aplikację Node.js Express.
W oknie konsoli utwórz i przejdź do nowego katalogu aplikacji o nazwie
form-recognizer-app.mkdir form-recognizer-app cd form-recognizer-appUruchom polecenie ,
npm initaby zainicjować aplikację i szkielet projektu.npm initOkreśl atrybuty projektu przy użyciu monitów przedstawionych w terminalu.
- Najważniejsze atrybuty to nazwa, numer wersji i punkt wejścia.
- Zalecamy zachowanie
index.jsnazwy punktu wejścia. Opis, polecenie testowe, repozytorium GitHub, słowa kluczowe, autor i informacje o licencji są atrybutami opcjonalnymi. Możesz pominąć je dla tego projektu. - Wybierz klawisz Enter, aby zaakceptować sugestie w nawiasach.
Po zakończeniu monitów polecenie tworzy
package.jsonplik w katalogu form-recognizer-app .Zainstaluj bibliotekę
ai-form-recognizerklienta iazure/identitypakiety npm:npm i @azure/ai-form-recognizer @azure/identity
Plik package.json aplikacji jest aktualizowany przy użyciu zależności.
Utwórz plik o nazwie index.js w katalogu aplikacji.
Napiwek
Nowy plik można utworzyć przy użyciu programu PowerShell. Otwórz okno programu PowerShell w katalogu projektu, trzymając wciśnięty klawisz Shift i klikając prawym przyciskiem myszy folder, a następnie wpisz następujące polecenie: New-Item index.js.
Kompilowanie aplikacji
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utworzysz element AzureKeyCredential z kluczem z witryny Azure Portal i DocumentAnalysisClient wystąpieniem z AzureKeyCredential punktem końcowym analizy dokumentów i .
index.js Otwórz plik w programie Visual Studio Code lub ulubionym środowisku IDE i wybierz jeden z następujących przykładów kodu i skopiuj/wklej do aplikacji:
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
readmodelu jako podstawy do wyodrębniania tekstów z dokumentów. - Wstępnie utworzony model układu wyodrębnia lokalizacje tekstu i tekstu, tabele, znaczniki zaznaczenia i informacje o strukturze z dokumentów i obrazów.
- Wstępnie utworzony model tax.us.w2 wyodrębnia informacje zgłaszane na formularzach podatkowych us Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Wstępnie utworzony model faktury wyodrębnia informacje zgłoszone w formularzach podatkowych us Internal Revenue Service.
- Wstępnie utworzony model paragonu wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z drukowanych i odręcznych paragonów sprzedaży.
- Wstępnie utworzony model idDocument wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z amerykańskich licencji kierowców; międzynarodowe strony biograficzne paszportu; Identyfikatory stanów USA; karty ubezpieczenia społecznego; i stałe karty zamieszkania.
Korzystanie z modelu odczytu
const { AzureKeyCredential, DocumentAnalysisClient } = require("@azure/ai-form-recognizer");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['FR_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['FR_ENDPOINT'];
// sample document
const documentUrlRead = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png"
// helper function
function* getTextOfSpans(content, spans) {
for (const span of spans) {
yield content.slice(span.offset, span.offset + span.length);
}
}
async function main() {
// create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
const client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-read", documentUrlRead);
const {
content,
pages,
languages,
styles
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (pages.length <= 0) {
console.log("No pages were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Pages:");
for (const page of pages) {
console.log("- Page", page.pageNumber, `(unit: ${page.unit})`);
console.log(` ${page.width}x${page.height}, angle: ${page.angle}`);
console.log(` ${page.lines.length} lines, ${page.words.length} words`);
if (page.lines.length > 0) {
console.log(" Lines:");
for (const line of page.lines) {
console.log(` - "${line.content}"`);
// The words of the line can also be iterated independently. The words are computed based on their
// corresponding spans.
for (const word of line.words()) {
console.log(` - "${word.content}"`);
}
}
}
}
}
if (languages.length <= 0) {
console.log("No language spans were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Languages:");
for (const languageEntry of languages) {
console.log(
`- Found language: ${languageEntry.languageCode} (confidence: ${languageEntry.confidence})`
);
for (const text of getTextOfSpans(content, languageEntry.spans)) {
const escapedText = text.replace(/\r?\n/g, "\\n").replace(/"/g, '\\"');
console.log(` - "${escapedText}"`);
}
}
}
if (styles.length <= 0) {
console.log("No text styles were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Styles:");
for (const style of styles) {
console.log(
`- Handwritten: ${style.isHandwritten ? "yes" : "no"} (confidence=${style.confidence})`
);
for (const word of getTextOfSpans(content, style.spans)) {
console.log(` - "${word}"`);
}
}
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl read dane wyjściowe modelu.
Korzystanie z modelu układu
const { AzureKeyCredential, DocumentAnalysisClient } = require("@azure/ai-form-recognizer");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['FR_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['FR_ENDPOINT'];
// sample document
const layoutUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png"
async function main() {
const client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl(
"prebuilt-layout", layoutUrl);
// Layout extraction produces basic elements such as pages, words, lines, etc. as well as information about the
// appearance (styles) of textual elements.
const { pages, tables } = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (!pages || pages.length <= 0) {
console.log("No pages were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Pages:");
for (const page of pages) {
console.log("- Page", page.pageNumber, `(unit: ${page.unit})`);
console.log(` ${page.width}x${page.height}, angle: ${page.angle}`);
console.log(
` ${page.lines && page.lines.length} lines, ${page.words && page.words.length} words`
);
if (page.lines && page.lines.length > 0) {
console.log(" Lines:");
for (const line of page.lines) {
console.log(` - "${line.content}"`);
// The words of the line can also be iterated independently. The words are computed based on their
// corresponding spans.
for (const word of line.words()) {
console.log(` - "${word.content}"`);
}
}
}
}
}
if (!tables || tables.length <= 0) {
console.log("No tables were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Tables:");
for (const table of tables) {
console.log(
`- Extracted table: ${table.columnCount} columns, ${table.rowCount} rows (${table.cells.length} cells)`
);
}
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu układu.
Korzystanie z ogólnego modelu dokumentów
const { AzureKeyCredential, DocumentAnalysisClient } = require("@azure/ai-form-recognizer");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['FR_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['FR_ENDPOINT'];
// sample document
const documentUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-layout.pdf"
async function main() {
const client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocumentFromUrl("prebuilt-document", documentUrl);
const {
keyValuePairs
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (!keyValuePairs || keyValuePairs.length <= 0) {
console.log("No key-value pairs were extracted from the document.");
} else {
console.log("Key-Value Pairs:");
for (const {
key,
value,
confidence
} of keyValuePairs) {
console.log("- Key :", `"${key.content}"`);
console.log(" Value:", `"${(value && value.content) || "<undefined>"}" (${confidence})`);
}
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl ogólne dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu.
Korzystanie z modelu podatkowego W-2
const { AzureKeyCredential, DocumentAnalysisClient } = require("@azure/ai-form-recognizer");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['FR_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['FR_ENDPOINT'];
const w2DocumentURL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png"
async function main() {
const client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-tax.us.w2", w2DocumentURL);
const {
documents: [result]
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (result) {
const { Employee, Employer, ControlNumber, TaxYear, AdditionalInfo } = result.fields;
if (Employee) {
const { Name, Address, SocialSecurityNumber } = Employee.properties;
console.log("Employee:");
console.log(" Name:", Name && Name.content);
console.log(" SSN/TIN:", SocialSecurityNumber && SocialSecurityNumber.content);
if (Address && Address.value) {
const { streetAddress, postalCode } = Address.value;
console.log(" Address:");
console.log(" Street Address:", streetAddress);
console.log(" Postal Code:", postalCode);
}
} else {
console.log("No employee information extracted.");
}
if (Employer) {
const { Name, Address, IdNumber } = Employer.properties;
console.log("Employer:");
console.log(" Name:", Name && Name.content);
console.log(" ID (EIN):", IdNumber && IdNumber.content);
if (Address && Address.value) {
const { streetAddress, postalCode } = Address.value;
console.log(" Address:");
console.log(" Street Address:", streetAddress);
console.log(" Postal Code:", postalCode);
}
} else {
console.log("No employer information extracted.");
}
console.log("Control Number:", ControlNumber && ControlNumber.content);
console.log("Tax Year:", TaxYear && TaxYear.content);
if (AdditionalInfo) {
console.log("Additional Info:");
for (const info of AdditionalInfo.values) {
const { LetterCode, Amount } = info.properties;
console.log(`- ${LetterCode && LetterCode.content}: ${Amount && Amount.content}`);
}
}
} else {
throw new Error("Expected at least one document in the result.");
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2.
Korzystanie z modelu faktury
const { AzureKeyCredential, DocumentAnalysisClient } = require("@azure/ai-form-recognizer");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['FR_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['FR_ENDPOINT'];
// sample url
const invoiceUrl = "https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/raw/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/invoice.pdf";
async function main() {
const client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-invoice", invoiceUrl);
const {
documents: [result]
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (result) {
const invoice = result.fields;
console.log("Vendor Name:", invoice.VendorName?.content);
console.log("Customer Name:", invoice.CustomerName?.content);
console.log("Invoice Date:", invoice.InvoiceDate?.content);
console.log("Due Date:", invoice.DueDate?.content);
console.log("Items:");
for (const {
properties: item
} of invoice.Items?.values ?? []) {
console.log("-", item.ProductCode?.content ?? "<no product code>");
console.log(" Description:", item.Description?.content);
console.log(" Quantity:", item.Quantity?.content);
console.log(" Date:", item.Date?.content);
console.log(" Unit:", item.Unit?.content);
console.log(" Unit Price:", item.UnitPrice?.content);
console.log(" Tax:", item.Tax?.content);
console.log(" Amount:", item.Amount?.content);
}
console.log("Subtotal:", invoice.SubTotal?.content);
console.log("Previous Unpaid Balance:", invoice.PreviousUnpaidBalance?.content);
console.log("Tax:", invoice.TotalTax?.content);
console.log("Amount Due:", invoice.AmountDue?.content);
} else {
throw new Error("Expected at least one receipt in the result.");
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu faktury.
Korzystanie z modelu paragonu
const { AzureKeyCredential, DocumentAnalysisClient } = require("@azure/ai-form-recognizer");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['FR_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['FR_ENDPOINT'];
// sample url
const receiptUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png";
async function main() {
const client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-receipt", receiptUrl);
const {
documents: [result]
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (result) {
const {
MerchantName,
Items,
Total
} = result.fields;
console.log("=== Receipt Information ===");
console.log("Type:", result.docType);
console.log("Merchant:", MerchantName && MerchantName.content);
console.log("Items:");
for (const item of (Items && Items.values) || []) {
const {
Description,
TotalPrice
} = item.properties;
console.log("- Description:", Description && Description.content);
console.log(" Total Price:", TotalPrice && TotalPrice.content);
}
console.log("Total:", Total && Total.content);
} else {
throw new Error("Expected at least one receipt in the result.");
}
}
main().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu.
Korzystanie z modelu dokumentów identyfikatorów
const { AzureKeyCredential, DocumentAnalysisClient } = require("@azure/ai-form-recognizer");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['FR_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['FR_ENDPOINT'];
// sample document
const idDocumentURL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png"
async function main() {
const client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-idDocument", idDocumentURL);
const {
documents: [result]
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (result) {
// The identity document model has multiple document types, so we need to know which document type was actually
extracted.
if (result.docType === "idDocument.driverLicense") {
const { FirstName, LastName, DocumentNumber, DateOfBirth, DateOfExpiration, Height, Weight, EyeColor, Endorsements, Restrictions, VehicleClassifications} = result.fields;
// For the sake of the example, we'll only show a few of the fields that are produced.
console.log("Extracted a Driver License:");
console.log(" Name:", FirstName && FirstName.content, LastName && LastName.content);
console.log(" License No.:", DocumentNumber && DocumentNumber.content);
console.log(" Date of Birth:", DateOfBirth && DateOfBirth.content);
console.log(" Expiration:", DateOfExpiration && DateOfExpiration.content);
console.log(" Height:", Height && Height.content);
console.log(" Weight:", Weight && Weight.content);
console.log(" Eye color:", EyeColor && EyeColor.content);
console.log(" Restrictions:", Restrictions && Restrictions.content);
console.log(" Endorsements:", Endorsements && Endorsements.content);
console.log(" Class:", VehicleClassifications && VehicleClassifications.content);
} else if (result.docType === "idDocument.passport") {
// The passport document type extracts and parses the Passport's machine-readable zone
if (!result.fields.machineReadableZone) {
throw new Error("No Machine Readable Zone extracted from passport.");
}
const {
FirstName,
LastName,
DateOfBirth,
Nationality,
DocumentNumber,
CountryRegion,
DateOfExpiration,
} = result.fields.machineReadableZone.properties;
console.log("Extracted a Passport:");
console.log(" Name:", FirstName && FirstName.content, LastName && LastName.content);
console.log(" Date of Birth:", DateOfBirth && DateOfBirth.content);
console.log(" Nationality:", Nationality && natiNationalityonality.content);
console.log(" Passport No.:", DocumentNumber && DocumentNumber.content);
console.log(" Issuer:", CountryRegion && CountryRegion.content);
console.log(" Expiration Date:", DateOfExpiration && DateOfExpiration.content);
} else {
// The only reason this would happen is if the client library's schema for the prebuilt identity document model is
out of date, and a new document type has been introduced.
console.error("Unknown document type in result:", result);
}
} else {
throw new Error("Expected at least one receipt in the result.");
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu identyfikatora.
Korzystanie z modelu wizytówek
const { AzureKeyCredential, DocumentAnalysisClient } = require("@azure/ai-form-recognizer");
//use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
const key = process.env['FR_KEY'];
const endpoint = process.env['FR_ENDPOINT'];
// sample document
const businessCardURL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/de5e0d8982ab754823c54de47a47e8e499351523/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/business_card.jpg"
async function main() {
const client = new DocumentAnalysisClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
const poller = await client.beginAnalyzeDocument("prebuilt-businessCard", businessCardURL);
const {
documents: [result]
} = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (result) {
const businessCard = result.fields;
console.log("=== Business Card Information ===");
// There are more fields than just these few, and the model allows for multiple contact & company names as well as
// phone numbers, though we'll only show the first extracted values here.
const name = businessCard.ContactNames && businessCard.ContactNames.values[0];
if (name) {
const {
FirstName,
LastName
} = name.properties;
console.log("Name:", FirstName && FirstName.content, LastName && LastName.content);
}
const company = businessCard.CompanyNames && businessCard.CompanyNames.values[0];
if (company) {
console.log("Company:", company.content);
}
const address = businessCard.Addresses && businessCard.Addresses.values[0];
if (address) {
console.log("Address:", address.content);
}
const jobTitle = businessCard.JobTitles && businessCard.JobTitles.values[0];
if (jobTitle) {
console.log("Job title:", jobTitle.content);
}
const department = businessCard.Departments && businessCard.Departments.values[0];
if (department) {
console.log("Department:", department.content);
}
const email = businessCard.Emails && businessCard.Emails.values[0];
if (email) {
console.log("Email:", email.content);
}
const workPhone = businessCard.WorkPhones && businessCard.WorkPhones.values[0];
if (workPhone) {
console.log("Work phone:", workPhone.content);
}
const website = businessCard.Websites && businessCard.Websites.values[0];
if (website) {
console.log("Website:", website.content);
}
} else {
throw new Error("Expected at least one business card in the result.");
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu wizytówek.
Dokumentacja interfejsu API REST ( | PyPi) | Przykłady | obsługiwanej wersji interfejsu API REST biblioteki klienta | |
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Środowisko Python w wersji 3.7 lub nowszej. Instalacja języka Python powinna zawierać narzędzie pip. Możesz sprawdzić, czy masz zainstalowane narzędzie pip, uruchamiając polecenie
pip --versionw wierszu polecenia. Pobierz narzędzie pip, instalując najnowszą wersję języka Python.Najnowsza wersja programu Visual Studio Code lub preferowanego środowiska IDE. Zobacz Wprowadzenie do języka Python w programie Visual Studio Code.
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Plik dokumentu pod adresem URL. W tym projekcie można użyć przykładowych formularzy podanych w poniższej tabeli dla każdej funkcji:
Funkcja modelID document-url Odczyt modelu odczyt wstępnie utworzony Broszura przykładowa Model układu wstępnie utworzony układ Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej Model formularza W-2 prebuilt-tax.us.w2 Przykładowy formularz W-2 Model faktury wstępnie utworzona faktura Przykładowa faktura Model paragonu wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie Przykładowe potwierdzenie Model dokumentu identyfikatora prebuilt-idDocument Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze
Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Otwórz okno konsoli w środowisku lokalnym i zainstaluj bibliotekę klienta azure AI Document Intelligence dla języka Python za pomocą narzędzia pip:
pip install azure-ai-documentintelligence==1.0.0b2
Tworzenie aplikacji w języku Python
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentIntelligenceClient klasy . W tym celu utworzysz element AzureKeyCredential z kluczem z witryny Azure Portal i DocumentIntelligenceClient wystąpieniem z AzureKeyCredential punktem końcowym analizy dokumentów i .
Utwórz nowy plik języka Python o nazwie form_recognizer_quickstart.py w edytorze lub środowisku IDE.
Otwórz plik form_recognizer_quickstart.py i wybierz jeden z następujących przykładów kodu i skopiuj/wklej do aplikacji:
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
readmodelu jako podstawy do wyodrębniania tekstów z dokumentów. - Wstępnie utworzony model układu wyodrębnia lokalizacje tekstu i tekstu, tabele, znaczniki zaznaczenia i informacje o strukturze z dokumentów i obrazów.
- Wstępnie utworzony model tax.us.w2 wyodrębnia informacje zgłaszane na formularzach podatkowych us Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Wstępnie utworzony model faktury wyodrębnia pola kluczy i elementy wiersza z faktur sprzedaży w różnych formatach.
- Wstępnie utworzony model paragonu wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z drukowanych i odręcznych paragonów sprzedaży.
- Wstępnie utworzony model idDocument wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z amerykańskich licencji kierowców; międzynarodowe strony biograficzne paszportu; Identyfikatory stanów USA; karty ubezpieczenia społecznego; i stałe karty zamieszkania.
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
Uruchom kod języka Python z wiersza polecenia.
python form_recognizer_quickstart.py
Korzystanie z modelu odczytu
import os
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.ai.documentintelligence import DocumentIntelligenceClient
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import AnalyzeResult
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('DI_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('DI_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_polygon(polygon):
if not polygon:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join(["[{}, {}]".format(p.x, p.y) for p in polygon])
def analyze_read():
# sample document
formUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png"
client = DocumentIntelligenceClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = client.begin_analyze_document(
"prebuilt-read", formUrl
)
result = poller.result()
print("Document contains content: ", result.content)
for idx, style in enumerate(result.styles):
print(
"Document contains {} content".format(
"handwritten" if style.is_handwritten else "no handwritten"
)
)
for page in result.pages:
print("----Analyzing Read from page #{}----".format(page.page_number))
print(
"Page has width: {} and height: {}, measured with unit: {}".format(
page.width, page.height, page.unit
)
)
for line_idx, line in enumerate(page.lines):
print(
"...Line # {} has text content '{}' within bounding box '{}'".format(
line_idx,
line.content,
format_polygon(line.polygon),
)
)
for word in page.words:
print(
"...Word '{}' has a confidence of {}".format(
word.content, word.confidence
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_read()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl read dane wyjściowe modelu.
Korzystanie z modelu układu
import os
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.ai.documentintelligence import DocumentIntelligenceClient
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import AnalyzeResult
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('DI_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('DI_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_polygon(polygon):
if not polygon:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join(["[{}, {}]".format(p.x, p.y) for p in polygon])
def analyze_layout():
# sample document
formUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png"
client = DocumentIntelligenceClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = client.begin_analyze_document(
"prebuilt-layout", formUrl
)
result = poller.result()
for idx, style in enumerate(result.styles):
print(
"Document contains {} content".format(
"handwritten" if style.is_handwritten else "no handwritten"
)
)
for page in result.pages:
print("----Analyzing layout from page #{}----".format(page.page_number))
print(
"Page has width: {} and height: {}, measured with unit: {}".format(
page.width, page.height, page.unit
)
)
for line_idx, line in enumerate(page.lines):
words = line.get_words()
print(
"...Line # {} has word count {} and text '{}' within bounding box '{}'".format(
line_idx,
len(words),
line.content,
format_polygon(line.polygon),
)
)
for word in words:
print(
"......Word '{}' has a confidence of {}".format(
word.content, word.confidence
)
)
for selection_mark in page.selection_marks:
print(
"...Selection mark is '{}' within bounding box '{}' and has a confidence of {}".format(
selection_mark.state,
format_polygon(selection_mark.polygon),
selection_mark.confidence,
)
)
for table_idx, table in enumerate(result.tables):
print(
"Table # {} has {} rows and {} columns".format(
table_idx, table.row_count, table.column_count
)
)
for region in table.bounding_regions:
print(
"Table # {} location on page: {} is {}".format(
table_idx,
region.page_number,
format_polygon(region.polygon),
)
)
for cell in table.cells:
print(
"...Cell[{}][{}] has content '{}'".format(
cell.row_index,
cell.column_index,
cell.content,
)
)
for region in cell.bounding_regions:
print(
"...content on page {} is within bounding box '{}'".format(
region.page_number,
format_polygon(region.polygon),
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_layout()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu układu.
Korzystanie z ogólnego modelu dokumentów
import os
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.ai.documentintelligence import DocumentIntelligenceClient
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import AnalyzeResult
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('DI_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('DI_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_bounding_region(bounding_regions):
if not bounding_regions:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join("Page #{}: {}".format(region.page_number, format_polygon(region.polygon)) for region in bounding_regions)
# formatting function
def format_polygon(polygon):
if not polygon:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join(["[{}, {}]".format(p.x, p.y) for p in polygon])
def analyze_general_documents():
# sample document
docUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-layout.pdf"
# create your `DocumentIntelligenceClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
client = DocumentIntelligenceClient(endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key))
poller = client.begin_analyze_document(
"prebuilt-document", docUrl)
result = poller.result()
for style in result.styles:
if style.is_handwritten:
print("Document contains handwritten content: ")
print(",".join([result.content[span.offset:span.offset + span.length] for span in style.spans]))
print("----Key-value pairs found in document----")
for kv_pair in result.key_value_pairs:
if kv_pair.key:
print(
"Key '{}' found within '{}' bounding regions".format(
kv_pair.key.content,
format_bounding_region(kv_pair.key.bounding_regions),
)
)
if kv_pair.value:
print(
"Value '{}' found within '{}' bounding regions\n".format(
kv_pair.value.content,
format_bounding_region(kv_pair.value.bounding_regions),
)
)
for page in result.pages:
print("----Analyzing document from page #{}----".format(page.page_number))
print(
"Page has width: {} and height: {}, measured with unit: {}".format(
page.width, page.height, page.unit
)
)
for line_idx, line in enumerate(page.lines):
print(
"...Line # {} has text content '{}' within bounding box '{}'".format(
line_idx,
line.content,
format_polygon(line.polygon),
)
)
for word in page.words:
print(
"...Word '{}' has a confidence of {}".format(
word.content, word.confidence
)
)
for selection_mark in page.selection_marks:
print(
"...Selection mark is '{}' within bounding box '{}' and has a confidence of {}".format(
selection_mark.state,
format_polygon(selection_mark.polygon),
selection_mark.confidence,
)
)
for table_idx, table in enumerate(result.tables):
print(
"Table # {} has {} rows and {} columns".format(
table_idx, table.row_count, table.column_count
)
)
for region in table.bounding_regions:
print(
"Table # {} location on page: {} is {}".format(
table_idx,
region.page_number,
format_polygon(region.polygon),
)
)
for cell in table.cells:
print(
"...Cell[{}][{}] has content '{}'".format(
cell.row_index,
cell.column_index,
cell.content,
)
)
for region in cell.bounding_regions:
print(
"...content on page {} is within bounding box '{}'\n".format(
region.page_number,
format_polygon(region.polygon),
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_general_documents()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl ogólne dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu.
Korzystanie z modelu podatkowego W-2
import os
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.ai.documentintelligence import DocumentIntelligenceClient
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import AnalyzeResult
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('DI_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('DI_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_address_value(address_value):
return f"\n......House/building number: {address_value.house_number}\n......Road: {address_value.road}\n......City: {address_value.city}\n......State: {address_value.state}\n......Postal code: {address_value.postal_code}"
def analyze_tax_us_w2():
# sample document
formUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png"
client = DocumentIntelligenceClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = client.begin_analyze_document(
"prebuilt-tax.us.w2", formUrl
)
w2s = poller.result()
for idx, w2 in enumerate(w2s.documents):
print("--------Analyzing US Tax W-2 Form #{}--------".format(idx 1))
form_variant = w2.fields.get("W2FormVariant")
if form_variant:
print(
"Form variant: {} has confidence: {}".format(
form_variant.value, form_variant.confidence
)
)
tax_year = w2.fields.get("TaxYear")
if tax_year:
print(
"Tax year: {} has confidence: {}".format(
tax_year.value, tax_year.confidence
)
)
w2_copy = w2.fields.get("W2Copy")
if w2_copy:
print(
"W-2 Copy: {} has confidence: {}".format(
w2_copy.value,
w2_copy.confidence,
)
)
employee = w2.fields.get("Employee")
if employee:
print("Employee data:")
employee_name = employee.value.get("Name")
if employee_name:
print(
"...Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employee_name.value, employee_name.confidence
)
)
employee_ssn = employee.value.get("SocialSecurityNumber")
if employee_ssn:
print(
"...SSN: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employee_ssn.value, employee_ssn.confidence
)
)
employee_address = employee.value.get("Address")
if employee_address:
print(
"...Address: {}\n......has confidence: {}".format(
format_address_value(employee_address.value),
employee_address.confidence,
)
)
employee_zipcode = employee.value.get("ZipCode")
if employee_zipcode:
print(
"...Zipcode: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employee_zipcode.value, employee_zipcode.confidence
)
)
control_number = w2.fields.get("ControlNumber")
if control_number:
print(
"Control Number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
control_number.value, control_number.confidence
)
)
employer = w2.fields.get("Employer")
if employer:
print("Employer data:")
employer_name = employer.value.get("Name")
if employer_name:
print(
"...Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employer_name.value, employer_name.confidence
)
)
employer_id = employer.value.get("IdNumber")
if employer_id:
print(
"...ID Number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employer_id.value, employer_id.confidence
)
)
employer_address = employer.value.get("Address")
if employer_address:
print(
"...Address: {}\n......has confidence: {}".format(
format_address_value(employer_address.value),
employer_address.confidence,
)
)
employer_zipcode = employer.value.get("ZipCode")
if employer_zipcode:
print(
"...Zipcode: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employer_zipcode.value, employer_zipcode.confidence
)
)
wages_tips = w2.fields.get("WagesTipsAndOtherCompensation")
if wages_tips:
print(
"Wages, tips, and other compensation: {} has confidence: {}".format(
wages_tips.value,
wages_tips.confidence,
)
)
fed_income_tax_withheld = w2.fields.get("FederalIncomeTaxWithheld")
if fed_income_tax_withheld:
print(
"Federal income tax withheld: {} has confidence: {}".format(
fed_income_tax_withheld.value, fed_income_tax_withheld.confidence
)
)
social_security_wages = w2.fields.get("SocialSecurityWages")
if social_security_wages:
print(
"Social Security wages: {} has confidence: {}".format(
social_security_wages.value, social_security_wages.confidence
)
)
social_security_tax_withheld = w2.fields.get("SocialSecurityTaxWithheld")
if social_security_tax_withheld:
print(
"Social Security tax withheld: {} has confidence: {}".format(
social_security_tax_withheld.value,
social_security_tax_withheld.confidence,
)
)
medicare_wages_tips = w2.fields.get("MedicareWagesAndTips")
if medicare_wages_tips:
print(
"Medicare wages and tips: {} has confidence: {}".format(
medicare_wages_tips.value, medicare_wages_tips.confidence
)
)
medicare_tax_withheld = w2.fields.get("MedicareTaxWithheld")
if medicare_tax_withheld:
print(
"Medicare tax withheld: {} has confidence: {}".format(
medicare_tax_withheld.value, medicare_tax_withheld.confidence
)
)
social_security_tips = w2.fields.get("SocialSecurityTips")
if social_security_tips:
print(
"Social Security tips: {} has confidence: {}".format(
social_security_tips.value, social_security_tips.confidence
)
)
allocated_tips = w2.fields.get("AllocatedTips")
if allocated_tips:
print(
"Allocated tips: {} has confidence: {}".format(
allocated_tips.value,
allocated_tips.confidence,
)
)
verification_code = w2.fields.get("VerificationCode")
if verification_code:
print(
"Verification code: {} has confidence: {}".format(
verification_code.value, verification_code.confidence
)
)
dependent_care_benefits = w2.fields.get("DependentCareBenefits")
if dependent_care_benefits:
print(
"Dependent care benefits: {} has confidence: {}".format(
dependent_care_benefits.value,
dependent_care_benefits.confidence,
)
)
non_qualified_plans = w2.fields.get("NonQualifiedPlans")
if non_qualified_plans:
print(
"Non-qualified plans: {} has confidence: {}".format(
non_qualified_plans.value,
non_qualified_plans.confidence,
)
)
additional_info = w2.fields.get("AdditionalInfo")
if additional_info:
print("Additional information:")
for item in additional_info.value:
letter_code = item.value.get("LetterCode")
if letter_code:
print(
"...Letter code: {} has confidence: {}".format(
letter_code.value, letter_code.confidence
)
)
amount = item.value.get("Amount")
if amount:
print(
"...Amount: {} has confidence: {}".format(
amount.value, amount.confidence
)
)
is_statutory_employee = w2.fields.get("IsStatutoryEmployee")
if is_statutory_employee:
print(
"Is statutory employee: {} has confidence: {}".format(
is_statutory_employee.value, is_statutory_employee.confidence
)
)
is_retirement_plan = w2.fields.get("IsRetirementPlan")
if is_retirement_plan:
print(
"Is retirement plan: {} has confidence: {}".format(
is_retirement_plan.value, is_retirement_plan.confidence
)
)
third_party_sick_pay = w2.fields.get("IsThirdPartySickPay")
if third_party_sick_pay:
print(
"Is third party sick pay: {} has confidence: {}".format(
third_party_sick_pay.value, third_party_sick_pay.confidence
)
)
other_info = w2.fields.get("Other")
if other_info:
print(
"Other information: {} has confidence: {}".format(
other_info.value,
other_info.confidence,
)
)
state_tax_info = w2.fields.get("StateTaxInfos")
if state_tax_info:
print("State Tax info:")
for tax in state_tax_info.value:
state = tax.value.get("State")
if state:
print(
"...State: {} has confidence: {}".format(
state.value, state.confidence
)
)
employer_state_id_number = tax.value.get("EmployerStateIdNumber")
if employer_state_id_number:
print(
"...Employer state ID number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employer_state_id_number.value,
employer_state_id_number.confidence,
)
)
state_wages_tips = tax.value.get("StateWagesTipsEtc")
if state_wages_tips:
print(
"...State wages, tips, etc: {} has confidence: {}".format(
state_wages_tips.value, state_wages_tips.confidence
)
)
state_income_tax = tax.value.get("StateIncomeTax")
if state_income_tax:
print(
"...State income tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(
state_income_tax.value, state_income_tax.confidence
)
)
local_tax_info = w2.fields.get("LocalTaxInfos")
if local_tax_info:
print("Local Tax info:")
for tax in local_tax_info.value:
local_wages_tips = tax.value.get("LocalWagesTipsEtc")
if local_wages_tips:
print(
"...Local wages, tips, etc: {} has confidence: {}".format(
local_wages_tips.value, local_wages_tips.confidence
)
)
local_income_tax = tax.value.get("LocalIncomeTax")
if local_income_tax:
print(
"...Local income tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(
local_income_tax.value, local_income_tax.confidence
)
)
locality_name = tax.value.get("LocalityName")
if locality_name:
print(
"...Locality name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
locality_name.value, locality_name.confidence
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_tax_us_w2()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2.
Korzystanie z modelu faktury
import os
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.ai.documentintelligence import DocumentIntelligenceClient
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import AnalyzeResult
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('DI_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('DI_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_bounding_region(bounding_regions):
if not bounding_regions:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join("Page #{}: {}".format(region.page_number, format_polygon(region.polygon)) for region in bounding_regions)
# formatting function
def format_polygon(polygon):
if not polygon:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join(["[{}, {}]".format(p.x, p.y) for p in polygon])
def analyze_invoice():
invoiceUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-invoice.pdf"
client = DocumentIntelligenceClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = client.begin_analyze_document(
"prebuilt-invoice", invoiceUrl)
invoices = poller.result()
for idx, invoice in enumerate(invoices.documents):
print("--------Recognizing invoice #{}--------".format(idx + 1))
vendor_name = invoice.fields.get("VendorName")
if vendor_name:
print(
"Vendor Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
vendor_name.value, vendor_name.confidence
)
)
vendor_address = invoice.fields.get("VendorAddress")
if vendor_address:
print(
"Vendor Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
vendor_address.value, vendor_address.confidence
)
)
vendor_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("VendorAddressRecipient")
if vendor_address_recipient:
print(
"Vendor Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
vendor_address_recipient.value, vendor_address_recipient.confidence
)
)
customer_name = invoice.fields.get("CustomerName")
if customer_name:
print(
"Customer Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
customer_name.value, customer_name.confidence
)
)
customer_id = invoice.fields.get("CustomerId")
if customer_id:
print(
"Customer Id: {} has confidence: {}".format(
customer_id.value, customer_id.confidence
)
)
customer_address = invoice.fields.get("CustomerAddress")
if customer_address:
print(
"Customer Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
customer_address.value, customer_address.confidence
)
)
customer_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("CustomerAddressRecipient")
if customer_address_recipient:
print(
"Customer Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
customer_address_recipient.value,
customer_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
invoice_id = invoice.fields.get("InvoiceId")
if invoice_id:
print(
"Invoice Id: {} has confidence: {}".format(
invoice_id.value, invoice_id.confidence
)
)
invoice_date = invoice.fields.get("InvoiceDate")
if invoice_date:
print(
"Invoice Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
invoice_date.value, invoice_date.confidence
)
)
invoice_total = invoice.fields.get("InvoiceTotal")
if invoice_total:
print(
"Invoice Total: {} has confidence: {}".format(
invoice_total.value, invoice_total.confidence
)
)
due_date = invoice.fields.get("DueDate")
if due_date:
print(
"Due Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
due_date.value, due_date.confidence
)
)
purchase_order = invoice.fields.get("PurchaseOrder")
if purchase_order:
print(
"Purchase Order: {} has confidence: {}".format(
purchase_order.value, purchase_order.confidence
)
)
billing_address = invoice.fields.get("BillingAddress")
if billing_address:
print(
"Billing Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
billing_address.value, billing_address.confidence
)
)
billing_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("BillingAddressRecipient")
if billing_address_recipient:
print(
"Billing Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
billing_address_recipient.value,
billing_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
shipping_address = invoice.fields.get("ShippingAddress")
if shipping_address:
print(
"Shipping Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
shipping_address.value, shipping_address.confidence
)
)
shipping_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("ShippingAddressRecipient")
if shipping_address_recipient:
print(
"Shipping Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
shipping_address_recipient.value,
shipping_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
print("Invoice items:")
for idx, item in enumerate(invoice.fields.get("Items").value):
print("...Item #{}".format(idx + 1))
item_description = item.value.get("Description")
if item_description:
print(
"......Description: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_description.value, item_description.confidence
)
)
item_quantity = item.value.get("Quantity")
if item_quantity:
print(
"......Quantity: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_quantity.value, item_quantity.confidence
)
)
unit = item.value.get("Unit")
if unit:
print(
"......Unit: {} has confidence: {}".format(
unit.value, unit.confidence
)
)
unit_price = item.value.get("UnitPrice")
if unit_price:
print(
"......Unit Price: {} has confidence: {}".format(
unit_price.value, unit_price.confidence
)
)
product_code = item.value.get("ProductCode")
if product_code:
print(
"......Product Code: {} has confidence: {}".format(
product_code.value, product_code.confidence
)
)
item_date = item.value.get("Date")
if item_date:
print(
"......Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_date.value, item_date.confidence
)
)
tax = item.value.get("Tax")
if tax:
print(
"......Tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(tax.value, tax.confidence)
)
amount = item.value.get("Amount")
if amount:
print(
"......Amount: {} has confidence: {}".format(
amount.value, amount.confidence
)
)
subtotal = invoice.fields.get("SubTotal")
if subtotal:
print(
"Subtotal: {} has confidence: {}".format(
subtotal.value, subtotal.confidence
)
)
total_tax = invoice.fields.get("TotalTax")
if total_tax:
print(
"Total Tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(
total_tax.value, total_tax.confidence
)
)
previous_unpaid_balance = invoice.fields.get("PreviousUnpaidBalance")
if previous_unpaid_balance:
print(
"Previous Unpaid Balance: {} has confidence: {}".format(
previous_unpaid_balance.value, previous_unpaid_balance.confidence
)
)
amount_due = invoice.fields.get("AmountDue")
if amount_due:
print(
"Amount Due: {} has confidence: {}".format(
amount_due.value, amount_due.confidence
)
)
service_start_date = invoice.fields.get("ServiceStartDate")
if service_start_date:
print(
"Service Start Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
service_start_date.value, service_start_date.confidence
)
)
service_end_date = invoice.fields.get("ServiceEndDate")
if service_end_date:
print(
"Service End Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
service_end_date.value, service_end_date.confidence
)
)
service_address = invoice.fields.get("ServiceAddress")
if service_address:
print(
"Service Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
service_address.value, service_address.confidence
)
)
service_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("ServiceAddressRecipient")
if service_address_recipient:
print(
"Service Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
service_address_recipient.value,
service_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
remittance_address = invoice.fields.get("RemittanceAddress")
if remittance_address:
print(
"Remittance Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
remittance_address.value, remittance_address.confidence
)
)
remittance_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("RemittanceAddressRecipient")
if remittance_address_recipient:
print(
"Remittance Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
remittance_address_recipient.value,
remittance_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_invoice()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu faktury.
Korzystanie z modelu paragonu
import os
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.ai.documentintelligence import DocumentIntelligenceClient
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import AnalyzeResult
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('DI_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('DI_ENDPOINT')
def analyze_receipts():
# sample document
receiptUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png"
client = DocumentIntelligenceClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = client.begin_analyze_document(
"prebuilt-receipt", receiptUrl, locale="en-US"
)
receipts = poller.result()
for idx, receipt in enumerate(receipts.documents):
print("--------Analysis of receipt #{}--------".format(idx 1))
print("Receipt type: {}".format(receipt.doc_type or "N/A"))
merchant_name = receipt.fields.get("MerchantName")
if merchant_name:
print(
"Merchant Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
merchant_name.value, merchant_name.confidence
)
)
transaction_date = receipt.fields.get("TransactionDate")
if transaction_date:
print(
"Transaction Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
transaction_date.value, transaction_date.confidence
)
)
if receipt.fields.get("Items"):
print("Receipt items:")
for idx, item in enumerate(receipt.fields.get("Items").value):
print("...Item #{}".format(idx 1))
item_description = item.value.get("Description")
if item_description:
print(
"......Item Description: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_description.value, item_description.confidence
)
)
item_quantity = item.value.get("Quantity")
if item_quantity:
print(
"......Item Quantity: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_quantity.value, item_quantity.confidence
)
)
item_price = item.value.get("Price")
if item_price:
print(
"......Individual Item Price: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_price.value, item_price.confidence
)
)
item_total_price = item.value.get("TotalPrice")
if item_total_price:
print(
"......Total Item Price: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_total_price.value, item_total_price.confidence
)
)
subtotal = receipt.fields.get("Subtotal")
if subtotal:
print(
"Subtotal: {} has confidence: {}".format(
subtotal.value, subtotal.confidence
)
)
tax = receipt.fields.get("TotalTax")
if tax:
print("Total tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(tax.value, tax.confidence))
tip = receipt.fields.get("Tip")
if tip:
print("Tip: {} has confidence: {}".format(tip.value, tip.confidence))
total = receipt.fields.get("Total")
if total:
print("Total: {} has confidence: {}".format(total.value, total.confidence))
print("--------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_receipts()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu.
Korzystanie z modelu dokumentów identyfikatorów
import os
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.ai.documentintelligence import DocumentIntelligenceClient
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import AnalyzeResult
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('DI_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('DI_ENDPOINT')
def analyze_identity_documents():
# sample document
identityUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png"
client = DocumentIntelligenceClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller =client.begin_analyze_document(
"prebuilt-idDocument", identityUrl
)
id_documents = poller.result()
for idx, id_document in enumerate(id_documents.documents):
print("--------Analyzing ID document #{}--------".format(idx + 1))
first_name = id_document.fields.get("FirstName")
if first_name:
print(
"First Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
first_name.value, first_name.confidence
)
)
last_name = id_document.fields.get("LastName")
if last_name:
print(
"Last Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
last_name.value, last_name.confidence
)
)
document_number = id_document.fields.get("DocumentNumber")
if document_number:
print(
"Document Number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
document_number.value, document_number.confidence
)
)
dob = id_document.fields.get("DateOfBirth")
if dob:
print(
"Date of Birth: {} has confidence: {}".format(dob.value, dob.confidence)
)
doe = id_document.fields.get("DateOfExpiration")
if doe:
print(
"Date of Expiration: {} has confidence: {}".format(
doe.value, doe.confidence
)
)
sex = id_document.fields.get("Sex")
if sex:
print("Sex: {} has confidence: {}".format(sex.value, sex.confidence))
address = id_document.fields.get("Address")
if address:
print(
"Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
address.value, address.confidence
)
)
country_region = id_document.fields.get("CountryRegion")
if country_region:
print(
"Country/Region: {} has confidence: {}".format(
country_region.value, country_region.confidence
)
)
region = id_document.fields.get("Region")
if region:
print(
"Region: {} has confidence: {}".format(region.value, region.confidence)
)
print("--------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_identity_documents()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu identyfikatora.
Dokumentacja interfejsu API REST ( | PyPi) | Przykłady | obsługiwanych wersji interfejsu API REST biblioteki klienta | |
Dokumentacja interfejsu API REST ( | PyPi) | Przykłady | obsługiwanych wersji interfejsu API REST biblioteki klienta | |
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Środowisko Python w wersji 3.7 lub nowszej. Instalacja języka Python powinna zawierać narzędzie pip. Możesz sprawdzić, czy masz zainstalowane narzędzie pip, uruchamiając polecenie
pip --versionw wierszu polecenia. Pobierz narzędzie pip, instalując najnowszą wersję języka Python.Najnowsza wersja programu Visual Studio Code lub preferowanego środowiska IDE. Zobacz Wprowadzenie do języka Python w programie Visual Studio Code.
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Plik dokumentu pod adresem URL. W tym projekcie można użyć przykładowych formularzy podanych w poniższej tabeli dla każdej funkcji:
Funkcja modelID document-url Odczyt modelu odczyt wstępnie utworzony Broszura przykładowa Model układu wstępnie utworzony układ Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej Model formularza W-2 prebuilt-tax.us.w2 Przykładowy formularz W-2 Model faktury wstępnie utworzona faktura Przykładowa faktura Model paragonu wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie Przykładowe potwierdzenie Model dokumentu identyfikatora prebuilt-idDocument Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze Model wizytówek wstępnie utworzona karta biznesowa Przykładowa wizytówka
Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Otwórz okno konsoli w środowisku lokalnym i zainstaluj bibliotekę klienta azure AI Document Intelligence dla języka Python za pomocą narzędzia pip:
pip install azure-ai-formrecognizer==3.2.0
Tworzenie aplikacji w języku Python
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utworzysz element AzureKeyCredential z kluczem z witryny Azure Portal i DocumentAnalysisClient wystąpieniem z AzureKeyCredential punktem końcowym analizy dokumentów i .
Utwórz nowy plik języka Python o nazwie form_recognizer_quickstart.py w edytorze lub środowisku IDE.
Otwórz plik form_recognizer_quickstart.py i wybierz jeden z następujących przykładów kodu i skopiuj/wklej do aplikacji:
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
readmodelu jako podstawy do wyodrębniania tekstów z dokumentów. - Wstępnie utworzony model układu wyodrębnia lokalizacje tekstu i tekstu, tabele, znaczniki zaznaczenia i informacje o strukturze z dokumentów i obrazów.
- Wstępnie utworzony model tax.us.w2 wyodrębnia informacje zgłaszane na formularzach podatkowych us Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Wstępnie utworzony model faktury wyodrębnia pola kluczy i elementy wiersza z faktur sprzedaży w różnych formatach.
- Wstępnie utworzony model paragonu wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z drukowanych i odręcznych paragonów sprzedaży.
- Wstępnie utworzony model idDocument wyodrębnia kluczowe informacje z amerykańskich licencji kierowców; międzynarodowe strony biograficzne paszportu; Identyfikatory stanów USA; karty ubezpieczenia społecznego; i stałe karty zamieszkania.
- Wstępnie utworzony model odczytu jest podstawą wszystkich modeli analizy dokumentów i może wykrywać wiersze, wyrazy, lokalizacje i języki. Układ, ogólny dokument, wstępnie utworzone i niestandardowe modele używają
Uruchom kod języka Python z wiersza polecenia.
python form_recognizer_quickstart.py
Korzystanie z modelu odczytu
import os
from azure.ai.formrecognizer import DocumentAnalysisClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('FR_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('FR_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_polygon(polygon):
if not polygon:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join(["[{}, {}]".format(p.x, p.y) for p in polygon])
def analyze_read():
# sample document
formUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png"
document_analysis_client = DocumentAnalysisClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = document_analysis_client.begin_analyze_document_from_url(
"prebuilt-read", formUrl
)
result = poller.result()
print("Document contains content: ", result.content)
for idx, style in enumerate(result.styles):
print(
"Document contains {} content".format(
"handwritten" if style.is_handwritten else "no handwritten"
)
)
for page in result.pages:
print("----Analyzing Read from page #{}----".format(page.page_number))
print(
"Page has width: {} and height: {}, measured with unit: {}".format(
page.width, page.height, page.unit
)
)
for line_idx, line in enumerate(page.lines):
print(
"...Line # {} has text content '{}' within bounding box '{}'".format(
line_idx,
line.content,
format_polygon(line.polygon),
)
)
for word in page.words:
print(
"...Word '{}' has a confidence of {}".format(
word.content, word.confidence
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_read()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl read dane wyjściowe modelu.
Korzystanie z modelu układu
import os
from azure.ai.formrecognizer import DocumentAnalysisClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('FR_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('FR_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_polygon(polygon):
if not polygon:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join(["[{}, {}]".format(p.x, p.y) for p in polygon])
def analyze_layout():
# sample document
formUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png"
document_analysis_client = DocumentAnalysisClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = document_analysis_client.begin_analyze_document_from_url(
"prebuilt-layout", formUrl
)
result = poller.result()
for idx, style in enumerate(result.styles):
print(
"Document contains {} content".format(
"handwritten" if style.is_handwritten else "no handwritten"
)
)
for page in result.pages:
print("----Analyzing layout from page #{}----".format(page.page_number))
print(
"Page has width: {} and height: {}, measured with unit: {}".format(
page.width, page.height, page.unit
)
)
for line_idx, line in enumerate(page.lines):
words = line.get_words()
print(
"...Line # {} has word count {} and text '{}' within bounding box '{}'".format(
line_idx,
len(words),
line.content,
format_polygon(line.polygon),
)
)
for word in words:
print(
"......Word '{}' has a confidence of {}".format(
word.content, word.confidence
)
)
for selection_mark in page.selection_marks:
print(
"...Selection mark is '{}' within bounding box '{}' and has a confidence of {}".format(
selection_mark.state,
format_polygon(selection_mark.polygon),
selection_mark.confidence,
)
)
for table_idx, table in enumerate(result.tables):
print(
"Table # {} has {} rows and {} columns".format(
table_idx, table.row_count, table.column_count
)
)
for region in table.bounding_regions:
print(
"Table # {} location on page: {} is {}".format(
table_idx,
region.page_number,
format_polygon(region.polygon),
)
)
for cell in table.cells:
print(
"...Cell[{}][{}] has content '{}'".format(
cell.row_index,
cell.column_index,
cell.content,
)
)
for region in cell.bounding_regions:
print(
"...content on page {} is within bounding box '{}'".format(
region.page_number,
format_polygon(region.polygon),
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_layout()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu układu.
Korzystanie z ogólnego modelu dokumentów
import os
from azure.ai.formrecognizer import DocumentAnalysisClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('FR_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('FR_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_bounding_region(bounding_regions):
if not bounding_regions:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join("Page #{}: {}".format(region.page_number, format_polygon(region.polygon)) for region in bounding_regions)
# formatting function
def format_polygon(polygon):
if not polygon:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join(["[{}, {}]".format(p.x, p.y) for p in polygon])
def analyze_general_documents():
# sample document
docUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-layout.pdf"
# create your `DocumentAnalysisClient` instance and `AzureKeyCredential` variable
document_analysis_client = DocumentAnalysisClient(endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key))
poller = document_analysis_client.begin_analyze_document_from_url(
"prebuilt-document", docUrl)
result = poller.result()
for style in result.styles:
if style.is_handwritten:
print("Document contains handwritten content: ")
print(",".join([result.content[span.offset:span.offset + span.length] for span in style.spans]))
print("----Key-value pairs found in document----")
for kv_pair in result.key_value_pairs:
if kv_pair.key:
print(
"Key '{}' found within '{}' bounding regions".format(
kv_pair.key.content,
format_bounding_region(kv_pair.key.bounding_regions),
)
)
if kv_pair.value:
print(
"Value '{}' found within '{}' bounding regions\n".format(
kv_pair.value.content,
format_bounding_region(kv_pair.value.bounding_regions),
)
)
for page in result.pages:
print("----Analyzing document from page #{}----".format(page.page_number))
print(
"Page has width: {} and height: {}, measured with unit: {}".format(
page.width, page.height, page.unit
)
)
for line_idx, line in enumerate(page.lines):
print(
"...Line # {} has text content '{}' within bounding box '{}'".format(
line_idx,
line.content,
format_polygon(line.polygon),
)
)
for word in page.words:
print(
"...Word '{}' has a confidence of {}".format(
word.content, word.confidence
)
)
for selection_mark in page.selection_marks:
print(
"...Selection mark is '{}' within bounding box '{}' and has a confidence of {}".format(
selection_mark.state,
format_polygon(selection_mark.polygon),
selection_mark.confidence,
)
)
for table_idx, table in enumerate(result.tables):
print(
"Table # {} has {} rows and {} columns".format(
table_idx, table.row_count, table.column_count
)
)
for region in table.bounding_regions:
print(
"Table # {} location on page: {} is {}".format(
table_idx,
region.page_number,
format_polygon(region.polygon),
)
)
for cell in table.cells:
print(
"...Cell[{}][{}] has content '{}'".format(
cell.row_index,
cell.column_index,
cell.content,
)
)
for region in cell.bounding_regions:
print(
"...content on page {} is within bounding box '{}'\n".format(
region.page_number,
format_polygon(region.polygon),
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_general_documents()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl ogólne dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu.
Korzystanie z modelu podatkowego W-2
import os
from azure.ai.formrecognizer import DocumentAnalysisClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('FR_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('FR_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_address_value(address_value):
return f"\n......House/building number: {address_value.house_number}\n......Road: {address_value.road}\n......City: {address_value.city}\n......State: {address_value.state}\n......Postal code: {address_value.postal_code}"
def analyze_tax_us_w2():
# sample document
formUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png"
document_analysis_client = DocumentAnalysisClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = document_analysis_client.begin_analyze_document_from_url(
"prebuilt-tax.us.w2", formUrl
)
w2s = poller.result()
for idx, w2 in enumerate(w2s.documents):
print("--------Analyzing US Tax W-2 Form #{}--------".format(idx 1))
form_variant = w2.fields.get("W2FormVariant")
if form_variant:
print(
"Form variant: {} has confidence: {}".format(
form_variant.value, form_variant.confidence
)
)
tax_year = w2.fields.get("TaxYear")
if tax_year:
print(
"Tax year: {} has confidence: {}".format(
tax_year.value, tax_year.confidence
)
)
w2_copy = w2.fields.get("W2Copy")
if w2_copy:
print(
"W-2 Copy: {} has confidence: {}".format(
w2_copy.value,
w2_copy.confidence,
)
)
employee = w2.fields.get("Employee")
if employee:
print("Employee data:")
employee_name = employee.value.get("Name")
if employee_name:
print(
"...Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employee_name.value, employee_name.confidence
)
)
employee_ssn = employee.value.get("SocialSecurityNumber")
if employee_ssn:
print(
"...SSN: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employee_ssn.value, employee_ssn.confidence
)
)
employee_address = employee.value.get("Address")
if employee_address:
print(
"...Address: {}\n......has confidence: {}".format(
format_address_value(employee_address.value),
employee_address.confidence,
)
)
employee_zipcode = employee.value.get("ZipCode")
if employee_zipcode:
print(
"...Zipcode: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employee_zipcode.value, employee_zipcode.confidence
)
)
control_number = w2.fields.get("ControlNumber")
if control_number:
print(
"Control Number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
control_number.value, control_number.confidence
)
)
employer = w2.fields.get("Employer")
if employer:
print("Employer data:")
employer_name = employer.value.get("Name")
if employer_name:
print(
"...Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employer_name.value, employer_name.confidence
)
)
employer_id = employer.value.get("IdNumber")
if employer_id:
print(
"...ID Number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employer_id.value, employer_id.confidence
)
)
employer_address = employer.value.get("Address")
if employer_address:
print(
"...Address: {}\n......has confidence: {}".format(
format_address_value(employer_address.value),
employer_address.confidence,
)
)
employer_zipcode = employer.value.get("ZipCode")
if employer_zipcode:
print(
"...Zipcode: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employer_zipcode.value, employer_zipcode.confidence
)
)
wages_tips = w2.fields.get("WagesTipsAndOtherCompensation")
if wages_tips:
print(
"Wages, tips, and other compensation: {} has confidence: {}".format(
wages_tips.value,
wages_tips.confidence,
)
)
fed_income_tax_withheld = w2.fields.get("FederalIncomeTaxWithheld")
if fed_income_tax_withheld:
print(
"Federal income tax withheld: {} has confidence: {}".format(
fed_income_tax_withheld.value, fed_income_tax_withheld.confidence
)
)
social_security_wages = w2.fields.get("SocialSecurityWages")
if social_security_wages:
print(
"Social Security wages: {} has confidence: {}".format(
social_security_wages.value, social_security_wages.confidence
)
)
social_security_tax_withheld = w2.fields.get("SocialSecurityTaxWithheld")
if social_security_tax_withheld:
print(
"Social Security tax withheld: {} has confidence: {}".format(
social_security_tax_withheld.value,
social_security_tax_withheld.confidence,
)
)
medicare_wages_tips = w2.fields.get("MedicareWagesAndTips")
if medicare_wages_tips:
print(
"Medicare wages and tips: {} has confidence: {}".format(
medicare_wages_tips.value, medicare_wages_tips.confidence
)
)
medicare_tax_withheld = w2.fields.get("MedicareTaxWithheld")
if medicare_tax_withheld:
print(
"Medicare tax withheld: {} has confidence: {}".format(
medicare_tax_withheld.value, medicare_tax_withheld.confidence
)
)
social_security_tips = w2.fields.get("SocialSecurityTips")
if social_security_tips:
print(
"Social Security tips: {} has confidence: {}".format(
social_security_tips.value, social_security_tips.confidence
)
)
allocated_tips = w2.fields.get("AllocatedTips")
if allocated_tips:
print(
"Allocated tips: {} has confidence: {}".format(
allocated_tips.value,
allocated_tips.confidence,
)
)
verification_code = w2.fields.get("VerificationCode")
if verification_code:
print(
"Verification code: {} has confidence: {}".format(
verification_code.value, verification_code.confidence
)
)
dependent_care_benefits = w2.fields.get("DependentCareBenefits")
if dependent_care_benefits:
print(
"Dependent care benefits: {} has confidence: {}".format(
dependent_care_benefits.value,
dependent_care_benefits.confidence,
)
)
non_qualified_plans = w2.fields.get("NonQualifiedPlans")
if non_qualified_plans:
print(
"Non-qualified plans: {} has confidence: {}".format(
non_qualified_plans.value,
non_qualified_plans.confidence,
)
)
additional_info = w2.fields.get("AdditionalInfo")
if additional_info:
print("Additional information:")
for item in additional_info.value:
letter_code = item.value.get("LetterCode")
if letter_code:
print(
"...Letter code: {} has confidence: {}".format(
letter_code.value, letter_code.confidence
)
)
amount = item.value.get("Amount")
if amount:
print(
"...Amount: {} has confidence: {}".format(
amount.value, amount.confidence
)
)
is_statutory_employee = w2.fields.get("IsStatutoryEmployee")
if is_statutory_employee:
print(
"Is statutory employee: {} has confidence: {}".format(
is_statutory_employee.value, is_statutory_employee.confidence
)
)
is_retirement_plan = w2.fields.get("IsRetirementPlan")
if is_retirement_plan:
print(
"Is retirement plan: {} has confidence: {}".format(
is_retirement_plan.value, is_retirement_plan.confidence
)
)
third_party_sick_pay = w2.fields.get("IsThirdPartySickPay")
if third_party_sick_pay:
print(
"Is third party sick pay: {} has confidence: {}".format(
third_party_sick_pay.value, third_party_sick_pay.confidence
)
)
other_info = w2.fields.get("Other")
if other_info:
print(
"Other information: {} has confidence: {}".format(
other_info.value,
other_info.confidence,
)
)
state_tax_info = w2.fields.get("StateTaxInfos")
if state_tax_info:
print("State Tax info:")
for tax in state_tax_info.value:
state = tax.value.get("State")
if state:
print(
"...State: {} has confidence: {}".format(
state.value, state.confidence
)
)
employer_state_id_number = tax.value.get("EmployerStateIdNumber")
if employer_state_id_number:
print(
"...Employer state ID number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
employer_state_id_number.value,
employer_state_id_number.confidence,
)
)
state_wages_tips = tax.value.get("StateWagesTipsEtc")
if state_wages_tips:
print(
"...State wages, tips, etc: {} has confidence: {}".format(
state_wages_tips.value, state_wages_tips.confidence
)
)
state_income_tax = tax.value.get("StateIncomeTax")
if state_income_tax:
print(
"...State income tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(
state_income_tax.value, state_income_tax.confidence
)
)
local_tax_info = w2.fields.get("LocalTaxInfos")
if local_tax_info:
print("Local Tax info:")
for tax in local_tax_info.value:
local_wages_tips = tax.value.get("LocalWagesTipsEtc")
if local_wages_tips:
print(
"...Local wages, tips, etc: {} has confidence: {}".format(
local_wages_tips.value, local_wages_tips.confidence
)
)
local_income_tax = tax.value.get("LocalIncomeTax")
if local_income_tax:
print(
"...Local income tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(
local_income_tax.value, local_income_tax.confidence
)
)
locality_name = tax.value.get("LocalityName")
if locality_name:
print(
"...Locality name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
locality_name.value, locality_name.confidence
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_tax_us_w2()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2.
Korzystanie z modelu faktury
import os
from azure.ai.formrecognizer import DocumentAnalysisClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('FR_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('FR_ENDPOINT')
# formatting function
def format_bounding_region(bounding_regions):
if not bounding_regions:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join("Page #{}: {}".format(region.page_number, format_polygon(region.polygon)) for region in bounding_regions)
# formatting function
def format_polygon(polygon):
if not polygon:
return "N/A"
return ", ".join(["[{}, {}]".format(p.x, p.y) for p in polygon])
def analyze_invoice():
invoiceUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/sample-invoice.pdf"
document_analysis_client = DocumentAnalysisClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = document_analysis_client.begin_analyze_document_from_url(
"prebuilt-invoice", invoiceUrl)
invoices = poller.result()
for idx, invoice in enumerate(invoices.documents):
print("--------Recognizing invoice #{}--------".format(idx + 1))
vendor_name = invoice.fields.get("VendorName")
if vendor_name:
print(
"Vendor Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
vendor_name.value, vendor_name.confidence
)
)
vendor_address = invoice.fields.get("VendorAddress")
if vendor_address:
print(
"Vendor Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
vendor_address.value, vendor_address.confidence
)
)
vendor_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("VendorAddressRecipient")
if vendor_address_recipient:
print(
"Vendor Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
vendor_address_recipient.value, vendor_address_recipient.confidence
)
)
customer_name = invoice.fields.get("CustomerName")
if customer_name:
print(
"Customer Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
customer_name.value, customer_name.confidence
)
)
customer_id = invoice.fields.get("CustomerId")
if customer_id:
print(
"Customer Id: {} has confidence: {}".format(
customer_id.value, customer_id.confidence
)
)
customer_address = invoice.fields.get("CustomerAddress")
if customer_address:
print(
"Customer Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
customer_address.value, customer_address.confidence
)
)
customer_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("CustomerAddressRecipient")
if customer_address_recipient:
print(
"Customer Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
customer_address_recipient.value,
customer_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
invoice_id = invoice.fields.get("InvoiceId")
if invoice_id:
print(
"Invoice Id: {} has confidence: {}".format(
invoice_id.value, invoice_id.confidence
)
)
invoice_date = invoice.fields.get("InvoiceDate")
if invoice_date:
print(
"Invoice Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
invoice_date.value, invoice_date.confidence
)
)
invoice_total = invoice.fields.get("InvoiceTotal")
if invoice_total:
print(
"Invoice Total: {} has confidence: {}".format(
invoice_total.value, invoice_total.confidence
)
)
due_date = invoice.fields.get("DueDate")
if due_date:
print(
"Due Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
due_date.value, due_date.confidence
)
)
purchase_order = invoice.fields.get("PurchaseOrder")
if purchase_order:
print(
"Purchase Order: {} has confidence: {}".format(
purchase_order.value, purchase_order.confidence
)
)
billing_address = invoice.fields.get("BillingAddress")
if billing_address:
print(
"Billing Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
billing_address.value, billing_address.confidence
)
)
billing_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("BillingAddressRecipient")
if billing_address_recipient:
print(
"Billing Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
billing_address_recipient.value,
billing_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
shipping_address = invoice.fields.get("ShippingAddress")
if shipping_address:
print(
"Shipping Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
shipping_address.value, shipping_address.confidence
)
)
shipping_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("ShippingAddressRecipient")
if shipping_address_recipient:
print(
"Shipping Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
shipping_address_recipient.value,
shipping_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
print("Invoice items:")
for idx, item in enumerate(invoice.fields.get("Items").value):
print("...Item #{}".format(idx + 1))
item_description = item.value.get("Description")
if item_description:
print(
"......Description: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_description.value, item_description.confidence
)
)
item_quantity = item.value.get("Quantity")
if item_quantity:
print(
"......Quantity: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_quantity.value, item_quantity.confidence
)
)
unit = item.value.get("Unit")
if unit:
print(
"......Unit: {} has confidence: {}".format(
unit.value, unit.confidence
)
)
unit_price = item.value.get("UnitPrice")
if unit_price:
print(
"......Unit Price: {} has confidence: {}".format(
unit_price.value, unit_price.confidence
)
)
product_code = item.value.get("ProductCode")
if product_code:
print(
"......Product Code: {} has confidence: {}".format(
product_code.value, product_code.confidence
)
)
item_date = item.value.get("Date")
if item_date:
print(
"......Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_date.value, item_date.confidence
)
)
tax = item.value.get("Tax")
if tax:
print(
"......Tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(tax.value, tax.confidence)
)
amount = item.value.get("Amount")
if amount:
print(
"......Amount: {} has confidence: {}".format(
amount.value, amount.confidence
)
)
subtotal = invoice.fields.get("SubTotal")
if subtotal:
print(
"Subtotal: {} has confidence: {}".format(
subtotal.value, subtotal.confidence
)
)
total_tax = invoice.fields.get("TotalTax")
if total_tax:
print(
"Total Tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(
total_tax.value, total_tax.confidence
)
)
previous_unpaid_balance = invoice.fields.get("PreviousUnpaidBalance")
if previous_unpaid_balance:
print(
"Previous Unpaid Balance: {} has confidence: {}".format(
previous_unpaid_balance.value, previous_unpaid_balance.confidence
)
)
amount_due = invoice.fields.get("AmountDue")
if amount_due:
print(
"Amount Due: {} has confidence: {}".format(
amount_due.value, amount_due.confidence
)
)
service_start_date = invoice.fields.get("ServiceStartDate")
if service_start_date:
print(
"Service Start Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
service_start_date.value, service_start_date.confidence
)
)
service_end_date = invoice.fields.get("ServiceEndDate")
if service_end_date:
print(
"Service End Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
service_end_date.value, service_end_date.confidence
)
)
service_address = invoice.fields.get("ServiceAddress")
if service_address:
print(
"Service Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
service_address.value, service_address.confidence
)
)
service_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("ServiceAddressRecipient")
if service_address_recipient:
print(
"Service Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
service_address_recipient.value,
service_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
remittance_address = invoice.fields.get("RemittanceAddress")
if remittance_address:
print(
"Remittance Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
remittance_address.value, remittance_address.confidence
)
)
remittance_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("RemittanceAddressRecipient")
if remittance_address_recipient:
print(
"Remittance Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(
remittance_address_recipient.value,
remittance_address_recipient.confidence,
)
)
print("----------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_invoice()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu faktury.
Korzystanie z modelu paragonu
import os
from azure.ai.formrecognizer import DocumentAnalysisClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('FR_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('FR_ENDPOINT')
def analyze_receipts():
# sample document
receiptUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png"
document_analysis_client = DocumentAnalysisClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = document_analysis_client.begin_analyze_document_from_url(
"prebuilt-receipt", receiptUrl, locale="en-US"
)
receipts = poller.result()
for idx, receipt in enumerate(receipts.documents):
print("--------Analysis of receipt #{}--------".format(idx 1))
print("Receipt type: {}".format(receipt.doc_type or "N/A"))
merchant_name = receipt.fields.get("MerchantName")
if merchant_name:
print(
"Merchant Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
merchant_name.value, merchant_name.confidence
)
)
transaction_date = receipt.fields.get("TransactionDate")
if transaction_date:
print(
"Transaction Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(
transaction_date.value, transaction_date.confidence
)
)
if receipt.fields.get("Items"):
print("Receipt items:")
for idx, item in enumerate(receipt.fields.get("Items").value):
print("...Item #{}".format(idx 1))
item_description = item.value.get("Description")
if item_description:
print(
"......Item Description: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_description.value, item_description.confidence
)
)
item_quantity = item.value.get("Quantity")
if item_quantity:
print(
"......Item Quantity: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_quantity.value, item_quantity.confidence
)
)
item_price = item.value.get("Price")
if item_price:
print(
"......Individual Item Price: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_price.value, item_price.confidence
)
)
item_total_price = item.value.get("TotalPrice")
if item_total_price:
print(
"......Total Item Price: {} has confidence: {}".format(
item_total_price.value, item_total_price.confidence
)
)
subtotal = receipt.fields.get("Subtotal")
if subtotal:
print(
"Subtotal: {} has confidence: {}".format(
subtotal.value, subtotal.confidence
)
)
tax = receipt.fields.get("TotalTax")
if tax:
print("Total tax: {} has confidence: {}".format(tax.value, tax.confidence))
tip = receipt.fields.get("Tip")
if tip:
print("Tip: {} has confidence: {}".format(tip.value, tip.confidence))
total = receipt.fields.get("Total")
if total:
print("Total: {} has confidence: {}".format(total.value, total.confidence))
print("--------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_receipts()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu.
Korzystanie z modelu dokumentów identyfikatorów
import os
from azure.ai.formrecognizer import DocumentAnalysisClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('FR_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('FR_ENDPOINT')
def analyze_identity_documents():
# sample document
identityUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png"
document_analysis_client = DocumentAnalysisClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = document_analysis_client.begin_analyze_document_from_url(
"prebuilt-idDocument", identityUrl
)
id_documents = poller.result()
for idx, id_document in enumerate(id_documents.documents):
print("--------Analyzing ID document #{}--------".format(idx + 1))
first_name = id_document.fields.get("FirstName")
if first_name:
print(
"First Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
first_name.value, first_name.confidence
)
)
last_name = id_document.fields.get("LastName")
if last_name:
print(
"Last Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
last_name.value, last_name.confidence
)
)
document_number = id_document.fields.get("DocumentNumber")
if document_number:
print(
"Document Number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
document_number.value, document_number.confidence
)
)
dob = id_document.fields.get("DateOfBirth")
if dob:
print(
"Date of Birth: {} has confidence: {}".format(dob.value, dob.confidence)
)
doe = id_document.fields.get("DateOfExpiration")
if doe:
print(
"Date of Expiration: {} has confidence: {}".format(
doe.value, doe.confidence
)
)
sex = id_document.fields.get("Sex")
if sex:
print("Sex: {} has confidence: {}".format(sex.value, sex.confidence))
address = id_document.fields.get("Address")
if address:
print(
"Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
address.value, address.confidence
)
)
country_region = id_document.fields.get("CountryRegion")
if country_region:
print(
"Country/Region: {} has confidence: {}".format(
country_region.value, country_region.confidence
)
)
region = id_document.fields.get("Region")
if region:
print(
"Region: {} has confidence: {}".format(region.value, region.confidence)
)
print("--------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_identity_documents()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu identyfikatora.
Korzystanie z modelu wizytówek
import os
from azure.ai.formrecognizer import DocumentAnalysisClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
# use your `key` and `endpoint` environment variables
key = os.environ.get('FR_KEY')
endpoint = os.environ.get('FR_ENDPOINT')
def analyze_business_card():
# sample document
businessCardUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/de5e0d8982ab754823c54de47a47e8e499351523/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/business_card.jpg"
document_analysis_client = DocumentAnalysisClient(
endpoint=endpoint, credential=AzureKeyCredential(key)
)
poller = document_analysis_client.begin_analyze_document_from_url(
"prebuilt-businessCard", businessCardUrl, locale="en-US"
)
business_cards = poller.result()
for idx, business_card in enumerate(business_cards.documents):
print("--------Analyzing business card #{}--------".format(idx + 1))
contact_names = business_card.fields.get("ContactNames")
if contact_names:
for contact_name in contact_names.value:
print(
"Contact First Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
contact_name.value["FirstName"].value,
contact_name.value[
"FirstName"
].confidence,
)
)
print(
"Contact Last Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
contact_name.value["LastName"].value,
contact_name.value[
"LastName"
].confidence,
)
)
company_names = business_card.fields.get("CompanyNames")
if company_names:
for company_name in company_names.value:
print(
"Company Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
company_name.value, company_name.confidence
)
)
departments = business_card.fields.get("Departments")
if departments:
for department in departments.value:
print(
"Department: {} has confidence: {}".format(
department.value, department.confidence
)
)
job_titles = business_card.fields.get("JobTitles")
if job_titles:
for job_title in job_titles.value:
print(
"Job Title: {} has confidence: {}".format(
job_title.value, job_title.confidence
)
)
emails = business_card.fields.get("Emails")
if emails:
for email in emails.value:
print(
"Email: {} has confidence: {}".format(email.value, email.confidence)
)
websites = business_card.fields.get("Websites")
if websites:
for website in websites.value:
print(
"Website: {} has confidence: {}".format(
website.value, website.confidence
)
)
addresses = business_card.fields.get("Addresses")
if addresses:
for address in addresses.value:
print(
"Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(
address.value, address.confidence
)
)
mobile_phones = business_card.fields.get("MobilePhones")
if mobile_phones:
for phone in mobile_phones.value:
print(
"Mobile phone number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
phone.content, phone.confidence
)
)
faxes = business_card.fields.get("Faxes")
if faxes:
for fax in faxes.value:
print(
"Fax number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
fax.content, fax.confidence
)
)
work_phones = business_card.fields.get("WorkPhones")
if work_phones:
for work_phone in work_phones.value:
print(
"Work phone number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
work_phone.content, work_phone.confidence
)
)
other_phones = business_card.fields.get("OtherPhones")
if other_phones:
for other_phone in other_phones.value:
print(
"Other phone number: {} has confidence: {}".format(
other_phone.value, other_phone.confidence
)
)
print("--------------------------------------")
if __name__ == "__main__":
analyze_business_card()
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w witrynie GitHub i wyświetl dane wyjściowe modelu wizytówek.
Uwaga
Ten projekt używa narzędzia wiersza polecenia cURL do wykonywania wywołań interfejsu API REST.
| Interfejs API | REST analizy dokumentów — obsługiwane zestawy Azure SDK
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Zainstalowane narzędzie wiersza polecenia cURL. Systemy Windows 10 i Windows 11 są dostarczane z kopią biblioteki cURL. W wierszu polecenia wpisz następujące polecenie cURL. Jeśli są wyświetlane opcje pomocy, program cURL jest zainstalowany w środowisku systemu Windows.
curl -helpJeśli nie zainstalowano biblioteki cURL, możesz ją uzyskać tutaj:
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Analizowanie dokumentów i uzyskiwanie wyników
Żądanie POST służy do analizowania dokumentów przy użyciu wstępnie utworzonego lub niestandardowego modelu. Żądanie GET służy do pobierania wyniku wywołania analizy dokumentu. Element modelId jest używany z operacjami POST i resultId GET.
Dla ułatwienia można skorzystać z poniższej tabeli. Zastąp wartości modelId> i <document-url> żądanymi wartościami:<
| Model | modelId | opis | document-url |
|---|---|---|---|
| Odczyt modelu | odczyt wstępnie utworzony | Broszura przykładowa | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png |
| Model układu | wstępnie utworzony układ | Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png |
| Model formularza W-2 | prebuilt-tax.us.w2 | Przykładowy formularz W-2 | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png |
| Model faktury | wstępnie utworzona faktura | Przykładowa faktura | https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/raw/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/invoice.pdf |
| Model paragonu | wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie | Przykładowe potwierdzenie | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png |
| Model dokumentu identyfikatora | prebuilt-idDocument | Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png |
Żądanie POST
Otwórz okno konsoli i uruchom następujące polecenie cURL. Polecenia obejmują punkty końcowe i kluczowe zmienne środowiskowe utworzone wcześniej w sekcji ustaw zmienne środowiskowe. Zastąp te zmienne, jeśli nazwy zmiennych różnią się. Pamiętaj, aby zastąpić parametry modelId> i <document-url>.<
curl -i -X POST "%DI_ENDPOINT%/documentintelligence/documentModels/{modelId}:analyze?api-version=2024-02-29-preview" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: %DI_KEY%" --data-ascii "{'urlSource': '<document-url>'}"
Aby włączyć możliwości dodatku, użyj parametru features zapytania w żądaniu POST. Istnieją cztery funkcje dodatkowe dostępne w 2023-07-31 wersjach (GA) i nowszych: ocr.highResolution, ocr.formula, ocr.font i queryFields.premium. Aby dowiedzieć się więcej o każdej z możliwości, zobacz Modele niestandardowe.
Funkcje highResolution, formuły i czcionki można wywoływać tylko dla modelu Odczyt i układ oraz możliwości queryFields dla modelu Dokumenty ogólne. W poniższym przykładzie pokazano, jak wywołać funkcje highResolution, formuły i czcionki dla modelu Układu.
curl -i -X POST "%DI_ENDPOINT%documentintelligence/documentModels/prebuilt-layout:analyze?features=ocr.highResolution,ocr.formula,ocr.font?api-version=2024-02-29-preview" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: %DI_KEY%" --data-ascii "{'urlSource': '<document-url>'}"
Odpowiedź POST
202 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź zawierającą Operation-location nagłówek. Użyj wartości tego nagłówka, aby pobrać wyniki odpowiedzi.

Uzyskiwanie wyniku analizy (żądanie GET)
Po wywołaniu interfejsu Analyze document API wywołaj interfejs API [Get analyze result}(/rest/api/aiservices/document-models/get-analyze-result?view=rest-aiservices-2024-02-29-preview&preserve-view=true&tabs=HTTP), aby uzyskać stan operacji i wyodrębnionych danych.
Narzędzie wiersza polecenia cURL nie formatuje odpowiedzi interfejsu API, które zawierają zawartość JSON, co może utrudnić odczytywanie zawartości. Aby sformatować odpowiedź JSON, dołącz znak potoku, po którym następuje narzędzie formatowania JSON z żądaniem GET.
Użyj narzędzia json nodeJS jako narzędzia formatującego JSON dla biblioteki cURL. Jeśli nie masz zainstalowanej Node.js , pobierz i zainstaluj najnowszą wersję.
Otwórz okno konsoli i zainstaluj narzędzie json przy użyciu następującego polecenia:
npm install -g jsontoolDość wydrukuj dane wyjściowe JSON, dołączając znak
| jsonpotoku do żądań GET.curl -i -X GET "<endpoint>documentintelligence/documentModels/prebuilt-read/analyzeResults/0e49604a-2d8e-4b15-b6b8-bb456e5d3e0a?api-version=2024-02-29-preview"-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <subscription key>" | json
Żądanie GET
Przed uruchomieniem następującego polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <odpowiedź> POST nagłówkiem
Operation-locationz odpowiedzi POST. - Zastąp <DI_KEY zmienną zmiennej środowiskowej, jeśli różni się ona od nazwy w kodzie.
- Zastąp element *<json-tool> narzędziem do formatowania JSON.
curl -i -X GET "<POST response>" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: %DI_KEY%" | `<json-tool>`
Sprawdzanie odpowiedzi
200 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z danymi wyjściowymi JSON. Pierwsze pole , statuswskazuje stan operacji. Jeśli operacja nie została ukończona, wartość to statusrunning lub notStarted. Wywołaj ponownie interfejs API ręcznie lub za pomocą skryptu. Zalecamy interwał co najmniej jednej sekundy między wywołaniami.
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w usłudze GitHub, aby wyświetlić GET odpowiedź dla każdego z modeli analizy dokumentów:
| Model | Adres URL danych wyjściowych |
|---|---|
| Odczyt modelu | Odczytywanie danych wyjściowych modelu |
| Model układu | Dane wyjściowe modelu układu |
| Model podatkowy W-2 | Dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2 |
| Model faktury | Dane wyjściowe modelu faktury |
| Model paragonu | Dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu |
| Model dokumentu identyfikatora | Dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu identyfikatora |
Uwaga
Ten projekt używa narzędzia wiersza polecenia do wykonywania wywołań interfejsu cURL API REST.
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Zainstalowane narzędzie wiersza polecenia cURL. Systemy Windows 10 i Windows 11 są dostarczane z kopią biblioteki cURL. W wierszu polecenia wpisz następujące polecenie cURL. Jeśli są wyświetlane opcje pomocy, program cURL jest zainstalowany w środowisku systemu Windows.
curl -helpJeśli nie zainstalowano biblioteki cURL, możesz ją uzyskać tutaj:
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Ustawianie zmiennych środowiskowych
Aby wchodzić w interakcje z usługą Analizy dokumentów, musisz utworzyć wystąpienie DocumentAnalysisClient klasy . W tym celu utwórz wystąpienie klienta za pomocą witryny key Azure Portal.endpoint W tym projekcie użyj zmiennych środowiskowych do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu.
Ważne
Nie dołączaj klucza bezpośrednio do kodu i nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznego sposobu przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu, takich jak usługa Azure Key Vault. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Aby ustawić zmienną środowiskową dla klucza zasobu analizy dokumentów, otwórz okno konsoli i postępuj zgodnie z instrukcjami dotyczącymi systemu operacyjnego i środowiska programistycznego. Zastąp <ciąg yourKey> i <yourEndpoint> wartościami z zasobu w witrynie Azure Portal.
Zmienne środowiskowe w systemie Windows nie są uwzględniane wielkości liter. Są one zwykle deklarowane wielkimi literami, ze słowami połączonymi podkreśleniami. W wierszu polecenia uruchom następujące polecenia:
Ustaw zmienną klucza:
setx DI_KEY <yourKey>Ustawianie zmiennej punktu końcowego
setx DI_ENDPOINT <yourEndpoint>Zamknij okno wiersza polecenia po ustawieniu zmiennych środowiskowych. Wartości pozostają do momentu ich ponownej zmiany.
Uruchom ponownie wszystkie uruchomione programy, które odczytują zmienną środowiskową. Jeśli na przykład używasz programu Visual Studio lub Visual Studio Code jako edytora, uruchom ponownie przed uruchomieniem przykładowego kodu.
Oto kilka bardziej przydatnych poleceń do użycia ze zmiennymi środowiskowymi:
| Polecenie | Akcja | Przykład |
|---|---|---|
setx VARIABLE_NAME= |
Usuń zmienną środowiskową, ustawiając wartość na pusty ciąg. | setx DI_KEY= |
setx VARIABLE_NAME=value |
Ustaw lub zmień wartość zmiennej środowiskowej. | setx DI_KEY=<yourKey> |
set VARIABLE_NAME |
Wyświetl wartość określonej zmiennej środowiskowej. | set DI_KEY |
set |
Wyświetl wszystkie zmienne środowiskowe. | set |
Analizowanie dokumentów i uzyskiwanie wyników
Żądanie POST służy do analizowania dokumentów przy użyciu wstępnie utworzonego lub niestandardowego modelu. Żądanie GET służy do pobierania wyniku wywołania analizy dokumentu. Element modelId jest używany z operacjami POST i resultId GET.
Dla ułatwienia można skorzystać z poniższej tabeli. Zastąp wartości modelId> i <document-url> żądanymi wartościami:<
| Model | modelId | opis | document-url |
|---|---|---|---|
| Odczyt modelu | odczyt wstępnie utworzony | Broszura przykładowa | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/read.png |
| Model układu | wstępnie utworzony układ | Potwierdzenie rezerwacji przykładowej | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/layout.png |
| Model formularza W-2 | prebuilt-tax.us.w2 | Przykładowy formularz W-2 | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/w2.png |
| Model faktury | wstępnie utworzona faktura | Przykładowa faktura | https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/raw/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/invoice.pdf |
| Model paragonu | wstępnie utworzone potwierdzenie | Przykładowe potwierdzenie | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/receipt.png |
| Model dokumentu identyfikatora | prebuilt-idDocument | Przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/rest-api/identity_documents.png |
Żądanie POST
Otwórz okno konsoli i uruchom następujące polecenie cURL. Polecenia obejmują punkty końcowe i kluczowe zmienne środowiskowe utworzone wcześniej w sekcji ustaw zmienne środowiskowe. Zastąp te zmienne, jeśli nazwy zmiennych różnią się. Pamiętaj, aby zastąpić parametry modelId> i <document-url>.<
curl -i -X POST "%FR_ENDPOINT%formrecognizer/documentModels/<modelId>:analyze?api-version=2023-07-31" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: %FR_KEY%" --data-ascii "{'urlSource': '<document-url>'}"
Aby włączyć możliwości dodatku, użyj parametru features zapytania w żądaniu POST. Dostępne są cztery funkcje 2023-07-31 dodatku w wersji (GA): ocr.highResolution, ocr.formula, ocr.font i queryFields.premium. Aby dowiedzieć się więcej o każdej z możliwości, zobacz Modele niestandardowe.
Funkcje highResolution, formuły i czcionki można wywoływać tylko dla modelu Odczyt i układ oraz możliwości queryFields dla modelu Dokumenty ogólne. W poniższym przykładzie pokazano, jak wywołać funkcje highResolution, formuły i czcionki dla modelu Układu.
curl -i -X POST "%FR_ENDPOINT%formrecognizer/documentModels/prebuilt-layout:analyze?features=ocr.highResolution,ocr.formula,ocr.font?api-version=2023-07-31" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: %FR_KEY%" --data-ascii "{'urlSource': '<document-url>'}"
Odpowiedź POST
202 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź zawierającą Operation-location nagłówek. Użyj wartości tego nagłówka, aby pobrać wyniki odpowiedzi.

Uzyskiwanie wyniku analizy (żądanie GET)
Po wywołaniu interfejsu Analyze document API wywołaj interfejs API [Get analyze result}(/rest/api/aiservices/document-models/get-analyze-result?view=rest-aiservices-2023-07-31-31&preserve-view=true&tabs=HTTP), aby uzyskać stan operacji i wyodrębnionych danych.
Narzędzie wiersza polecenia cURL nie formatuje odpowiedzi interfejsu API, które zawierają zawartość JSON, co może utrudnić odczytywanie zawartości. Aby sformatować odpowiedź JSON, dołącz znak potoku, po którym następuje narzędzie formatowania JSON z żądaniem GET.
Użyj narzędzia json nodeJS jako narzędzia formatującego JSON dla biblioteki cURL. Jeśli nie masz zainstalowanej Node.js , pobierz i zainstaluj najnowszą wersję.
Otwórz okno konsoli i zainstaluj narzędzie json przy użyciu następującego polecenia:
npm install -g jsontoolDość wydrukuj dane wyjściowe JSON, dołączając znak
| jsonpotoku do żądań GET.curl -i -X GET "<endpoint>formrecognizer/documentModels/prebuilt-read/analyzeResults/0e49604a-2d8e-4b15-b6b8-bb456e5d3e0a?api-version=2023-07-31"-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <subscription key>" | json
Żądanie GET
Przed uruchomieniem następującego polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <odpowiedź> POST nagłówkiem
Operation-locationz odpowiedzi POST. - Zastąp <FR_KEY zmienną zmiennej środowiskowej, jeśli różni się ona od nazwy w kodzie.
- Zastąp element *<json-tool> narzędziem do formatowania JSON.
curl -i -X GET "<POST response>" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: %FR_KEY%" | `<json-tool>`
Sprawdzanie odpowiedzi
200 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z danymi wyjściowymi JSON. Pierwsze pole , statuswskazuje stan operacji. Jeśli operacja nie została ukończona, wartość to statusrunning lub notStarted. Wywołaj ponownie interfejs API ręcznie lub za pomocą skryptu. Zalecamy interwał co najmniej jednej sekundy między wywołaniami.
Odwiedź repozytorium przykładów platformy Azure w usłudze GitHub, aby wyświetlić GET odpowiedź dla każdego z modeli analizy dokumentów:
| Model | Adres URL danych wyjściowych |
|---|---|
| Odczyt modelu | Odczytywanie danych wyjściowych modelu |
| Model układu | Dane wyjściowe modelu układu |
| Model podatkowy W-2 | Dane wyjściowe modelu podatkowego W-2 |
| Model faktury | Dane wyjściowe modelu faktury |
| Model paragonu | Dane wyjściowe modelu paragonu |
| Model dokumentu identyfikatora | Dane wyjściowe modelu dokumentu identyfikatora |
Następne kroki
Gratulacje! Wiesz już, jak używać modeli analizy dokumentów do analizowania różnych dokumentów na różne sposoby. Następnie zapoznaj się z dokumentacją programu Document Intelligence Studio i dokumentacją referencyjną.
Z tego przewodnika z instrukcjami dowiesz się, jak dodać analizę dokumentów do aplikacji i przepływów pracy. Użyj wybranego języka programowania lub interfejsu API REST. Azure AI Document Intelligence to oparta na chmurze usługa Azure AI, która używa uczenia maszynowego do wyodrębniania par klucz-wartość, tekstu i tabel z dokumentów. Zalecamy korzystanie z bezpłatnej usługi podczas uczenia się technologii. Pamiętaj, że liczba bezpłatnych stron jest ograniczona do 500 miesięcznie.
Za pomocą następujących interfejsów API wyodrębnisz dane ustrukturyzowane z formularzy i dokumentów:
Ważne
Ten projekt jest przeznaczony dla interfejsu API REST analizy dokumentów w wersji 2.1.
Kod w tym artykule używa metod synchronicznych i magazynu poświadczeń niezabezpieczonych.
Dokumentacja referencyjna — pakiet | kodu | źródłowego biblioteki źródłowej (NuGet)Samples |
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Środowisko IDE programu Visual Studio lub bieżąca wersja platformy .NET Core.
Obiekt blob usługi Azure Storage zawierający zestaw danych szkoleniowych. Zobacz Tworzenie i trenowanie niestandardowego modelu , aby uzyskać porady i opcje łączenia zestawu danych treningowych. W tym projekcie możesz użyć plików w folderze Train (Trenowanie ) przykładowego zestawu danych. Pobierz i wyodrębnij sample_data.zip.
Zasób analizy. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
W oknie konsoli użyj dotnet new polecenia , aby utworzyć nową aplikację konsolową o nazwie formrecognizer-project. To polecenie tworzy prosty projekt języka C# "Hello World" z jednym plikiem źródłowym: program.cs.
dotnet new console -n formrecognizer-project
Zmień katalog na nowo utworzony folder aplikacji. Aplikację można utworzyć za pomocą następującego polecenia:
dotnet build
Dane wyjściowe kompilacji nie powinny zawierać żadnych ostrzeżeń ani błędów.
...
Build succeeded.
0 Warning(s)
0 Error(s)
...
Instalowanie biblioteki klienta
W katalogu aplikacji zainstaluj bibliotekę klienta analizy dokumentów dla platformy .NET za pomocą następującego polecenia:
dotnet add package Azure.AI.FormRecognizer --version 3.1.1
W katalogu projektu otwórz plik Program.cs w edytorze lub środowisku IDE. Dodaj następujące using dyrektywy:
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.Models;
using Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.Training;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
W klasie Program aplikacji utwórz zmienne dla punktu końcowego i klucza zasobu.
Ważne
Przejdź do portalu Azure Portal. Jeśli zasób analizy dokumentów utworzony w sekcji Wymagania wstępne został wdrożony pomyślnie, wybierz przycisk Przejdź do zasobu w obszarze Następne kroki. W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie w obszarze Zarządzanie zasobami wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
Pamiętaj, aby usunąć klucz z kodu po zakończeniu. Nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznych metod do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
private static readonly string endpoint = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_ENDPOINT_HERE";
private static readonly string apiKey = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY_HERE";
private static readonly AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(apiKey);
W metodzie aplikacji Main dodaj wywołanie do zadań asynchronicznych używanych w tym projekcie:
static void Main(string[] args) {
// new code:
var recognizeContent = RecognizeContent(recognizerClient);
Task.WaitAll(recognizeContent);
var analyzeReceipt = AnalyzeReceipt(recognizerClient, receiptUrl);
Task.WaitAll(analyzeReceipt);
var analyzeBusinessCard = AnalyzeBusinessCard(recognizerClient, bcUrl);
Task.WaitAll(analyzeBusinessCard);
var analyzeInvoice = AnalyzeInvoice(recognizerClient, invoiceUrl);
Task.WaitAll(analyzeInvoice);
var analyzeId = AnalyzeId(recognizerClient, idUrl);
Task.WaitAll(analyzeId);
var trainModel = TrainModel(trainingClient, trainingDataUrl);
Task.WaitAll(trainModel);
var trainModelWithLabels = TrainModelWithLabels(trainingClient, trainingDataUrl);
Task.WaitAll(trainModel);
var analyzeForm = AnalyzePdfForm(recognizerClient, modelId, formUrl);
Task.WaitAll(analyzeForm);
var manageModels = ManageModels(trainingClient, trainingDataUrl);
Task.WaitAll(manageModels);
}
Korzystanie z modelu obiektów
Za pomocą analizy dokumentów można utworzyć dwa różne typy klientów. Pierwszy element , wysyła zapytanie do usługi w FormRecognizerClientcelu rozpoznawania pól formularzy i zawartości. Drugi element , FormTrainingClienttworzy modele niestandardowe i zarządza nimi w celu poprawy rozpoznawania.
FormRecognizerClient udostępnia następujące operacje:
- Rozpoznawanie pól formularzy i zawartości przy użyciu modeli niestandardowych wytrenowanych do analizowania formularzy niestandardowych. Te wartości są zwracane w kolekcji
RecognizedFormobiektów. Zobacz Analizowanie formularzy za pomocą modelu niestandardowego. - Rozpoznawanie zawartości formularza, w tym tabel, wierszy i wyrazów bez konieczności trenowania modelu. Zawartość formularza jest zwracana w kolekcji
FormPageobiektów. Zobacz Analizowanie układu. - Rozpoznawanie typowych pól z amerykańskich paragonów, wizytówek, faktur i dokumentów identyfikatorów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu w usłudze Analizy dokumentów.
FormTrainingClient zapewnia następujące operacje:
- Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania wszystkich pól i wartości znalezionych w formularzach niestandardowych. Zwracany jest element wskazujący
CustomFormModeltypy formularzy, które model analizuje i pola wyodrębniane dla każdego typu formularza. - Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania określonych pól i wartości określonych przez etykietowanie formularzy niestandardowych. Zwracany jest element ,
CustomFormModelktóry wskazuje pola wyodrębniane przez model i szacowaną dokładność dla każdego pola. - Zarządzanie modelami utworzonymi na koncie.
- Skopiuj model niestandardowy z jednego zasobu analizy dokumentów do innego.
Przykłady można znaleźć w temacie Train a Model and Manage Custom Models (Trenowanie modelu i zarządzanie modelami niestandardowymi).
Uwaga
Modele można również wytrenować przy użyciu graficznego interfejsu użytkownika, takiego jak narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego.
Uwierzytelnianie użytkownika
W obszarze Mainutwórz metodę o nazwie AuthenticateClient. Ta metoda w innych zadaniach służy do uwierzytelniania żądań w usłudze Document Intelligence. Ta metoda używa AzureKeyCredential obiektu , aby w razie potrzeby można zaktualizować klucz bez tworzenia nowych obiektów klienta.
private static FormRecognizerClient AuthenticateClient()
{
var credential = new AzureKeyCredential(apiKey);
var client = new FormRecognizerClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
return client;
}
Powtórz kroki dla nowej metody, która uwierzytelnia klienta szkoleniowego.
static private FormTrainingClient AuthenticateTrainingClient()
{
var credential = new AzureKeyCredential(apiKey);
var client = new FormTrainingClient(new Uri(endpoint), credential);
return client;
}
Pobieranie zasobów na potrzeby testowania
Należy również dodać odwołania do adresów URL dla danych szkoleniowych i testowych. Dodaj te odwołania do katalogu głównego Program klasy.
Aby pobrać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego dla danych trenowania modelu niestandardowego, przejdź do zasobu magazynu w witrynie Azure Portal i wybierz pozycję Kontenery magazynu>danych.
Przejdź do kontenera, kliknij prawym przyciskiem myszy i wybierz pozycję Generuj sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego.
Pobierz sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego dla kontenera, a nie dla samego konta magazynu.
Upewnij się, że wybrano uprawnienia Odczyt, Zapis, Usuwanie i Lista , a następnie wybierz pozycję Generuj token SAS i adres URL.
Skopiuj wartość w sekcji Adres URL do lokalizacji tymczasowej. Powinna ona mieć postać:
https://<storage account>.blob.core.windows.net/<container name>?<SAS value>.
Powtórz poprzednie kroki, aby uzyskać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego pojedynczego dokumentu w kontenerze magazynu obiektów blob. Zapisz również ten adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego w lokalizacji tymczasowej.
Zapisz adres URL dołączonego przykładowego obrazu. Ten obraz jest również dostępny w witrynie GitHub).
string trainingDataUrl = "PASTE_YOUR_SAS_URL_OF_YOUR_FORM_FOLDER_IN_BLOB_STORAGE_HERE";
string formUrl = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_FORM_URL_HERE";
string receiptUrl = "https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/cognitive-services/form-recognizer/media" + "/contoso-allinone.jpg";
string bcUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-python/master/sdk/formrecognizer/azure-ai-formrecognizer/samples/sample_forms/business_cards/business-card-english.jpg";
string invoiceUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/simple-invoice.png";
string idUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/id-license.jpg";
Analizowanie układu
Analiza dokumentów umożliwia analizowanie tabel, wierszy i słów w dokumentach bez konieczności trenowania modelu. Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją obiektów FormPage . Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej strony w przesłanym dokumencie. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat wyodrębniania układu, zobacz Model układu analizy dokumentów.
Aby przeanalizować zawartość pliku pod danym adresem URL, użyj StartRecognizeContentFromUri metody .
private static async Task RecognizeContent(FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient)
{
var invoiceUri = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/simple-invoice.png";
FormPageCollection formPages = await recognizerClient
.StartRecognizeContentFromUri(new Uri(invoiceUri))
.WaitForCompletionAsync();
Napiwek
Możesz również pobrać zawartość z pliku lokalnego. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak StartRecognizeContent. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Pozostałe zadania wyświetla informacje o zawartości w konsoli programu .
foreach (FormPage page in formPages)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Form Page {page.PageNumber} has {page.Lines.Count} lines.");
for (int i = 0; i < page.Lines.Count; i++)
{
FormLine line = page.Lines[i];
Console.WriteLine($" Line {i} has {line.Words.Count} word{(line.Words.Count > 1 ? "s" : "")}, and text: '{line.Text}'.");
}
for (int i = 0; i < page.Tables.Count; i++)
{
FormTable table = page.Tables[i];
Console.WriteLine($"Table {i} has {table.RowCount} rows and {table.ColumnCount} columns.");
foreach (FormTableCell cell in table.Cells)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Cell ({cell.RowIndex}, {cell.ColumnIndex}) contains text: '{cell.Text}'.");
}
}
}
}
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Form Page 1 has 18 lines.
Line 0 has 1 word, and text: 'Contoso'.
Line 1 has 1 word, and text: 'Address:'.
Line 2 has 3 words, and text: 'Invoice For: Microsoft'.
Line 3 has 4 words, and text: '1 Redmond way Suite'.
Line 4 has 3 words, and text: '1020 Enterprise Way'.
Line 5 has 3 words, and text: '6000 Redmond, WA'.
Line 6 has 3 words, and text: 'Sunnayvale, CA 87659'.
Line 7 has 1 word, and text: '99243'.
Line 8 has 2 words, and text: 'Invoice Number'.
Line 9 has 2 words, and text: 'Invoice Date'.
Line 10 has 3 words, and text: 'Invoice Due Date'.
Line 11 has 1 word, and text: 'Charges'.
Line 12 has 2 words, and text: 'VAT ID'.
Line 13 has 1 word, and text: '34278587'.
Line 14 has 1 word, and text: '6/18/2017'.
Line 15 has 1 word, and text: '6/24/2017'.
Line 16 has 1 word, and text: '$56,651.49'.
Line 17 has 1 word, and text: 'PT'.
Table 0 has 2 rows and 6 columns.
Cell (0, 0) contains text: 'Invoice Number'.
Cell (0, 1) contains text: 'Invoice Date'.
Cell (0, 2) contains text: 'Invoice Due Date'.
Cell (0, 3) contains text: 'Charges'.
Cell (0, 5) contains text: 'VAT ID'.
Cell (1, 0) contains text: '34278587'.
Cell (1, 1) contains text: '6/18/2017'.
Cell (1, 2) contains text: '6/24/2017'.
Cell (1, 3) contains text: '$56,651.49'.
Cell (1, 5) contains text: 'PT'.
Analizowanie paragonów
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z amerykańskich paragonów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu paragonu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy paragonów, zobacz Model paragonu analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować paragony z adresu URL, użyj StartRecognizeReceiptsFromUri metody .
private static async Task AnalyzeReceipt(
FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient, string receiptUri)
{
RecognizedFormCollection receipts = await recognizerClient.StartRecognizeReceiptsFromUri(new Uri(receiptUrl)).WaitForCompletionAsync();
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy paragonów. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak StartRecognizeReceipts. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją RecognizedForm obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej strony w przesłanym dokumencie. Poniższy kod przetwarza potwierdzenie przy użyciu danego identyfikatora URI i wyświetla główne pola i wartości w konsoli.
foreach (RecognizedForm receipt in receipts)
{
FormField merchantNameField;
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("MerchantName", out merchantNameField))
{
if (merchantNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String)
{
string merchantName = merchantNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($"Merchant Name: '{merchantName}', with confidence {merchantNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField transactionDateField;
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("TransactionDate", out transactionDateField))
{
if (transactionDateField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Date)
{
DateTime transactionDate = transactionDateField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($"Transaction Date: '{transactionDate}', with confidence {transactionDateField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField itemsField;
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("Items", out itemsField))
{
if (itemsField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List)
{
foreach (FormField itemField in itemsField.Value.AsList())
{
Console.WriteLine("Item:");
if (itemField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Dictionary)
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, FormField> itemFields = itemField.Value.AsDictionary();
FormField itemNameField;
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("Name", out itemNameField))
{
if (itemNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String)
{
string itemName = itemNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($" Name: '{itemName}', with confidence {itemNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField itemTotalPriceField;
if (itemFields.TryGetValue("TotalPrice", out itemTotalPriceField))
{
if (itemTotalPriceField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Float)
{
float itemTotalPrice = itemTotalPriceField.Value.AsFloat();
Console.WriteLine($" Total Price: '{itemTotalPrice}', with confidence {itemTotalPriceField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
FormField totalField;
if (receipt.Fields.TryGetValue("Total", out totalField))
{
if (totalField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Float)
{
float total = totalField.Value.AsFloat();
Console.WriteLine($"Total: '{total}', with confidence '{totalField.Confidence}'");
}
}
}
}
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Form Page 1 has 18 lines.
Line 0 has 1 word, and text: 'Contoso'.
Line 1 has 1 word, and text: 'Address:'.
Line 2 has 3 words, and text: 'Invoice For: Microsoft'.
Line 3 has 4 words, and text: '1 Redmond way Suite'.
Line 4 has 3 words, and text: '1020 Enterprise Way'.
Line 5 has 3 words, and text: '6000 Redmond, WA'.
Line 6 has 3 words, and text: 'Sunnayvale, CA 87659'.
Line 7 has 1 word, and text: '99243'.
Line 8 has 2 words, and text: 'Invoice Number'.
Line 9 has 2 words, and text: 'Invoice Date'.
Line 10 has 3 words, and text: 'Invoice Due Date'.
Line 11 has 1 word, and text: 'Charges'.
Line 12 has 2 words, and text: 'VAT ID'.
Line 13 has 1 word, and text: '34278587'.
Line 14 has 1 word, and text: '6/18/2017'.
Line 15 has 1 word, and text: '6/24/2017'.
Line 16 has 1 word, and text: '$56,651.49'.
Line 17 has 1 word, and text: 'PT'.
Table 0 has 2 rows and 6 columns.
Cell (0, 0) contains text: 'Invoice Number'.
Cell (0, 1) contains text: 'Invoice Date'.
Cell (0, 2) contains text: 'Invoice Due Date'.
Cell (0, 3) contains text: 'Charges'.
Cell (0, 5) contains text: 'VAT ID'.
Cell (1, 0) contains text: '34278587'.
Cell (1, 1) contains text: '6/18/2017'.
Cell (1, 2) contains text: '6/24/2017'.
Cell (1, 3) contains text: '$56,651.49'.
Cell (1, 5) contains text: 'PT'.
Merchant Name: 'Contoso Contoso', with confidence 0.516
Transaction Date: '6/10/2019 12:00:00 AM', with confidence 0.985
Item:
Name: '8GB RAM (Black)', with confidence 0.916
Total Price: '999', with confidence 0.559
Item:
Name: 'SurfacePen', with confidence 0.858
Total Price: '99.99', with confidence 0.386
Total: '1203.39', with confidence '0.774'
Analizowanie wizytówek
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z angielskich wizytówek przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy wizytówek, zobacz Model wizytówek analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować wizytówki z adresu URL, użyj StartRecognizeBusinessCardsFromUriAsync metody .
private static async Task AnalyzeBusinessCard(
FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient, string bcUrl) {
RecognizedFormCollection businessCards = await recognizerClient.StartRecognizeBusinessCardsFromUriAsync(bcUrl).WaitForCompletionAsync();
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy wizytówek. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak StartRecognizeBusinessCards. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Poniższy kod przetwarza wizytówkę w danym identyfikatorze URI i wyświetla główne pola i wartości w konsoli.
foreach(RecognizedForm businessCard in businessCards) {
FormField ContactNamesField;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("ContactNames", out ContactNamesField)) {
if (ContactNamesField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField contactNameField in ContactNamesField.Value.AsList()) {
Console.WriteLine($ "Contact Name: {contactNameField.ValueData.Text}");
if (contactNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Dictionary) {
IReadOnlyDictionary < string,
FormField > contactNameFields = contactNameField.Value.AsDictionary();
FormField firstNameField;
if (contactNameFields.TryGetValue("FirstName", out firstNameField)) {
if (firstNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string firstName = firstNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " First Name: '{firstName}', with confidence {firstNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField lastNameField;
if (contactNameFields.TryGetValue("LastName", out lastNameField)) {
if (lastNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string lastName = lastNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Last Name: '{lastName}', with confidence {lastNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
FormField jobTitlesFields;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("JobTitles", out jobTitlesFields)) {
if (jobTitlesFields.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField jobTitleField in jobTitlesFields.Value.AsList()) {
if (jobTitleField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string jobTitle = jobTitleField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Job Title: '{jobTitle}', with confidence {jobTitleField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
FormField departmentFields;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Departments", out departmentFields)) {
if (departmentFields.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField departmentField in departmentFields.Value.AsList()) {
if (departmentField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string department = departmentField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Department: '{department}', with confidence {departmentField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
FormField emailFields;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Emails", out emailFields)) {
if (emailFields.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField emailField in emailFields.Value.AsList()) {
if (emailField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string email = emailField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Email: '{email}', with confidence {emailField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
FormField websiteFields;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Websites", out websiteFields)) {
if (websiteFields.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField websiteField in websiteFields.Value.AsList()) {
if (websiteField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string website = websiteField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Website: '{website}', with confidence {websiteField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
FormField mobilePhonesFields;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("MobilePhones", out mobilePhonesFields)) {
if (mobilePhonesFields.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField mobilePhoneField in mobilePhonesFields.Value.AsList()) {
if (mobilePhoneField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.PhoneNumber) {
string mobilePhone = mobilePhoneField.Value.AsPhoneNumber();
Console.WriteLine($ " Mobile phone number: '{mobilePhone}', with confidence {mobilePhoneField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
FormField otherPhonesFields;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("OtherPhones", out otherPhonesFields)) {
if (otherPhonesFields.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField otherPhoneField in otherPhonesFields.Value.AsList()) {
if (otherPhoneField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.PhoneNumber) {
string otherPhone = otherPhoneField.Value.AsPhoneNumber();
Console.WriteLine($ " Other phone number: '{otherPhone}', with confidence {otherPhoneField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
FormField faxesFields;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Faxes", out faxesFields)) {
if (faxesFields.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField faxField in faxesFields.Value.AsList()) {
if (faxField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.PhoneNumber) {
string fax = faxField.Value.AsPhoneNumber();
Console.WriteLine($ " Fax phone number: '{fax}', with confidence {faxField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
FormField addressesFields;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("Addresses", out addressesFields)) {
if (addressesFields.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField addressField in addressesFields.Value.AsList()) {
if (addressField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string address = addressField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Address: '{address}', with confidence {addressField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
FormField companyNamesFields;
if (businessCard.Fields.TryGetValue("CompanyNames", out companyNamesFields)) {
if (companyNamesFields.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.List) {
foreach(FormField companyNameField in companyNamesFields.Value.AsList()) {
if (companyNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string companyName = companyNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Company name: '{companyName}', with confidence {companyNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
Analizowanie faktur
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z faktur sprzedaży przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy faktur, zobacz Model faktury analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować faktury z adresu URL, użyj StartRecognizeInvoicesFromUriAsync metody .
private static async Task AnalyzeInvoice(
FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient, string invoiceUrl) {
var options = new RecognizeInvoicesOptions() {
Locale = "en-US"
};
RecognizedFormCollection invoices = await recognizerClient.StartRecognizeInvoicesFromUriAsync(invoiceUrl, options).WaitForCompletionAsync();
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy faktur. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak StartRecognizeInvoices. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Poniższy kod przetwarza fakturę w danym identyfikatorze URI i wyświetla główne pola i wartości w konsoli.
RecognizedForm invoice = invoices.Single();
FormField invoiceIdField;
if (invoice.Fields.TryGetValue("InvoiceId", out invoiceIdField)) {
if (invoiceIdField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string invoiceId = invoiceIdField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Invoice Id: '{invoiceId}', with confidence {invoiceIdField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField invoiceDateField;
if (invoice.Fields.TryGetValue("InvoiceDate", out invoiceDateField)) {
if (invoiceDateField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Date) {
DateTime invoiceDate = invoiceDateField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($ " Invoice Date: '{invoiceDate}', with confidence {invoiceDateField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField dueDateField;
if (invoice.Fields.TryGetValue("DueDate", out dueDateField)) {
if (dueDateField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Date) {
DateTime dueDate = dueDateField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($ " Due Date: '{dueDate}', with confidence {dueDateField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField vendorNameField;
if (invoice.Fields.TryGetValue("VendorName", out vendorNameField)) {
if (vendorNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string vendorName = vendorNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Vendor Name: '{vendorName}', with confidence {vendorNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField vendorAddressField;
if (invoice.Fields.TryGetValue("VendorAddress", out vendorAddressField)) {
if (vendorAddressField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string vendorAddress = vendorAddressField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Vendor Address: '{vendorAddress}', with confidence {vendorAddressField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField customerNameField;
if (invoice.Fields.TryGetValue("CustomerName", out customerNameField)) {
if (customerNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string customerName = customerNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Customer Name: '{customerName}', with confidence {customerNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField customerAddressField;
if (invoice.Fields.TryGetValue("CustomerAddress", out customerAddressField)) {
if (customerAddressField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string customerAddress = customerAddressField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Customer Address: '{customerAddress}', with confidence {customerAddressField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField customerAddressRecipientField;
if (invoice.Fields.TryGetValue("CustomerAddressRecipient", out customerAddressRecipientField)) {
if (customerAddressRecipientField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string customerAddressRecipient = customerAddressRecipientField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ " Customer address recipient: '{customerAddressRecipient}', with confidence {customerAddressRecipientField.Confidence}");
}
}
FormField invoiceTotalField;
if (invoice.Fields.TryGetValue("InvoiceTotal", out invoiceTotalField)) {
if (invoiceTotalField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Float) {
float invoiceTotal = invoiceTotalField.Value.AsFloat();
Console.WriteLine($ " Invoice Total: '{invoiceTotal}', with confidence {invoiceTotalField.Confidence}");
}
}
}
Analizowanie dokumentów identyfikatorów
W tej sekcji przedstawiono sposób analizowania i wyodrębniania kluczowych informacji z dokumentów identyfikacyjnych wystawionych przez instytucje rządowe — paszportów na całym świecie i licencji kierowców USA przy użyciu wstępnie utworzonego modelu identyfikatora analizy dokumentów. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy dokumentów identyfikatorów, zobacz model dokumentu identyfikatora analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować dokumenty identyfikatorów z identyfikatora URI, użyj StartRecognizeIdentityDocumentsFromUriAsync metody .
private static async Task AnalyzeId(
FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient, string idUrl) {
RecognizedFormCollection identityDocument = await recognizerClient.StartRecognizeIdDocumentsFromUriAsync(idUrl).WaitForCompletionAsync();
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy dokumentów identyfikatorów. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak StartRecognizeIdentityDocumentsAsync. Zobacz również przykładowy kod w witrynie GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Poniższy kod przetwarza dokument o identyfikatorze w danym identyfikatorze URI i wyświetla główne pola i wartości w konsoli.
RecognizedForm identityDocument = identityDocuments.Single();
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("Address", out FormField addressField)) {
if (addressField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string address = addressField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ "Address: '{address}', with confidence {addressField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("CountryRegion", out FormField countryRegionField)) {
if (countryRegionField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.CountryRegion) {
string countryRegion = countryRegionField.Value.AsCountryRegion();
Console.WriteLine($ "CountryRegion: '{countryRegion}', with confidence {countryRegionField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DateOfBirth", out FormField dateOfBirthField)) {
if (dateOfBirthField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Date) {
DateTime dateOfBirth = dateOfBirthField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($ "Date Of Birth: '{dateOfBirth}', with confidence {dateOfBirthField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DateOfExpiration", out FormField dateOfExpirationField)) {
if (dateOfExpirationField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Date) {
DateTime dateOfExpiration = dateOfExpirationField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($ "Date Of Expiration: '{dateOfExpiration}', with confidence {dateOfExpirationField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DocumentNumber", out FormField documentNumberField)) {
if (documentNumberField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string documentNumber = documentNumberField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ "Document Number: '{documentNumber}', with confidence {documentNumberField.Confidence}");
}
RecognizedForm identityDocument = identityDocuments.Single();
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("Address", out FormField addressField)) {
if (addressField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string address = addressField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ "Address: '{address}', with confidence {addressField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("CountryRegion", out FormField countryRegionField)) {
if (countryRegionField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.CountryRegion) {
string countryRegion = countryRegionField.Value.AsCountryRegion();
Console.WriteLine($ "CountryRegion: '{countryRegion}', with confidence {countryRegionField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DateOfBirth", out FormField dateOfBirthField)) {
if (dateOfBirthField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Date) {
DateTime dateOfBirth = dateOfBirthField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($ "Date Of Birth: '{dateOfBirth}', with confidence {dateOfBirthField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DateOfExpiration", out FormField dateOfExpirationField)) {
if (dateOfExpirationField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.Date) {
DateTime dateOfExpiration = dateOfExpirationField.Value.AsDate();
Console.WriteLine($ "Date Of Expiration: '{dateOfExpiration}', with confidence {dateOfExpirationField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("DocumentNumber", out FormField documentNumberField)) {
if (documentNumberField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string documentNumber = documentNumberField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ "Document Number: '{documentNumber}', with confidence {documentNumberField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("FirstName", out FormField firstNameField)) {
if (firstNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string firstName = firstNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ "First Name: '{firstName}', with confidence {firstNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("LastName", out FormField lastNameField)) {
if (lastNameField.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string lastName = lastNameField.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ "Last Name: '{lastName}', with confidence {lastNameField.Confidence}");
}
}
if (identityDocument.Fields.TryGetValue("Region", out FormField regionfield)) {
if (regionfield.Value.ValueType == FieldValueType.String) {
string region = regionfield.Value.AsString();
Console.WriteLine($ "Region: '{region}', with confidence {regionfield.Confidence}");
}
}
Trenowanie modelu niestandardowego
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak wytrenować model przy użyciu własnych danych. Wytrenowany model może wyświetlać dane ustrukturyzowane, które zawierają relacje klucz/wartość w oryginalnym dokumencie. Po wytrenowania modelu można testować, ponownie trenować i w końcu używać go do niezawodnego wyodrębniania danych z większej liczby formularzy zgodnie z potrzebami.
Uwaga
Modele można również trenować za pomocą graficznego interfejsu użytkownika, takiego jak narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów.
Trenowanie modelu bez etykiet
Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania wszystkich pól i wartości znalezionych w formularzach niestandardowych bez ręcznego etykietowania dokumentów szkoleniowych. Poniższa metoda trenuje model na danym zestawie dokumentów i wyświetla stan modelu w konsoli.
private static async Task<String> TrainModel(
FormTrainingClient trainingClient, string trainingDataUrl)
{
CustomFormModel model = await trainingClient
.StartTrainingAsync(new Uri(trainingDataUrl), useTrainingLabels: false)
.WaitForCompletionAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Custom Model Info:");
Console.WriteLine($" Model Id: {model.ModelId}");
Console.WriteLine($" Model Status: {model.Status}");
Console.WriteLine($" Training model started on: {model.TrainingStartedOn}");
Console.WriteLine($" Training model completed on: {model.TrainingCompletedOn}");
Zwrócony CustomFormModel obiekt zawiera informacje na temat typów formularzy, które model może analizować, a pola, które mogą wyodrębniać z każdego typu formularza. Poniższy blok kodu wyświetla te informacje w konsoli programu .
foreach (CustomFormSubmodel submodel in model.Submodels)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Submodel Form Type: {submodel.FormType}");
foreach (CustomFormModelField field in submodel.Fields.Values)
{
Console.Write($" FieldName: {field.Name}");
if (field.Label != null)
{
Console.Write($", FieldLabel: {field.Label}");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
}
Na koniec zwróć wytrenowany identyfikator modelu do użycia w kolejnych krokach.
return model.ModelId;
}
Te dane wyjściowe zostały obcięte w celu zapewnienia czytelności.
Merchant Name: 'Contoso Contoso', with confidence 0.516
Transaction Date: '6/10/2019 12:00:00 AM', with confidence 0.985
Item:
Name: '8GB RAM (Black)', with confidence 0.916
Total Price: '999', with confidence 0.559
Item:
Name: 'SurfacePen', with confidence 0.858
Total Price: '99.99', with confidence 0.386
Total: '1203.39', with confidence '0.774'
Form Page 1 has 18 lines.
Line 0 has 1 word, and text: 'Contoso'.
Line 1 has 1 word, and text: 'Address:'.
Line 2 has 3 words, and text: 'Invoice For: Microsoft'.
Line 3 has 4 words, and text: '1 Redmond way Suite'.
Line 4 has 3 words, and text: '1020 Enterprise Way'.
...
Table 0 has 2 rows and 6 columns.
Cell (0, 0) contains text: 'Invoice Number'.
Cell (0, 1) contains text: 'Invoice Date'.
Cell (0, 2) contains text: 'Invoice Due Date'.
Cell (0, 3) contains text: 'Charges'.
...
Custom Model Info:
Model Id: 95035721-f19d-40eb-8820-0c806b42798b
Model Status: Ready
Training model started on: 8/24/2020 6:36:44 PM +00:00
Training model completed on: 8/24/2020 6:36:50 PM +00:00
Submodel Form Type: form-95035721-f19d-40eb-8820-0c806b42798b
FieldName: CompanyAddress
FieldName: CompanyName
FieldName: CompanyPhoneNumber
...
Custom Model Info:
Model Id: e7a1181b-1fb7-40be-bfbe-1ee154183633
Model Status: Ready
Training model started on: 8/24/2020 6:36:44 PM +00:00
Training model completed on: 8/24/2020 6:36:52 PM +00:00
Submodel Form Type: form-0
FieldName: field-0, FieldLabel: Additional Notes:
FieldName: field-1, FieldLabel: Address:
FieldName: field-2, FieldLabel: Company Name:
FieldName: field-3, FieldLabel: Company Phone:
FieldName: field-4, FieldLabel: Dated As:
FieldName: field-5, FieldLabel: Details
FieldName: field-6, FieldLabel: Email:
FieldName: field-7, FieldLabel: Hero Limited
FieldName: field-8, FieldLabel: Name:
FieldName: field-9, FieldLabel: Phone:
...
Trenowanie modelu przy użyciu etykiet
Modele niestandardowe można również trenować, ręcznie oznaczając dokumenty szkoleniowe. Trenowanie z etykietami prowadzi do lepszej wydajności w niektórych scenariuszach. Aby wytrenować za pomocą etykiet, musisz mieć specjalne pliki informacyjne etykiet (<nazwa pliku>.pdf.labels.json) w kontenerze magazynu obiektów blob wraz z dokumentami szkoleniowymi. Narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów udostępnia interfejs użytkownika, który ułatwia tworzenie tych plików etykiet. Po ich otrzymaniu można wywołać metodę StartTrainingAsync z parametrem ustawionym uselabels na true.
private static async Task<Guid> TrainModelWithLabelsAsync(
FormRecognizerClient trainingClient, string trainingDataUrl)
{
CustomFormModel model = await trainingClient
.StartTrainingAsync(new Uri(trainingDataUrl), useTrainingLabels: true)
.WaitForCompletionAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Custom Model Info:");
Console.WriteLine($" Model Id: {model.ModelId}");
Console.WriteLine($" Model Status: {model.Status}");
Console.WriteLine($" Training model started on: {model.TrainingStartedOn}");
Console.WriteLine($" Training model completed on: {model.TrainingCompletedOn}");
Zwrócony CustomFormModel element wskazuje pola, które model może wyodrębnić wraz z szacowaną dokładnością w każdym polu. Poniższy blok kodu wyświetla te informacje w konsoli programu .
foreach (CustomFormSubmodel submodel in model.Submodels)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Submodel Form Type: {submodel.FormType}");
foreach (CustomFormModelField field in submodel.Fields.Values)
{
Console.Write($" FieldName: {field.Name}");
if (field.Label != null)
{
Console.Write($", FieldLabel: {field.Label}");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
}
return model.ModelId;
}
Te dane wyjściowe zostały obcięte w celu zapewnienia czytelności.
Form Page 1 has 18 lines.
Line 0 has 1 word, and text: 'Contoso'.
Line 1 has 1 word, and text: 'Address:'.
Line 2 has 3 words, and text: 'Invoice For: Microsoft'.
Line 3 has 4 words, and text: '1 Redmond way Suite'.
Line 4 has 3 words, and text: '1020 Enterprise Way'.
Line 5 has 3 words, and text: '6000 Redmond, WA'.
...
Table 0 has 2 rows and 6 columns.
Cell (0, 0) contains text: 'Invoice Number'.
Cell (0, 1) contains text: 'Invoice Date'.
Cell (0, 2) contains text: 'Invoice Due Date'.
...
Merchant Name: 'Contoso Contoso', with confidence 0.516
Transaction Date: '6/10/2019 12:00:00 AM', with confidence 0.985
Item:
Name: '8GB RAM (Black)', with confidence 0.916
Total Price: '999', with confidence 0.559
Item:
Name: 'SurfacePen', with confidence 0.858
Total Price: '99.99', with confidence 0.386
Total: '1203.39', with confidence '0.774'
Custom Model Info:
Model Id: 63c013e3-1cab-43eb-84b0-f4b20cb9214c
Model Status: Ready
Training model started on: 8/24/2020 6:42:54 PM +00:00
Training model completed on: 8/24/2020 6:43:01 PM +00:00
Submodel Form Type: form-63c013e3-1cab-43eb-84b0-f4b20cb9214c
FieldName: CompanyAddress
FieldName: CompanyName
FieldName: CompanyPhoneNumber
FieldName: DatedAs
FieldName: Email
FieldName: Merchant
...
Analizowanie formularzy przy użyciu modelu niestandardowego
W tej sekcji przedstawiono sposób wyodrębniania informacji o klucz/wartość i innej zawartości z niestandardowych typów szablonów przy użyciu modeli wytrenowanych przy użyciu własnych formularzy.
Ważne
Aby zaimplementować ten scenariusz, musisz mieć już wytrenowany model, aby można było przekazać jego identyfikator do następującej metody.
Użyj metody StartRecognizeCustomFormsFromUri.
// Analyze PDF form data
private static async Task AnalyzePdfForm(
FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient, String modelId, string formUrl)
{
RecognizedFormCollection forms = await recognizerClient
.StartRecognizeCustomFormsFromUri(modelId, new Uri(formUrl))
.WaitForCompletionAsync();
Napiwek
Możesz również przeanalizować plik lokalny. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak StartRecognizeCustomForms. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją RecognizedForm obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej strony w przesłanym dokumencie. Poniższy kod wyświetla wyniki analizy w konsoli programu . Drukuje każde rozpoznane pole i odpowiadającą mu wartość wraz z współczynnikiem ufności.
foreach (RecognizedForm form in forms)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Form of type: {form.FormType}");
foreach (FormField field in form.Fields.Values)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Field '{field.Name}: ");
if (field.LabelData != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Label: '{field.LabelData.Text}");
}
Console.WriteLine($" Value: '{field.ValueData.Text}");
Console.WriteLine($" Confidence: '{field.Confidence}");
}
Console.WriteLine("Table data:");
foreach (FormPage page in form.Pages)
{
for (int i = 0; i < page.Tables.Count; i++)
{
FormTable table = page.Tables[i];
Console.WriteLine($"Table {i} has {table.RowCount} rows and {table.ColumnCount} columns.");
foreach (FormTableCell cell in table.Cells)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Cell ({cell.RowIndex}, {cell.ColumnIndex}) contains {(cell.IsHeader ? "header" : "text")}: '{cell.Text}'");
}
}
}
}
}
Ta odpowiedź wyjściowa została obcięta w celu zapewnienia czytelności.
Custom Model Info:
Model Id: 9b0108ee-65c8-450e-b527-bb309d054fc4
Model Status: Ready
Training model started on: 8/24/2020 7:00:31 PM +00:00
Training model completed on: 8/24/2020 7:00:32 PM +00:00
Submodel Form Type: form-9b0108ee-65c8-450e-b527-bb309d054fc4
FieldName: CompanyAddress
FieldName: CompanyName
FieldName: CompanyPhoneNumber
...
Form Page 1 has 18 lines.
Line 0 has 1 word, and text: 'Contoso'.
Line 1 has 1 word, and text: 'Address:'.
Line 2 has 3 words, and text: 'Invoice For: Microsoft'.
Line 3 has 4 words, and text: '1 Redmond way Suite'.
...
Table 0 has 2 rows and 6 columns.
Cell (0, 0) contains text: 'Invoice Number'.
Cell (0, 1) contains text: 'Invoice Date'.
Cell (0, 2) contains text: 'Invoice Due Date'.
...
Merchant Name: 'Contoso Contoso', with confidence 0.516
Transaction Date: '6/10/2019 12:00:00 AM', with confidence 0.985
Item:
Name: '8GB RAM (Black)', with confidence 0.916
Total Price: '999', with confidence 0.559
Item:
Name: 'SurfacePen', with confidence 0.858
Total Price: '99.99', with confidence 0.386
Total: '1203.39', with confidence '0.774'
Custom Model Info:
Model Id: dc115156-ce0e-4202-bbe4-7426e7bee756
Model Status: Ready
Training model started on: 8/24/2020 7:00:31 PM +00:00
Training model completed on: 8/24/2020 7:00:41 PM +00:00
Submodel Form Type: form-0
FieldName: field-0, FieldLabel: Additional Notes:
FieldName: field-1, FieldLabel: Address:
FieldName: field-2, FieldLabel: Company Name:
FieldName: field-3, FieldLabel: Company Phone:
FieldName: field-4, FieldLabel: Dated As:
...
Form of type: custom:form
Field 'Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.Models.FieldValue:
Value: '$56,651.49
Confidence: '0.249
Field 'Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.Models.FieldValue:
Value: 'PT
Confidence: '0.245
Field 'Azure.AI.FormRecognizer.Models.FieldValue:
Value: '99243
Confidence: '0.114
...
Zarządzanie modelami niestandardowymi
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak zarządzać modelami niestandardowymi przechowywanymi na koncie. Wykonano wiele operacji w ramach następującej metody:
private static async Task ManageModels(
FormTrainingClient trainingClient, string trainingFileUrl)
{
Sprawdzanie liczby modeli na koncie zasobu FormRecognizer
Poniższy blok kodu sprawdza liczbę modeli zapisanych na koncie analizy dokumentów i porównuje je z limitem konta.
// Check number of models in the FormRecognizer account,
// and the maximum number of models that can be stored.
AccountProperties accountProperties = trainingClient.GetAccountProperties();
Console.WriteLine($"Account has {accountProperties.CustomModelCount} models.");
Console.WriteLine($"It can have at most {accountProperties.CustomModelLimit} models.");
Wyjście
Account has 20 models.
It can have at most 5000 models.
Wyświetlanie listy modeli aktualnie przechowywanych na koncie zasobu
Poniższy kod blokuje bieżące modele na twoim koncie i wyświetla ich szczegóły w konsoli.
Pageable<CustomFormModelInfo> models = trainingClient.GetCustomModels();
foreach (CustomFormModelInfo modelInfo in models)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Custom Model Info:");
Console.WriteLine($" Model Id: {modelInfo.ModelId}");
Console.WriteLine($" Model Status: {modelInfo.Status}");
Console.WriteLine($" Training model started on: {modelInfo.TrainingStartedOn}");
Console.WriteLine($" Training model completed on: {modelInfo.TrainingCompletedOn}");
}
Te dane wyjściowe zostały obcięte w celu zapewnienia czytelności.
Custom Model Info:
Model Id: 05932d5a-a2f8-4030-a2ef-4e5ed7112515
Model Status: Creating
Training model started on: 8/24/2020 7:35:02 PM +00:00
Training model completed on: 8/24/2020 7:35:02 PM +00:00
Custom Model Info:
Model Id: 150828c4-2eb2-487e-a728-60d5d504bd16
Model Status: Ready
Training model started on: 8/24/2020 7:33:25 PM +00:00
Training model completed on: 8/24/2020 7:33:27 PM +00:00
Custom Model Info:
Model Id: 3303e9de-6cec-4dfb-9e68-36510a6ecbb2
Model Status: Ready
Training model started on: 8/24/2020 7:29:27 PM +00:00
Training model completed on: 8/24/2020 7:29:36 PM +00:00
Pobieranie określonego modelu przy użyciu identyfikatora modelu
Poniższy blok kodu trenuje nowy model, podobnie jak w sekcji Trenowanie modelu bez etykiet , a następnie pobiera drugie odwołanie do niego przy użyciu jego identyfikatora.
// Create a new model to store in the account
CustomFormModel model = await trainingClient.StartTrainingAsync(
new Uri(trainingFileUrl)).WaitForCompletionAsync();
// Get the model that was just created
CustomFormModel modelCopy = trainingClient.GetCustomModel(model.ModelId);
Console.WriteLine($"Custom Model {modelCopy.ModelId} recognizes the following form types:");
foreach (CustomFormSubmodel submodel in modelCopy.Submodels)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Submodel Form Type: {submodel.FormType}");
foreach (CustomFormModelField field in submodel.Fields.Values)
{
Console.Write($" FieldName: {field.Name}");
if (field.Label != null)
{
Console.Write($", FieldLabel: {field.Label}");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
}
Te dane wyjściowe zostały obcięte w celu zapewnienia czytelności.
Custom Model Info:
Model Id: 150828c4-2eb2-487e-a728-60d5d504bd16
Model Status: Ready
Training model started on: 8/24/2020 7:33:25 PM +00:00
Training model completed on: 8/24/2020 7:33:27 PM +00:00
Submodel Form Type: form-150828c4-2eb2-487e-a728-60d5d504bd16
FieldName: CompanyAddress
FieldName: CompanyName
FieldName: CompanyPhoneNumber
FieldName: DatedAs
FieldName: Email
FieldName: Merchant
FieldName: PhoneNumber
FieldName: PurchaseOrderNumber
FieldName: Quantity
FieldName: Signature
FieldName: Subtotal
FieldName: Tax
FieldName: Total
FieldName: VendorName
FieldName: Website
...
Usuwanie modelu z konta zasobu
Możesz również usunąć model z konta, odwołując się do jego identyfikatora. Ten krok zamyka również metodę .
// Delete the model from the account.
trainingClient.DeleteModel(model.ModelId);
}
Uruchamianie aplikacji
Uruchom aplikację z katalogu aplikacji za dotnet run pomocą polecenia .
dotnet run
Czyszczenie zasobów
Jeśli chcesz wyczyścić i usunąć subskrypcję usług Azure AI, możesz usunąć zasób lub grupę zasobów. Usunięcie grupy zasobów powoduje również usunięcie wszelkich innych skojarzonych z nią zasobów.
Rozwiązywanie problemów
W przypadku interakcji z biblioteką klienta usługi Azure AI Document Intelligence przy użyciu zestawu SDK platformy .NET błędy zwracane przez usługę RequestFailedExceptionpowodują wyświetlenie elementu . Zawierają one ten sam kod stanu HTTP, który zostanie zwrócony przez żądanie interfejsu API REST.
Jeśli na przykład przesyłasz obraz potwierdzenia z nieprawidłowym identyfikatorem URI, 400 zostanie zwrócony błąd wskazujący nieprawidłowe żądanie.
try
{
RecognizedReceiptCollection receipts = await client.StartRecognizeReceiptsFromUri(new Uri(receiptUri)).WaitForCompletionAsync();
}
catch (RequestFailedException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
Zauważysz, że rejestrowane są dodatkowe informacje, takie jak identyfikator żądania klienta operacji.
Message:
Azure.RequestFailedException: Service request failed.
Status: 400 (Bad Request)
Content:
{"error":{"code":"FailedToDownloadImage","innerError":
{"requestId":"8ca04feb-86db-4552-857c-fde903251518"},
"message":"Failed to download image from input URL."}}
Headers:
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
x-envoy-upstream-service-time: REDACTED
apim-request-id: REDACTED
Strict-Transport-Security: REDACTED
X-Content-Type-Options: REDACTED
Date: Mon, 20 Apr 2020 22:48:35 GMT
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Następne kroki
W tym projekcie użyto biblioteki klienta analizy dokumentów .NET do trenowania modeli i analizowania formularzy na różne sposoby. Następnie dowiedz się więcej na temat tworzenia lepszego zestawu danych treningowych i tworzenia bardziej dokładnych modeli.
Przykładowy kod dla tego projektu jest dostępny w witrynie GitHub.
Ważne
Ten projekt jest przeznaczony dla interfejsu API REST analizy dokumentów w wersji 2.1.
Dokumentacja referencyjna — pakiet | kodu | źródłowego biblioteki źródłowej (Maven)Samples |
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Bieżąca wersja zestawu Java Development Kit (JDK).
Narzędzie kompilacji narzędzia Gradle lub inny menedżer zależności.
Zasób analizy dokumentów. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Obiekt blob usługi Azure Storage zawierający zestaw danych szkoleniowych. Zobacz Tworzenie i trenowanie niestandardowego modelu , aby uzyskać porady i opcje łączenia zestawu danych treningowych. W tym projekcie można użyć plików w folderze Train (Trenowanie ) przykładowego zestawu danych. Pobierz i wyodrębnij sample_data.zip.
Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Aby skonfigurować środowisko programowania, utwórz projekt Gradle i zainstaluj bibliotekę klienta.
Tworzenie nowego projektu narzędzia Gradle
W oknie konsoli utwórz katalog dla aplikacji i przejdź do niego.
mkdir myapp
cd myapp
gradle init Uruchom polecenie z katalogu roboczego. To polecenie tworzy podstawowe pliki kompilacji dla narzędzia Gradle, w tym build.gradle.kts, które są używane w czasie wykonywania do tworzenia i konfigurowania aplikacji.
gradle init --type basic
Po wyświetleniu monitu o wybranie rozszerzenia DSL wybierz pozycję Kotlin.
Instalowanie biblioteki klienta
W tym projekcie jest używany menedżer zależności narzędzia Gradle. Bibliotekę klienta i informacje dotyczące innych menedżerów zależności można znaleźć w repozytorium centralnym programu Maven.
W pliku build.gradle.kts projektu dołącz bibliotekę klienta jako instrukcję implementation wraz z wymaganymi wtyczkami i ustawieniami.
plugins {
java
application
}
application {
mainClass.set("FormRecognizer")
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation(group = "com.azure", name = "azure-ai-formrecognizer", version = "3.1.1")
}
Tworzenie pliku języka Java
W katalogu roboczym uruchom następujące polecenie:
mkdir -p src/main/java
Przejdź do nowego folderu i utwórz plik o nazwie FormRecognizer.java. Otwórz go w edytorze lub środowisku IDE i dodaj następujące import instrukcje:
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.training.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.models.*;
import com.azure.ai.formrecognizer.training.models.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.http.rest.PagedIterable;
import com.azure.core.util.Context;
import com.azure.core.util.polling.SyncPoller;
W klasie FormRecognizer aplikacji utwórz zmienne dla klucza i punktu końcowego zasobu.
static final String key = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY_HERE";
static final String endpoint = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_ENDPOINT_HERE";
Ważne
Przejdź do portalu Azure Portal. Jeśli zasób analizy dokumentów utworzony w sekcji Wymagania wstępne został wdrożony pomyślnie, w obszarze Następne kroki wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu. Klucz i punkt końcowy można znaleźć w obszarze Zarządzanie zasobami w obszarze Klucze i punkt końcowy.
Pamiętaj, aby usunąć klucz z kodu po zakończeniu. Nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznych metod do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
W metodzie aplikacji main dodaj wywołania metod używanych w tym projekcie. Te wywołania zdefiniujesz później. Należy również dodać odwołania do adresów URL dla danych szkoleniowych i testowych.
Aby pobrać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego dla danych trenowania modelu niestandardowego, przejdź do zasobu magazynu w witrynie Azure Portal i wybierz pozycję Kontenery magazynu>danych.
Przejdź do kontenera, kliknij prawym przyciskiem myszy i wybierz pozycję Generuj sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego.
Pobierz sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego dla kontenera, a nie dla samego konta magazynu.
Upewnij się, że wybrano uprawnienia Odczyt, Zapis, Usuwanie i Lista , a następnie wybierz pozycję Generuj token SAS i adres URL.
Skopiuj wartość w sekcji Adres URL do lokalizacji tymczasowej. Powinna ona mieć postać:
https://<storage account>.blob.core.windows.net/<container name>?<SAS value>.
Aby uzyskać adres URL formularza do przetestowania, możesz użyć powyższych kroków, aby uzyskać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego pojedynczego dokumentu w magazynie obiektów blob. Możesz też pobrać adres URL dokumentu znajdującego się gdzie indziej.
Użyj poprzedniej metody, aby uzyskać również adres URL obrazu potwierdzenia.
String trainingDataUrl = "PASTE_YOUR_SAS_URL_OF_YOUR_FORM_FOLDER_IN_BLOB_STORAGE_HERE";
String formUrl = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_FORM_URL_HERE";
String receiptUrl = "https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/cognitive-services/form-recognizer/media" + "/contoso-allinone.jpg";
String bcUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-python/master/sdk/formrecognizer/azure-ai-formrecognizer/samples/sample_forms/business_cards/business-card-english.jpg";
String invoiceUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-python/master/sdk/formrecognizer/azure-ai-formrecognizer/samples/sample_forms/forms/Invoice_1.pdf";
String idUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/id-license.jpg"
// Call Form Recognizer scenarios:
System.out.println("Get form content...");
GetContent(recognizerClient, formUrl);
System.out.println("Analyze receipt...");
AnalyzeReceipt(recognizerClient, receiptUrl);
System.out.println("Analyze business card...");
AnalyzeBusinessCard(recognizerClient, bcUrl);
System.out.println("Analyze invoice...");
AnalyzeInvoice(recognizerClient, invoiceUrl);
System.out.println("Analyze id...");
AnalyzeId(recognizerClient, idUrl);
System.out.println("Train Model with training data...");
String modelId = TrainModel(trainingClient, trainingDataUrl);
System.out.println("Analyze PDF form...");
AnalyzePdfForm(recognizerClient, modelId, formUrl);
System.out.println("Manage models...");
ManageModels(trainingClient, trainingDataUrl);
Korzystanie z modelu obiektów
Za pomocą analizy dokumentów można utworzyć dwa różne typy klientów. Pierwszy element , FormRecognizerClientwysyła zapytanie do usługi w celu rozpoznawania pól formularzy i zawartości. Drugi element , FormTrainingClienttworzy modele niestandardowe i zarządza nimi w celu poprawy rozpoznawania.
FormRecognizerClient program udostępnia operacje dla następujących zadań:
- Rozpoznawanie pól formularzy i zawartości przy użyciu modeli niestandardowych wytrenowanych do analizowania formularzy niestandardowych. Te wartości są zwracane w kolekcji
RecognizedFormobiektów. Zobacz Analizowanie formularzy niestandardowych. - Rozpoznawanie zawartości formularza, w tym tabel, wierszy i wyrazów bez konieczności trenowania modelu. Zawartość formularza jest zwracana w kolekcji
FormPageobiektów. Zobacz Analizowanie układu. - Rozpoznawanie typowych pól z amerykańskich paragonów, wizytówek, faktur i dokumentów identyfikatorów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu w usłudze Analizy dokumentów.
FormTrainingClient zapewnia następujące operacje:
- Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania wszystkich pól i wartości znalezionych w formularzach niestandardowych. Zwracany
CustomFormModeljest element wskazujący typy formularzy, które model analizuje i pola wyodrębniane dla każdego typu formularza. - Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania określonych pól i wartości określonych przez etykietowanie formularzy niestandardowych. Zwracany jest element ,
CustomFormModelktóry wskazuje pola wyodrębniane przez model i szacowaną dokładność dla każdego pola. - Zarządzanie modelami utworzonymi na koncie.
- Skopiuj model niestandardowy z jednego zasobu analizy dokumentów do innego.
Uwaga
Modele można również wytrenować przy użyciu graficznego interfejsu użytkownika, takiego jak narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego.
Uwierzytelnianie użytkownika
W górnej części main metody dodaj następujący kod. Dwa obiekty klienta są uwierzytelniane przy użyciu zdefiniowanych wcześniej zmiennych subskrypcji. Należy użyć AzureKeyCredential obiektu, aby w razie potrzeby można zaktualizować klucz bez tworzenia nowych obiektów klienta.
FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient = new FormRecognizerClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key)).endpoint(endpoint).buildClient();
FormTrainingClient trainingClient = new FormTrainingClientBuilder().credential(new AzureKeyCredential(key))
.endpoint(endpoint).buildClient();
Analizowanie układu
Analiza dokumentów umożliwia analizowanie tabel, wierszy i słów w dokumentach bez konieczności trenowania modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat wyodrębniania układu, zobacz model układu analizy dokumentów.
Aby przeanalizować zawartość pliku pod danym adresem URL, użyj beginRecognizeContentFromUrl metody .
private static void GetContent(FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient, String invoiceUri) {
String analyzeFilePath = invoiceUri;
SyncPoller<FormRecognizerOperationResult, List<FormPage>> recognizeContentPoller = recognizerClient
.beginRecognizeContentFromUrl(analyzeFilePath);
List<FormPage> contentResult = recognizeContentPoller.getFinalResult();
Napiwek
Możesz również pobrać zawartość z pliku lokalnego. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak beginRecognizeContent. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją FormPage obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej strony w przesłanym dokumencie. Poniższy kod wykonuje iterację po tych obiektach i drukuje wyodrębnione pary klucz/wartość i dane tabeli.
contentResult.forEach(formPage -> {
// Table information
System.out.println("----Recognizing content ----");
System.out.printf("Has width: %f and height: %f, measured with unit: %s.%n", formPage.getWidth(),
formPage.getHeight(), formPage.getUnit());
formPage.getTables().forEach(formTable -> {
System.out.printf("Table has %d rows and %d columns.%n", formTable.getRowCount(),
formTable.getColumnCount());
formTable.getCells().forEach(formTableCell -> {
System.out.printf("Cell has text %s.%n", formTableCell.getText());
});
System.out.println();
});
});
}
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Get form content...
----Recognizing content ----
Has width: 8.500000 and height: 11.000000, measured with unit: inch.
Table has 2 rows and 6 columns.
Cell has text Invoice Number.
Cell has text Invoice Date.
Cell has text Invoice Due Date.
Cell has text Charges.
Cell has text VAT ID.
Cell has text 458176.
Cell has text 3/28/2018.
Cell has text 4/16/2018.
Cell has text $89,024.34.
Cell has text ET.
Analizowanie paragonów
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z amerykańskich paragonów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu paragonu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy paragonów, zobacz Model paragonu analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować wpływy z identyfikatora URI, użyj beginRecognizeReceiptsFromUrl metody .
private static void AnalyzeReceipt(FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient, String receiptUri) {
SyncPoller<FormRecognizerOperationResult, List<RecognizedForm>> syncPoller = recognizerClient
.beginRecognizeReceiptsFromUrl(receiptUri);
List<RecognizedForm> receiptPageResults = syncPoller.getFinalResult();
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy paragonów. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak beginRecognizeReceipts. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją RecognizedReceipt obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej strony w przesłanym dokumencie. Następny blok kodu wykonuje iterację po paragonach i drukuje ich szczegóły w konsoli.
for (int i = 0; i < receiptPageResults.size(); i++) {
RecognizedForm recognizedForm = receiptPageResults.get(i);
Map<String, FormField> recognizedFields = recognizedForm.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Recognized Receipt page %d -----------%n", i);
FormField merchantNameField = recognizedFields.get("MerchantName");
if (merchantNameField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == merchantNameField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String merchantName = merchantNameField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Merchant Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", merchantName,
merchantNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField merchantAddressField = recognizedFields.get("MerchantAddress");
if (merchantAddressField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == merchantAddressField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String merchantAddress = merchantAddressField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Merchant Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", merchantAddress,
merchantAddressField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField transactionDateField = recognizedFields.get("TransactionDate");
if (transactionDateField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.DATE == transactionDateField.getValue().getValueType()) {
LocalDate transactionDate = transactionDateField.getValue().asDate();
System.out.printf("Transaction Date: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", transactionDate,
transactionDateField.getConfidence());
}
}
Następny blok kodu wykonuje iterację po poszczególnych elementach wykrytych na paragonie i wyświetla ich szczegóły w konsoli.
FormField receiptItemsField = recognizedFields.get("Items");
if (receiptItemsField != null) {
System.out.printf("Receipt Items: %n");
if (FieldValueType.LIST == receiptItemsField.getValue().getValueType()) {
List<FormField> receiptItems = receiptItemsField.getValue().asList();
receiptItems.stream()
.filter(receiptItem -> FieldValueType.MAP == receiptItem.getValue().getValueType())
.map(formField -> formField.getValue().asMap())
.forEach(formFieldMap -> formFieldMap.forEach((key, formField) -> {
if ("Name".equals(key)) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == formField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String name = formField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Name: %s, confidence: %.2fs%n", name,
formField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("Quantity".equals(key)) {
if (FieldValueType.FLOAT == formField.getValue().getValueType()) {
Float quantity = formField.getValue().asFloat();
System.out.printf("Quantity: %f, confidence: %.2f%n", quantity,
formField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("Price".equals(key)) {
if (FieldValueType.FLOAT == formField.getValue().getValueType()) {
Float price = formField.getValue().asFloat();
System.out.printf("Price: %f, confidence: %.2f%n", price,
formField.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("TotalPrice".equals(key)) {
if (FieldValueType.FLOAT == formField.getValue().getValueType()) {
Float totalPrice = formField.getValue().asFloat();
System.out.printf("Total Price: %f, confidence: %.2f%n", totalPrice,
formField.getConfidence());
}
}
}));
}
}
}
}
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Analyze receipt...
----------- Recognized Receipt page 0 -----------
Merchant Name: Contoso Contoso, confidence: 0.62
Merchant Address: 123 Main Street Redmond, WA 98052, confidence: 0.99
Transaction Date: 2020-06-10, confidence: 0.90
Receipt Items:
Name: Cappuccino, confidence: 0.96s
Quantity: null, confidence: 0.957s]
Total Price: 2.200000, confidence: 0.95
Name: BACON & EGGS, confidence: 0.94s
Quantity: null, confidence: 0.927s]
Total Price: null, confidence: 0.93
Analizowanie wizytówek
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z angielskich wizytówek przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy wizytówek, zobacz Model wizytówek analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować wizytówki z adresu URL, użyj beginRecognizeBusinessCardsFromUrl metody .
private static void AnalyzeBusinessCard(FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient, String bcUrl) {
SyncPoller < FormRecognizerOperationResult,
List < RecognizedForm >> recognizeBusinessCardPoller = client.beginRecognizeBusinessCardsFromUrl(businessCardUrl);
List < RecognizedForm > businessCardPageResults = recognizeBusinessCardPoller.getFinalResult();
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy wizytówek. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak beginRecognizeBusinessCards. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją RecognizedForm obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej karty w dokumencie. Poniższy kod przetwarza wizytówkę w danym identyfikatorze URI i wyświetla główne pola i wartości w konsoli.
for (int i = 0; i < businessCardPageResults.size(); i++) {
RecognizedForm recognizedForm = businessCardPageResults.get(i);
Map < String,
FormField > recognizedFields = recognizedForm.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Recognized business card info for page %d -----------%n", i);
FormField contactNamesFormField = recognizedFields.get("ContactNames");
if (contactNamesFormField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == contactNamesFormField.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > contactNamesList = contactNamesFormField.getValue().asList();
contactNamesList.stream().filter(contactName - >FieldValueType.MAP == contactName.getValue().getValueType()).map(contactName - >{
System.out.printf("Contact name: %s%n", contactName.getValueData().getText());
return contactName.getValue().asMap();
}).forEach(contactNamesMap - >contactNamesMap.forEach((key, contactName) - >{
if ("FirstName".equals(key)) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == contactName.getValue().getValueType()) {
String firstName = contactName.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("\tFirst Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", firstName, contactName.getConfidence());
}
}
if ("LastName".equals(key)) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == contactName.getValue().getValueType()) {
String lastName = contactName.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("\tLast Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", lastName, contactName.getConfidence());
}
}
}));
}
}
FormField jobTitles = recognizedFields.get("JobTitles");
if (jobTitles != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == jobTitles.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > jobTitlesItems = jobTitles.getValue().asList();
jobTitlesItems.stream().forEach(jobTitlesItem - >{
if (FieldValueType.STRING == jobTitlesItem.getValue().getValueType()) {
String jobTitle = jobTitlesItem.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Job Title: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", jobTitle, jobTitlesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
FormField departments = recognizedFields.get("Departments");
if (departments != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == departments.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > departmentsItems = departments.getValue().asList();
departmentsItems.stream().forEach(departmentsItem - >{
if (FieldValueType.STRING == departmentsItem.getValue().getValueType()) {
String department = departmentsItem.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Department: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", department, departmentsItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
FormField emails = recognizedFields.get("Emails");
if (emails != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == emails.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > emailsItems = emails.getValue().asList();
emailsItems.stream().forEach(emailsItem - >{
if (FieldValueType.STRING == emailsItem.getValue().getValueType()) {
String email = emailsItem.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Email: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", email, emailsItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
FormField websites = recognizedFields.get("Websites");
if (websites != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == websites.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > websitesItems = websites.getValue().asList();
websitesItems.stream().forEach(websitesItem - >{
if (FieldValueType.STRING == websitesItem.getValue().getValueType()) {
String website = websitesItem.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Web site: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", website, websitesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
FormField mobilePhones = recognizedFields.get("MobilePhones");
if (mobilePhones != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == mobilePhones.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > mobilePhonesItems = mobilePhones.getValue().asList();
mobilePhonesItems.stream().forEach(mobilePhonesItem - >{
if (FieldValueType.PHONE_NUMBER == mobilePhonesItem.getValue().getValueType()) {
String mobilePhoneNumber = mobilePhonesItem.getValue().asPhoneNumber();
System.out.printf("Mobile phone number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", mobilePhoneNumber, mobilePhonesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
FormField otherPhones = recognizedFields.get("OtherPhones");
if (otherPhones != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == otherPhones.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > otherPhonesItems = otherPhones.getValue().asList();
otherPhonesItems.stream().forEach(otherPhonesItem - >{
if (FieldValueType.PHONE_NUMBER == otherPhonesItem.getValue().getValueType()) {
String otherPhoneNumber = otherPhonesItem.getValue().asPhoneNumber();
System.out.printf("Other phone number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", otherPhoneNumber, otherPhonesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
FormField faxes = recognizedFields.get("Faxes");
if (faxes != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == faxes.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > faxesItems = faxes.getValue().asList();
faxesItems.stream().forEach(faxesItem - >{
if (FieldValueType.PHONE_NUMBER == faxesItem.getValue().getValueType()) {
String faxPhoneNumber = faxesItem.getValue().asPhoneNumber();
System.out.printf("Fax phone number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", faxPhoneNumber, faxesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
FormField addresses = recognizedFields.get("Addresses");
if (addresses != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == addresses.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > addressesItems = addresses.getValue().asList();
addressesItems.stream().forEach(addressesItem - >{
if (FieldValueType.STRING == addressesItem.getValue().getValueType()) {
String address = addressesItem.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", address, addressesItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
FormField companyName = recognizedFields.get("CompanyNames");
if (companyName != null) {
if (FieldValueType.LIST == companyName.getValue().getValueType()) {
List < FormField > companyNameItems = companyName.getValue().asList();
companyNameItems.stream().forEach(companyNameItem - >{
if (FieldValueType.STRING == companyNameItem.getValue().getValueType()) {
String companyNameValue = companyNameItem.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Company name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", companyNameValue, companyNameItem.getConfidence());
}
});
}
}
}
}
Analizowanie faktur
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z faktur sprzedaży przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy faktur, zobacz Model faktury analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować faktury z adresu URL, użyj beginRecognizeInvoicesFromUrl metody .
private static void AnalyzeInvoice(FormRecognizerClient recognizerClient, String invoiceUrl) {
SyncPoller < FormRecognizerOperationResult,
List < RecognizedForm >> recognizeInvoicesPoller = client.beginRecognizeInvoicesFromUrl(invoiceUrl);
List < RecognizedForm > recognizedInvoices = recognizeInvoicesPoller.getFinalResult();
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować faktury lokalne. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak beginRecognizeInvoices. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją RecognizedForm obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej faktury w dokumencie. Poniższy kod przetwarza fakturę w danym identyfikatorze URI i wyświetla główne pola i wartości w konsoli.
for (int i = 0; i < recognizedInvoices.size(); i++) {
RecognizedForm recognizedInvoice = recognizedInvoices.get(i);
Map < String,
FormField > recognizedFields = recognizedInvoice.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Recognized invoice info for page %d -----------%n", i);
FormField vendorNameField = recognizedFields.get("VendorName");
if (vendorNameField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == vendorNameField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String merchantName = vendorNameField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Vendor Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", merchantName, vendorNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField vendorAddressField = recognizedFields.get("VendorAddress");
if (vendorAddressField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == vendorAddressField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String merchantAddress = vendorAddressField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Vendor address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", merchantAddress, vendorAddressField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField customerNameField = recognizedFields.get("CustomerName");
if (customerNameField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == customerNameField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String merchantAddress = customerNameField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Customer Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", merchantAddress, customerNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField customerAddressRecipientField = recognizedFields.get("CustomerAddressRecipient");
if (customerAddressRecipientField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == customerAddressRecipientField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String customerAddr = customerAddressRecipientField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Customer Address Recipient: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", customerAddr, customerAddressRecipientField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField invoiceIdField = recognizedFields.get("InvoiceId");
if (invoiceIdField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == invoiceIdField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String invoiceId = invoiceIdField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Invoice Id: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", invoiceId, invoiceIdField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField invoiceDateField = recognizedFields.get("InvoiceDate");
if (customerNameField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.DATE == invoiceDateField.getValue().getValueType()) {
LocalDate invoiceDate = invoiceDateField.getValue().asDate();
System.out.printf("Invoice Date: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", invoiceDate, invoiceDateField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField invoiceTotalField = recognizedFields.get("InvoiceTotal");
if (customerAddressRecipientField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.FLOAT == invoiceTotalField.getValue().getValueType()) {
Float invoiceTotal = invoiceTotalField.getValue().asFloat();
System.out.printf("Invoice Total: %.2f, confidence: %.2f%n", invoiceTotal, invoiceTotalField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
}
Analizowanie dokumentów identyfikatorów
W tej sekcji przedstawiono sposób analizowania i wyodrębniania kluczowych informacji z dokumentów identyfikacyjnych wystawionych przez instytucje rządowe — paszportów na całym świecie i licencji kierowców USA przy użyciu wstępnie utworzonego modelu identyfikatora analizy dokumentów. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy dokumentów identyfikatorów, zobacz model dokumentu identyfikatora analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować dokumenty identyfikatorów z identyfikatora URI, użyj beginRecognizeIdentityDocumentsFromUrl metody .
private static void AnalyzeId(FormRecognizerClient client, String idUrl) {
SyncPoller < FormRecognizerOperationResult,
List < RecognizedForm >> analyzeIdentityDocumentPoller = client.beginRecognizeIdentityDocumentsFromUrl(licenseDocumentUrl);
List < RecognizedForm > identityDocumentResults = analyzeIdentityDocumentPoller.getFinalResult();
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy dokumentów identyfikatorów. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak beginRecognizeIdentityDocuments. Zobacz również przykładowy kod w witrynie GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Poniższy kod przetwarza dokument o identyfikatorze w danym identyfikatorze URI i wyświetla główne pola i wartości w konsoli.
for (int i = 0; i < identityDocumentResults.size(); i++) {
RecognizedForm recognizedForm = identityDocumentResults.get(i);
Map < String,
FormField > recognizedFields = recognizedForm.getFields();
System.out.printf("----------- Recognized license info for page %d -----------%n", i);
FormField addressField = recognizedFields.get("Address");
if (addressField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == addressField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String address = addressField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Address: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", address, addressField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField countryRegionFormField = recognizedFields.get("CountryRegion");
if (countryRegionFormField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == countryRegionFormField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String countryRegion = countryRegionFormField.getValue().asCountryRegion();
System.out.printf("Country or region: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", countryRegion, countryRegionFormField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField dateOfBirthField = recognizedFields.get("DateOfBirth");
if (dateOfBirthField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.DATE == dateOfBirthField.getValue().getValueType()) {
LocalDate dateOfBirth = dateOfBirthField.getValue().asDate();
System.out.printf("Date of Birth: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", dateOfBirth, dateOfBirthField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField dateOfExpirationField = recognizedFields.get("DateOfExpiration");
if (dateOfExpirationField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.DATE == dateOfExpirationField.getValue().getValueType()) {
LocalDate expirationDate = dateOfExpirationField.getValue().asDate();
System.out.printf("Document date of expiration: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", expirationDate, dateOfExpirationField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField documentNumberField = recognizedFields.get("DocumentNumber");
if (documentNumberField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == documentNumberField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String documentNumber = documentNumberField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Document number: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", documentNumber, documentNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField firstNameField = recognizedFields.get("FirstName");
if (firstNameField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == firstNameField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String firstName = firstNameField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("First Name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", firstName, documentNumberField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField lastNameField = recognizedFields.get("LastName");
if (lastNameField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == lastNameField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String lastName = lastNameField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Last name: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", lastName, lastNameField.getConfidence());
}
}
FormField regionField = recognizedFields.get("Region");
if (regionField != null) {
if (FieldValueType.STRING == regionField.getValue().getValueType()) {
String region = regionField.getValue().asString();
System.out.printf("Region: %s, confidence: %.2f%n", region, regionField.getConfidence());
}
}
}
Trenowanie modelu niestandardowego
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak wytrenować model przy użyciu własnych danych. Wytrenowany model może wyświetlać dane ustrukturyzowane, które zawierają relacje klucz/wartość w oryginalnym dokumencie. Po wytrenowania modelu można testować, ponownie trenować i w końcu używać go do niezawodnego wyodrębniania danych z większej liczby formularzy zgodnie z potrzebami.
Uwaga
Modele można również trenować za pomocą graficznego interfejsu użytkownika, takiego jak narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów.
Trenowanie modelu bez etykiet
Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania wszystkich pól i wartości znalezionych w formularzach niestandardowych bez ręcznego etykietowania dokumentów szkoleniowych.
Poniższa metoda trenuje model na danym zestawie dokumentów i wyświetla stan modelu w konsoli.
private static String TrainModel(FormTrainingClient trainingClient, String trainingDataUrl) {
SyncPoller<FormRecognizerOperationResult, CustomFormModel> trainingPoller = trainingClient
.beginTraining(trainingDataUrl, false);
CustomFormModel customFormModel = trainingPoller.getFinalResult();
// Model Info
System.out.printf("Model Id: %s%n", customFormModel.getModelId());
System.out.printf("Model Status: %s%n", customFormModel.getModelStatus());
System.out.printf("Training started on: %s%n", customFormModel.getTrainingStartedOn());
System.out.printf("Training completed on: %s%n%n", customFormModel.getTrainingCompletedOn());
Zwrócony CustomFormModel obiekt zawiera informacje na temat typów formularzy, które model może analizować, a pola, które mogą wyodrębniać z każdego typu formularza. Poniższy blok kodu wyświetla te informacje w konsoli programu .
System.out.println("Recognized Fields:");
// looping through the subModels, which contains the fields they were trained on
// Since the given training documents are unlabeled, we still group them but
// they do not have a label.
customFormModel.getSubmodels().forEach(customFormSubmodel -> {
// Since the training data is unlabeled, we are unable to return the accuracy of
// this model
System.out.printf("The subModel has form type %s%n", customFormSubmodel.getFormType());
customFormSubmodel.getFields().forEach((field, customFormModelField) -> System.out
.printf("The model found field '%s' with label: %s%n", field, customFormModelField.getLabel()));
});
Na koniec ta metoda zwraca unikatowy identyfikator modelu.
return customFormModel.getModelId();
}
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Train Model with training data...
Model Id: 20c3544d-97b4-49d9-b39b-dc32d85f1358
Model Status: ready
Training started on: 2020-08-31T16:52:09Z
Training completed on: 2020-08-31T16:52:23Z
Recognized Fields:
The subModel has form type form-0
The model found field 'field-0' with label: Address:
The model found field 'field-1' with label: Charges
The model found field 'field-2' with label: Invoice Date
The model found field 'field-3' with label: Invoice Due Date
The model found field 'field-4' with label: Invoice For:
The model found field 'field-5' with label: Invoice Number
The model found field 'field-6' with label: VAT ID
Trenowanie modelu przy użyciu etykiet
Modele niestandardowe można również trenować, ręcznie oznaczając dokumenty szkoleniowe. Trenowanie z etykietami prowadzi do lepszej wydajności w niektórych scenariuszach. Aby wytrenować za pomocą etykiet, musisz mieć specjalne pliki informacyjne etykiet (<nazwa pliku>.pdf.labels.json) w kontenerze magazynu obiektów blob wraz z dokumentami szkoleniowymi. Narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów udostępnia interfejs użytkownika, który ułatwia tworzenie tych plików etykiet. Po ich otrzymaniu można wywołać metodę beginTraining z parametrem ustawionym useTrainingLabels na true.
private static String TrainModelWithLabels(FormTrainingClient trainingClient, String trainingDataUrl) {
// Train custom model
String trainingSetSource = trainingDataUrl;
SyncPoller<FormRecognizerOperationResult, CustomFormModel> trainingPoller = trainingClient
.beginTraining(trainingSetSource, true);
CustomFormModel customFormModel = trainingPoller.getFinalResult();
// Model Info
System.out.printf("Model Id: %s%n", customFormModel.getModelId());
System.out.printf("Model Status: %s%n", customFormModel.getModelStatus());
System.out.printf("Training started on: %s%n", customFormModel.getTrainingStartedOn());
System.out.printf("Training completed on: %s%n%n", customFormModel.getTrainingCompletedOn());
Zwrócone CustomFormModel pole wskazuje pola, które model może wyodrębnić wraz z szacowaną dokładnością w każdym polu. Poniższy blok kodu wyświetla te informacje w konsoli programu .
// looping through the subModels, which contains the fields they were trained on
// The labels are based on the ones you gave the training document.
System.out.println("Recognized Fields:");
// Since the data is labeled, we are able to return the accuracy of the model
customFormModel.getSubmodels().forEach(customFormSubmodel -> {
System.out.printf("The subModel with form type %s has accuracy: %.2f%n", customFormSubmodel.getFormType(),
customFormSubmodel.getAccuracy());
customFormSubmodel.getFields()
.forEach((label, customFormModelField) -> System.out.printf(
"The model found field '%s' to have name: %s with an accuracy: %.2f%n", label,
customFormModelField.getName(), customFormModelField.getAccuracy()));
});
return customFormModel.getModelId();
}
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Train Model with training data...
Model Id: 20c3544d-97b4-49d9-b39b-dc32d85f1358
Model Status: ready
Training started on: 2020-08-31T16:52:09Z
Training completed on: 2020-08-31T16:52:23Z
Recognized Fields:
The subModel has form type form-0
The model found field 'field-0' with label: Address:
The model found field 'field-1' with label: Charges
The model found field 'field-2' with label: Invoice Date
The model found field 'field-3' with label: Invoice Due Date
The model found field 'field-4' with label: Invoice For:
The model found field 'field-5' with label: Invoice Number
The model found field 'field-6' with label: VAT ID
Analizowanie formularzy przy użyciu modelu niestandardowego
W tej sekcji przedstawiono sposób wyodrębniania informacji o klucz/wartość i innej zawartości z niestandardowych typów szablonów przy użyciu modeli wytrenowanych przy użyciu własnych formularzy.
Ważne
Aby zaimplementować ten scenariusz, musisz mieć już wytrenowany model, aby można było przekazać jego identyfikator do operacji metody. Zobacz Trenowanie modelu z etykietami.
Użyj metody beginRecognizeCustomFormsFromUrl.
// Analyze PDF form data
private static void AnalyzePdfForm(FormRecognizerClient formClient, String modelId, String pdfFormUrl) {
SyncPoller<FormRecognizerOperationResult, List<RecognizedForm>> recognizeFormPoller = formClient
.beginRecognizeCustomFormsFromUrl(modelId, pdfFormUrl);
List<RecognizedForm> recognizedForms = recognizeFormPoller.getFinalResult();
Napiwek
Możesz również przeanalizować plik lokalny. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak beginRecognizeCustomForms. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami, które obejmują obrazy lokalne.
Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją RecognizedForm obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej strony w przesłanym dokumencie. Poniższy kod wyświetla wyniki analizy w konsoli programu . Drukuje każde rozpoznane pole i odpowiadającą mu wartość wraz z współczynnikiem ufności.
for (int i = 0; i < recognizedForms.size(); i++) {
final RecognizedForm form = recognizedForms.get(i);
System.out.printf("----------- Recognized custom form info for page %d -----------%n", i);
System.out.printf("Form type: %s%n", form.getFormType());
form.getFields().forEach((label, formField) ->
// label data is populated if you are using a model trained with unlabeled data,
// since the service needs to make predictions for labels if not explicitly
// given to it.
System.out.printf("Field '%s' has label '%s' with a confidence " + "score of %.2f.%n", label,
formField.getLabelData().getText(), formField.getConfidence()));
}
}
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Analyze PDF form...
----------- Recognized custom template info for page 0 -----------
Form type: form-0
Field 'field-0' has label 'Address:' with a confidence score of 0.91.
Field 'field-1' has label 'Invoice For:' with a confidence score of 1.00.
Field 'field-2' has label 'Invoice Number' with a confidence score of 1.00.
Field 'field-3' has label 'Invoice Date' with a confidence score of 1.00.
Field 'field-4' has label 'Invoice Due Date' with a confidence score of 1.00.
Field 'field-5' has label 'Charges' with a confidence score of 1.00.
Field 'field-6' has label 'VAT ID' with a confidence score of 1.00.
Zarządzanie modelami niestandardowymi
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak zarządzać modelami niestandardowymi przechowywanymi na koncie. Poniższy kod wykonuje wszystkie zadania zarządzania modelami w jednej metodzie, na przykład. Zacznij od skopiowania następującej sygnatury metody:
private static void ManageModels(FormTrainingClient trainingClient, String trainingFileUrl) {
Sprawdzanie liczby modeli na koncie zasobu FormRecognizer
Poniższy blok kodu sprawdza liczbę modeli zapisanych na koncie analizy dokumentów i porównuje je z limitem konta.
AtomicReference<String> modelId = new AtomicReference<>();
// First, we see how many custom models we have, and what our limit is
AccountProperties accountProperties = trainingClient.getAccountProperties();
System.out.printf("The account has %s custom models, and we can have at most %s custom models",
accountProperties.getCustomModelCount(), accountProperties.getCustomModelLimit());
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
The account has 12 custom models, and we can have at most 250 custom models
Wyświetlanie listy modeli aktualnie przechowywanych na koncie zasobu
Poniższy kod blokuje bieżące modele na twoim koncie i wyświetla ich szczegóły w konsoli.
// Next, we get a paged list of all of our custom models
PagedIterable<CustomFormModelInfo> customModels = trainingClient.listCustomModels();
System.out.println("We have following models in the account:");
customModels.forEach(customFormModelInfo -> {
System.out.printf("Model Id: %s%n", customFormModelInfo.getModelId());
// get custom model info
modelId.set(customFormModelInfo.getModelId());
CustomFormModel customModel = trainingClient.getCustomModel(customFormModelInfo.getModelId());
System.out.printf("Model Id: %s%n", customModel.getModelId());
System.out.printf("Model Status: %s%n", customModel.getModelStatus());
System.out.printf("Training started on: %s%n", customModel.getTrainingStartedOn());
System.out.printf("Training completed on: %s%n", customModel.getTrainingCompletedOn());
customModel.getSubmodels().forEach(customFormSubmodel -> {
System.out.printf("Custom Model Form type: %s%n", customFormSubmodel.getFormType());
System.out.printf("Custom Model Accuracy: %.2f%n", customFormSubmodel.getAccuracy());
if (customFormSubmodel.getFields() != null) {
customFormSubmodel.getFields().forEach((fieldText, customFormModelField) -> {
System.out.printf("Field Text: %s%n", fieldText);
System.out.printf("Field Accuracy: %.2f%n", customFormModelField.getAccuracy());
});
}
});
});
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Ta odpowiedź została obcięta w celu zapewnienia czytelności.
We have following models in the account:
Model Id: 0b048b60-86cc-47ec-9782-ad0ffaf7a5ce
Model Id: 0b048b60-86cc-47ec-9782-ad0ffaf7a5ce
Model Status: ready
Training started on: 2020-06-04T18:33:08Z
Training completed on: 2020-06-04T18:33:10Z
Custom Model Form type: form-0b048b60-86cc-47ec-9782-ad0ffaf7a5ce
Custom Model Accuracy: 1.00
Field Text: invoice date
Field Accuracy: 1.00
Field Text: invoice number
Field Accuracy: 1.00
...
Usuwanie modelu z konta zasobu
Możesz również usunąć model z konta, odwołując się do jego identyfikatora.
// Delete Custom Model
System.out.printf("Deleted model with model Id: %s, operation completed with status: %s%n", modelId.get(),
trainingClient.deleteModelWithResponse(modelId.get(), Context.NONE).getStatusCode());
}
Uruchamianie aplikacji
Wróć do głównego katalogu projektu. Następnie skompiluj aplikację za pomocą następującego polecenia:
gradle build
Uruchom aplikację z run celem:
gradle run
Czyszczenie zasobów
Jeśli chcesz wyczyścić i usunąć subskrypcję usług Azure AI, możesz usunąć zasób lub grupę zasobów. Usunięcie grupy zasobów powoduje również usunięcie wszelkich innych skojarzonych z nią zasobów.
Rozwiązywanie problemów
Klienci analizy dokumentów zgłaszają ErrorResponseException wyjątki. Jeśli na przykład spróbujesz podać nieprawidłowy adres URL źródła pliku, ErrorResponseException zostanie zgłoszony błąd wskazujący przyczynę błędu. W poniższym fragmencie kodu błąd jest obsługiwany bezpiecznie przez przechwycenie wyjątku i wyświetlenie dodatkowych informacji o błędzie.
try {
formRecognizerClient.beginRecognizeContentFromUrl("invalidSourceUrl");
} catch (ErrorResponseException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
Włączanie rejestrowania klientów
Zestawy SDK platformy Azure dla języka Java oferują spójny scenariusz rejestrowania, który pomaga w rozwiązywaniu problemów z błędami aplikacji i przyspieszaniu ich rozwiązywania. Dzienniki utworzone przechwytują przepływ aplikacji przed dotarciem do stanu terminalu, aby ułatwić zlokalizowanie głównego problemu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat włączania rejestrowania, zobacz witrynę typu wiki rejestrowania.
Następne kroki
W tym projekcie użyto biblioteki klienta Języka Java analizy dokumentów do trenowania modeli i analizowania formularzy na różne sposoby. Następnie dowiedz się więcej na temat tworzenia lepszego zestawu danych treningowych i tworzenia bardziej dokładnych modeli.
Przykładowy kod dla tego projektu można znaleźć w witrynie GitHub.
Ważne
Ten projekt jest przeznaczony dla interfejsu API REST analizy dokumentów w wersji 2.1.
Dokumentacja referencyjna — przykłady | pakietu kodu | źródłowego biblioteki źródłowej (npm)Samples |
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Najnowsza wersja programu Visual Studio Code.
Najnowsza wersja LTS Node.js.
Obiekt blob usługi Azure Storage zawierający zestaw danych szkoleniowych. Zobacz Tworzenie i trenowanie niestandardowego modelu , aby uzyskać porady i opcje łączenia zestawu danych treningowych. W tym projekcie możesz użyć plików w folderze Train (Trenowanie ) przykładowego zestawu danych. Pobierz i wyodrębnij sample_data.zip.
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz zasób analizy dokumentów. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Utwórz aplikację i zainstaluj bibliotekę klienta.
Tworzenie nowej aplikacji Node.js
W oknie konsoli utwórz katalog dla aplikacji i przejdź do niego.
mkdir myapp cd myappUruchom polecenie ,
npm initaby utworzyć aplikację węzła z plikiem package.json .npm init
Instalowanie biblioteki klienta
ai-form-recognizerZainstaluj pakiet npm:npm install @azure/ai-form-recognizerPlik package.json aplikacji jest aktualizowany przy użyciu zależności.
Utwórz plik o nazwie index.js, otwórz go i zaimportuj następujące biblioteki:
const { FormRecognizerClient, FormTrainingClient, AzureKeyCredential } = require("@azure/ai-form-recognizer"); const fs = require("fs");Utwórz zmienne dla klucza i punktu końcowego platformy Azure zasobu.
const apiKey = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY_HERE"; const endpoint = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_ENDPOINT_HERE";
Ważne
Przejdź do portalu Azure Portal. Jeśli zasób analizy dokumentów utworzony w sekcji Wymagania wstępne został wdrożony pomyślnie, w obszarze Następne kroki wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu. Klucz i punkt końcowy można znaleźć w obszarze Zarządzanie zasobami w obszarze Klucze i punkt końcowy.
Pamiętaj, aby usunąć klucz z kodu po zakończeniu. Nigdy nie publikuj go publicznie. W przypadku środowiska produkcyjnego użyj bezpiecznych metod do przechowywania poświadczeń i uzyskiwania do nich dostępu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zabezpieczenia usług Azure AI.
Korzystanie z modelu obiektów
Za pomocą analizy dokumentów można utworzyć dwa różne typy klientów. Pierwszy element , FormRecognizerClientwysyła zapytanie do usługi w celu rozpoznawania pól formularzy i zawartości. Drugi element , FormTrainingClienttworzy modele niestandardowe i zarządza nimi w celu poprawy rozpoznawania.
FormRecognizerClient udostępnia następujące operacje:
- Rozpoznawanie pól formularzy i zawartości przy użyciu modeli niestandardowych wytrenowanych do analizowania formularzy niestandardowych. Te wartości są zwracane w kolekcji
RecognizedFormobiektów. - Rozpoznawanie zawartości formularza, w tym tabel, wierszy i wyrazów bez konieczności trenowania modelu. Zawartość formularza jest zwracana w kolekcji
FormPageobiektów. - Rozpoznawanie typowych pól z amerykańskich paragonów, wizytówek, faktur i dokumentów identyfikatorów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu w usłudze Analizy dokumentów.
FormTrainingClient zapewnia następujące operacje:
- Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania wszystkich pól i wartości znalezionych w formularzach niestandardowych. Zwracany
CustomFormModeljest element wskazujący typy formularzy, które model analizuje i pola wyodrębniane dla każdego typu formularza. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz dokumentację usługi dotyczącą trenowania modelu bez etykiet. - Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania określonych pól i wartości określonych przez etykietowanie formularzy niestandardowych. Zwracany jest element ,
CustomFormModelktóry wskazuje pola wyodrębniane przez model i szacowaną dokładność dla każdego pola. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Trenowanie modelu z etykietami w tym artykule. - Zarządzanie modelami utworzonymi na koncie.
- Skopiuj model niestandardowy z jednego zasobu analizy dokumentów do innego.
Uwaga
Modele można również wytrenować przy użyciu graficznego interfejsu użytkownika, takiego jak narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego.
Uwierzytelnianie użytkownika
Uwierzytelnianie obiektu klienta przy użyciu zdefiniowanych zmiennych subskrypcji. AzureKeyCredential Użyj obiektu, aby w razie potrzeby można zaktualizować klucz bez tworzenia nowych obiektów klienta. Utworzysz również obiekt klienta trenowania.
const trainingClient = new FormTrainingClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(apiKey));
const client = new FormRecognizerClient(endpoint, new AzureKeyCredential(apiKey));
Pobieranie zasobów na potrzeby testowania
Należy również dodać odwołania do adresów URL dla danych szkoleniowych i testowych.
Aby pobrać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego dla danych trenowania modelu niestandardowego, przejdź do zasobu magazynu w witrynie Azure Portal i wybierz pozycję Kontenery magazynu>danych.
Przejdź do kontenera, kliknij prawym przyciskiem myszy i wybierz pozycję Generuj sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego.
Pobierz sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego dla kontenera, a nie dla samego konta magazynu.
Upewnij się, że wybrano uprawnienia Odczyt, Zapis, Usuwanie i Lista , a następnie wybierz pozycję Generuj token SAS i adres URL.
Skopiuj wartość w sekcji Adres URL do lokalizacji tymczasowej. Powinna ona mieć postać:
https://<storage account>.blob.core.windows.net/<container name>?<SAS value>.
Użyj przykładu z obrazów i paragonów zawartych w przykładach. Te obrazy są również dostępne w witrynie GitHub. Aby uzyskać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego pojedynczego dokumentu w magazynie obiektów blob, możesz użyć powyższych kroków.
Analizowanie układu
Analiza dokumentów umożliwia analizowanie tabel, wierszy i słów w dokumentach bez konieczności trenowania modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat wyodrębniania układu, zobacz model układu analizy dokumentów. Aby przeanalizować zawartość pliku w danym identyfikatorze URI, użyj beginRecognizeContentFromUrl metody .
async function recognizeContent() {
const formUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/simple-invoice.png";
const poller = await client.beginRecognizeContentFromUrl(formUrl);
const pages = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (!pages || pages.length === 0) {
throw new Error("Expecting non-empty list of pages!");
}
for (const page of pages) {
console.log(
`Page ${page.pageNumber}: width ${page.width} and height ${page.height} with unit ${page.unit}`
);
for (const table of page.tables) {
for (const cell of table.cells) {
console.log(`cell [${cell.rowIndex},${cell.columnIndex}] has text ${cell.text}`);
}
}
}
}
recognizeContent().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Napiwek
Możesz również pobrać zawartość z pliku lokalnego za pomocą metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak beginRecognizeContent.
Page 1: width 8.5 and height 11 with unit inch
cell [0,0] has text Invoice Number
cell [0,1] has text Invoice Date
cell [0,2] has text Invoice Due Date
cell [0,3] has text Charges
cell [0,5] has text VAT ID
cell [1,0] has text 34278587
cell [1,1] has text 6/18/2017
cell [1,2] has text 6/24/2017
cell [1,3] has text $56,651.49
cell [1,5] has text PT
Analizowanie paragonów
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z amerykańskich paragonów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu paragonu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy paragonów, zobacz Model paragonu analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować wpływy z identyfikatora URI, użyj beginRecognizeReceiptsFromUrl metody . Poniższy kod przetwarza potwierdzenie dla danego identyfikatora URI i wyświetla główne pola i wartości w konsoli.
async function recognizeReceipt() {
receiptUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-python/master/sdk/formrecognizer/azure-ai-formrecognizer/tests/sample_forms/receipt/contoso-receipt.png";
const poller = await client.beginRecognizeReceiptsFromUrl(receiptUrl, {
onProgress: (state) => { console.log(`status: ${state.status}`); }
});
const receipts = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (!receipts || receipts.length <= 0) {
throw new Error("Expecting at lease one receipt in analysis result");
}
const receipt = receipts[0];
console.log("First receipt:");
const receiptTypeField = receipt.fields["ReceiptType"];
if (receiptTypeField.valueType === "string") {
console.log(` Receipt Type: '${receiptTypeField.value || "<missing>"}', with confidence of ${receiptTypeField.confidence}`);
}
const merchantNameField = receipt.fields["MerchantName"];
if (merchantNameField.valueType === "string") {
console.log(` Merchant Name: '${merchantNameField.value || "<missing>"}', with confidence of ${merchantNameField.confidence}`);
}
const transactionDate = receipt.fields["TransactionDate"];
if (transactionDate.valueType === "date") {
console.log(` Transaction Date: '${transactionDate.value || "<missing>"}', with confidence of ${transactionDate.confidence}`);
}
const itemsField = receipt.fields["Items"];
if (itemsField.valueType === "array") {
for (const itemField of itemsField.value || []) {
if (itemField.valueType === "object") {
const itemNameField = itemField.value["Name"];
if (itemNameField.valueType === "string") {
console.log(` Item Name: '${itemNameField.value || "<missing>"}', with confidence of ${itemNameField.confidence}`);
}
}
}
}
const totalField = receipt.fields["Total"];
if (totalField.valueType === "number") {
console.log(` Total: '${totalField.value || "<missing>"}', with confidence of ${totalField.confidence}`);
}
}
recognizeReceipt().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy paragonów za pomocą metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak beginRecognizeReceipts.
status: notStarted
status: running
status: succeeded
First receipt:
Receipt Type: 'Itemized', with confidence of 0.659
Merchant Name: 'Contoso Contoso', with confidence of 0.516
Transaction Date: 'Sun Jun 09 2019 17:00:00 GMT-0700 (Pacific Daylight Time)', with confidence of 0.985
Item Name: '8GB RAM (Black)', with confidence of 0.916
Item Name: 'SurfacePen', with confidence of 0.858
Total: '1203.39', with confidence of 0.774
Analizowanie wizytówek
W tej sekcji przedstawiono sposób analizowania i wyodrębniania typowych pól z wizytówek w języku angielskim przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy wizytówek, zobacz Model wizytówek analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować wizytówki z adresu URL, użyj beginRecognizeBusinessCardsFromURL metody .
async function recognizeBusinessCards() {
bcUrl = "https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/curl/form-recognizer/businessCard.png";
const poller = await client.beginRecognizeBusinessCardsFromUrl(bcUrl, {
onProgress: (state) => {
console.log(`status: ${state.status}`);
}
});
const [businessCard] = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (businessCard === undefined) {
throw new Error("Failed to extract data from at least one business card.");
}
const contactNames = businessCard.fields["ContactNames"].value;
if (Array.isArray(contactNames)) {
console.log("- Contact Names:");
for (const contactName of contactNames) {
if (contactName.valueType === "object") {
const firstName = contactName.value?.["FirstName"].value ?? "<no first name>";
const lastName = contactName.value?.["LastName"].value ?? "<no last name>";
console.log(` - ${firstName} ${lastName} (${contactName.confidence} confidence)`);
}
}
}
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "CompanyNames");
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "Departments");
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "JobTitles");
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "Emails");
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "Websites");
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "Addresses");
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "MobilePhones");
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "Faxes");
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "WorkPhones");
printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, "OtherPhones");
}
// Helper function to print array field values.
function printSimpleArrayField(businessCard, fieldName) {
const fieldValues = businessCard.fields[fieldName]?.value;
if (Array.isArray(fieldValues)) {
console.log(`- ${fieldName}:`);
for (const item of fieldValues) {
console.log(` - ${item.value ?? "<no value>"} (${item.confidence} confidence)`);
}
} else if (fieldValues === undefined) {
console.log(`No ${fieldName} were found in the document.`);
} else {
console.error(
`Error: expected field "${fieldName}" to be an Array, but it was a(n) ${businessCard.fields[fieldName].valueType}`
);
}
}
recognizeBusinessCards().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy wizytówek za pomocą metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak beginRecognizeBusinessCards.
Analizowanie faktur
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z faktur sprzedaży przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy faktur, zobacz Model faktury analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować faktury z adresu URL, użyj beginRecognizeInvoicesFromUrl metody .
async function recognizeInvoices() {
invoiceUrl = "https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/curl/form-recognizer/invoice_sample.jpg";
const poller = await client.beginRecognizeInvoicesFromUrl(invoiceUrl, {
onProgress: (state) => {
console.log(`status: ${state.status}`);
}
});
const [invoice] = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (invoice === undefined) {
throw new Error("Failed to extract data from at least one invoice.");
}
// Helper function to print fields.
function fieldToString(field) {
const {
name,
valueType,
value,
confidence
} = field;
return `${name} (${valueType}): '${value}' with confidence ${confidence}'`;
}
console.log("Invoice fields:");
for (const [name, field] of Object.entries(invoice.fields)) {
if (field.valueType !== "array" && field.valueType !== "object") {
console.log(`- ${name} ${fieldToString(field)}`);
}
}
let idx = 0;
console.log("- Items:");
const items = invoice.fields["Items"]?.value;
for (const item of items ?? []) {
const value = item.value;
const subFields = [
"Description",
"Quantity",
"Unit",
"UnitPrice",
"ProductCode",
"Date",
"Tax",
"Amount"
]
.map((fieldName) => value[fieldName])
.filter((field) => field !== undefined);
console.log(
[
` - Item #${idx}`,
// Now we will convert those fields into strings to display
...subFields.map((field) => ` - ${fieldToString(field)}`)
].join("\n")
);
}
}
recognizeInvoices().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy paragonów za pomocą metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak beginRecognizeInvoices.
Analizowanie dokumentów identyfikatorów
W tej sekcji przedstawiono sposób analizowania i wyodrębniania kluczowych informacji z dokumentów identyfikacyjnych wystawionych przez instytucje rządowe, w tym paszportów na całym świecie i licencji kierowców USA, przy użyciu wstępnie utworzonego modelu identyfikatora analizy dokumentów. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy dokumentów identyfikatorów, zobacz model dokumentu identyfikatora analizy dokumentów.
Aby przeanalizować dokumenty identyfikatorów z adresu URL, użyj beginRecognizeIdDocumentsFromUrl metody .
async function recognizeIdDocuments() {
idUrl = "https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/curl/form-recognizer/id-license.jpg";
const poller = await client.beginRecognizeIdDocumentsFromUrl(idUrl, {
onProgress: (state) => {
console.log(`status: ${state.status}`);
}
});
const [idDocument] = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (idDocument === undefined) {
throw new Error("Failed to extract data from at least one identity document.");
}
console.log("Document Type:", idDocument.formType);
console.log("Identity Document Fields:");
function printField(fieldName) {
// Fields are extracted from the `fields` property of the document result
const field = idDocument.fields[fieldName];
console.log(
`- ${fieldName} (${field?.valueType}): '${field?.value ?? "<missing>"}', with confidence ${field?.confidence
}`
);
}
printField("FirstName");
printField("LastName");
printField("DocumentNumber");
printField("DateOfBirth");
printField("DateOfExpiration");
printField("Sex");
printField("Address");
printField("Country");
printField("Region");
}
recognizeIdDocuments().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Trenowanie modelu niestandardowego
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak wytrenować model przy użyciu własnych danych. Wytrenowany model może wyświetlać dane ustrukturyzowane, które zawierają relacje klucz/wartość w oryginalnym dokumencie. Po wytrenowania modelu można testować, ponownie trenować i w końcu używać go do niezawodnego wyodrębniania danych z większej liczby formularzy zgodnie z potrzebami.
Uwaga
Modele można również trenować za pomocą graficznego interfejsu użytkownika (GUI), takiego jak narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów.
Trenowanie modelu bez etykiet
Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania wszystkich pól i wartości znalezionych w formularzach niestandardowych bez ręcznego etykietowania dokumentów szkoleniowych.
Poniższa funkcja trenuje model na danym zestawie dokumentów i drukuje stan modelu w konsoli.
async function trainModel() {
const containerSasUrl = "<SAS-URL-of-your-form-folder-in-blob-storage>";
const poller = await trainingClient.beginTraining(containerSasUrl, false, {
onProgress: (state) => { console.log(`training status: ${state.status}`); }
});
const model = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (!model) {
throw new Error("Expecting valid training result!");
}
console.log(`Model ID: ${model.modelId}`);
console.log(`Status: ${model.status}`);
console.log(`Training started on: ${model.trainingStartedOn}`);
console.log(`Training completed on: ${model.trainingCompletedOn}`);
if (model.submodels) {
for (const submodel of model.submodels) {
// since the training data is unlabeled, we are unable to return the accuracy of this model
console.log("We have recognized the following fields");
for (const key in submodel.fields) {
const field = submodel.fields[key];
console.log(`The model found field '${field.name}'`);
}
}
}
// Training document information
if (model.trainingDocuments) {
for (const doc of model.trainingDocuments) {
console.log(`Document name: ${doc.name}`);
console.log(`Document status: ${doc.status}`);
console.log(`Document page count: ${doc.pageCount}`);
console.log(`Document errors: ${doc.errors}`);
}
}
}
trainModel().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Poniżej przedstawiono dane wyjściowe dla modelu trenowanego przy użyciu danych szkoleniowych dostępnych w zestawie SDK języka JavaScript. Ten przykładowy wynik został obcięty pod kątem czytelności.
training status: creating
training status: ready
Model ID: 9d893595-1690-4cf2-a4b1-fbac0fb11909
Status: ready
Training started on: Thu Aug 20 2020 20:27:26 GMT-0700 (Pacific Daylight Time)
Training completed on: Thu Aug 20 2020 20:27:37 GMT-0700 (Pacific Daylight Time)
We have recognized the following fields
The model found field 'field-0'
The model found field 'field-1'
The model found field 'field-2'
The model found field 'field-3'
The model found field 'field-4'
The model found field 'field-5'
The model found field 'field-6'
The model found field 'field-7'
...
Document name: Form_1.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors:
Document name: Form_2.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors:
Document name: Form_3.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors:
...
Trenowanie modelu przy użyciu etykiet
Modele niestandardowe można również trenować, ręcznie oznaczając dokumenty szkoleniowe. Trenowanie z etykietami prowadzi do lepszej wydajności w niektórych scenariuszach. Aby wytrenować za pomocą etykiet, musisz mieć specjalne pliki informacyjne etykiet (<nazwa pliku>.pdf.labels.json) w kontenerze magazynu obiektów blob wraz z dokumentami szkoleniowymi. Narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów udostępnia interfejs użytkownika, który ułatwia tworzenie tych plików etykiet. Po ich otrzymaniu można wywołać metodę beginTraining z parametrem ustawionym uselabels na true.
async function trainModelLabels() {
const containerSasUrl = "<SAS-URL-of-your-form-folder-in-blob-storage>";
const poller = await trainingClient.beginTraining(containerSasUrl, true, {
onProgress: (state) => { console.log(`training status: ${state.status}`); }
});
const model = await poller.pollUntilDone();
if (!model) {
throw new Error("Expecting valid training result!");
}
console.log(`Model ID: ${model.modelId}`);
console.log(`Status: ${model.status}`);
console.log(`Training started on: ${model.trainingStartedOn}`);
console.log(`Training completed on: ${model.trainingCompletedOn}`);
if (model.submodels) {
for (const submodel of model.submodels) {
// since the training data is unlabeled, we are unable to return the accuracy of this model
console.log("We have recognized the following fields");
for (const key in submodel.fields) {
const field = submodel.fields[key];
console.log(`The model found field '${field.name}'`);
}
}
}
// Training document information
if (model.trainingDocuments) {
for (const doc of model.trainingDocuments) {
console.log(`Document name: ${doc.name}`);
console.log(`Document status: ${doc.status}`);
console.log(`Document page count: ${doc.pageCount}`);
console.log(`Document errors: ${doc.errors}`);
}
}
}
trainModelLabels().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Poniżej przedstawiono dane wyjściowe dla modelu trenowanego przy użyciu danych szkoleniowych dostępnych w zestawie SDK języka JavaScript. Ten przykładowy wynik został obcięty pod kątem czytelności.
training status: creating
training status: ready
Model ID: 789b1b37-4cc3-4e36-8665-9dde68618072
Status: ready
Training started on: Thu Aug 20 2020 20:30:37 GMT-0700 (Pacific Daylight Time)
Training completed on: Thu Aug 20 2020 20:30:43 GMT-0700 (Pacific Daylight Time)
We have recognized the following fields
The model found field 'CompanyAddress'
The model found field 'CompanyName'
The model found field 'CompanyPhoneNumber'
The model found field 'DatedAs'
...
Document name: Form_1.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: undefined
Document name: Form_2.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: undefined
Document name: Form_3.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: undefined
...
Analizowanie formularzy przy użyciu modelu niestandardowego
W tej sekcji przedstawiono sposób wyodrębniania informacji o klucz/wartość i innej zawartości z niestandardowych typów szablonów przy użyciu modeli wytrenowanych przy użyciu własnych formularzy.
Ważne
Aby zaimplementować ten scenariusz, musisz mieć już wytrenowany model, aby można było przekazać jego identyfikator do operacji metody. Zobacz sekcję Train a model (Trenowanie modelu ).
Należy użyć beginRecognizeCustomFormsFromUrl metody . Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją RecognizedForm obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej strony w przesłanym dokumencie.
async function recognizeCustom() {
// Model ID from when you trained your model.
const modelId = "<modelId>";
const formUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/simple-invoice.png";
const poller = await client.beginRecognizeCustomForms(modelId, formUrl, {
onProgress: (state) => { console.log(`status: ${state.status}`); }
});
const forms = await poller.pollUntilDone();
console.log("Forms:");
for (const form of forms || []) {
console.log(`${form.formType}, page range: ${form.pageRange}`);
console.log("Pages:");
for (const page of form.pages || []) {
console.log(`Page number: ${page.pageNumber}`);
console.log("Tables");
for (const table of page.tables || []) {
for (const cell of table.cells) {
console.log(`cell (${cell.rowIndex},${cell.columnIndex}) ${cell.text}`);
}
}
}
console.log("Fields:");
for (const fieldName in form.fields) {
// each field is of type FormField
const field = form.fields[fieldName];
console.log(
`Field ${fieldName} has value '${field.value}' with a confidence score of ${field.confidence}`
);
}
}
}
recognizeCustom().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować pliki lokalne za pomocą metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak beginRecognizeCustomForms.
status: notStarted
status: succeeded
Forms:
custom:form, page range: [object Object]
Pages:
Page number: 1
Tables
cell (0,0) Invoice Number
cell (0,1) Invoice Date
cell (0,2) Invoice Due Date
cell (0,3) Charges
cell (0,5) VAT ID
cell (1,0) 34278587
cell (1,1) 6/18/2017
cell (1,2) 6/24/2017
cell (1,3) $56,651.49
cell (1,5) PT
Fields:
Field Merchant has value 'Invoice For:' with a confidence score of 0.116
Field CompanyPhoneNumber has value '$56,651.49' with a confidence score of 0.249
Field VendorName has value 'Charges' with a confidence score of 0.145
Field CompanyAddress has value '1 Redmond way Suite 6000 Redmond, WA' with a confidence score of 0.258
Field CompanyName has value 'PT' with a confidence score of 0.245
Field Website has value '99243' with a confidence score of 0.114
Field DatedAs has value 'undefined' with a confidence score of undefined
Field Email has value 'undefined' with a confidence score of undefined
Field PhoneNumber has value 'undefined' with a confidence score of undefined
Field PurchaseOrderNumber has value 'undefined' with a confidence score of undefined
Field Quantity has value 'undefined' with a confidence score of undefined
Field Signature has value 'undefined' with a confidence score of undefined
Field Subtotal has value 'undefined' with a confidence score of undefined
Field Tax has value 'undefined' with a confidence score of undefined
Field Total has value 'undefined' with a confidence score of undefined
Zarządzanie modelami niestandardowymi
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak zarządzać modelami niestandardowymi przechowywanymi na koncie. Poniższy kod wykonuje wszystkie zadania zarządzania modelami w jednej funkcji, na przykład.
Pobieranie liczby modeli
Poniższy blok kodu pobiera liczbę modeli aktualnie na twoim koncie.
async function countModels() {
// First, we see how many custom models we have, and what our limit is
const accountProperties = await trainingClient.getAccountProperties();
console.log(
`Our account has ${accountProperties.customModelCount} custom models, and we can have at most ${accountProperties.customModelLimit} custom models`
);
}
countModels().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Pobieranie listy modeli na koncie
Poniższy blok kodu zawiera pełną listę dostępnych modeli na twoim koncie, w tym informacje o tym, kiedy model został utworzony i jego bieżący stan.
async function listModels() {
// returns an async iteratable iterator that supports paging
const result = trainingClient.listCustomModels();
let i = 0;
for await (const modelInfo of result) {
console.log(`model ${i++}:`);
console.log(modelInfo);
}
}
listModels().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
model 0:
{
modelId: '453cc2e6-e3eb-4e9f-aab6-e1ac7b87e09e',
status: 'invalid',
trainingStartedOn: 2020-08-20T22:28:52.000Z,
trainingCompletedOn: 2020-08-20T22:28:53.000Z
}
model 1:
{
modelId: '628739de-779c-473d-8214-d35c72d3d4f7',
status: 'ready',
trainingStartedOn: 2020-08-20T23:16:51.000Z,
trainingCompletedOn: 2020-08-20T23:16:59.000Z
}
model 2:
{
modelId: '789b1b37-4cc3-4e36-8665-9dde68618072',
status: 'ready',
trainingStartedOn: 2020-08-21T03:30:37.000Z,
trainingCompletedOn: 2020-08-21T03:30:43.000Z
}
model 3:
{
modelId: '9d893595-1690-4cf2-a4b1-fbac0fb11909',
status: 'ready',
trainingStartedOn: 2020-08-21T03:27:26.000Z,
trainingCompletedOn: 2020-08-21T03:27:37.000Z
}
Pobieranie listy identyfikatorów modeli według strony
Ten blok kodu zawiera listę podzielonych na strony modeli i identyfikatorów modeli.
async function listModelsByPage() {
// using `byPage()`
i = 1;
for await (const response of trainingClient.listCustomModels().byPage()) {
for (const modelInfo of response.modelList) {
console.log(`model ${i++}: ${modelInfo.modelId}`);
}
}
}
listModelsByPage().catch((err) => {
console.error("The sample encountered an error:", err);
});
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
model 1: 453cc2e6-e3eb-4e9f-aab6-e1ac7b87e09e
model 2: 628739de-779c-473d-8214-d35c72d3d4f7
model 3: 789b1b37-4cc3-4e36-8665-9dde68618072
Pobieranie modelu według identyfikatora
Poniższa funkcja przyjmuje identyfikator modelu i pobiera pasujący obiekt modelu. Ta funkcja nie jest domyślnie wywoływana.
async function getModel(modelId) {
// Now we'll get the first custom model in the paged list
const model = await client.getCustomModel(modelId);
console.log("--- First Custom Model ---");
console.log(`Model Id: ${model.modelId}`);
console.log(`Status: ${model.status}`);
console.log("Documents used in training:");
for (const doc of model.trainingDocuments || []) {
console.log(`- ${doc.name}`);
}
}
Usuwanie modelu z konta zasobu
Możesz również usunąć model z konta, odwołując się do jego identyfikatora. Ta funkcja usuwa model z danym identyfikatorem. Ta funkcja nie jest domyślnie wywoływana.
async function deleteModel(modelId) {
await client.deleteModel(modelId);
try {
const deleted = await client.getCustomModel(modelId);
console.log(deleted);
} catch (err) {
// Expected
console.log(`Model with id ${modelId} has been deleted`);
}
}
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Model with id 789b1b37-4cc3-4e36-8665-9dde68618072 has been deleted
Uruchamianie aplikacji
Uruchom aplikację za pomocą node polecenia w pliku projektu.
node index.js
Czyszczenie zasobów
Jeśli chcesz wyczyścić i usunąć subskrypcję usług Azure AI, możesz usunąć zasób lub grupę zasobów. Usunięcie grupy zasobów powoduje również usunięcie wszelkich innych skojarzonych z nią zasobów.
Rozwiązywanie problemów
Możesz ustawić następującą zmienną środowiskową, aby wyświetlić dzienniki debugowania podczas korzystania z tej biblioteki.
export DEBUG=azure*
Aby uzyskać bardziej szczegółowe instrukcje dotyczące włączania dzienników, zobacz dokumentację pakietu @azure/rejestratora.
Następne kroki
W tym projekcie użyto biblioteki klienta Document Intelligence JavaScript do trenowania modeli i analizowania formularzy na różne sposoby. Następnie dowiedz się więcej na temat tworzenia lepszego zestawu danych treningowych i tworzenia bardziej dokładnych modeli.
Przykładowy kod z tego projektu można znaleźć w witrynie GitHub.
Ważne
Ten projekt jest przeznaczony dla interfejsu API REST analizy dokumentów w wersji 2.1.
Dokumentacja referencyjna — przykłady | pakietu kodu | źródłowego biblioteki źródłowej (PyPi)Samples |
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Python 3.x. Instalacja języka Python powinna zawierać narzędzie pip. Możesz sprawdzić, czy masz zainstalowane narzędzie pip, uruchamiając polecenie
pip --versionw wierszu polecenia. Pobierz narzędzie pip, instalując najnowszą wersję języka Python.Obiekt blob usługi Azure Storage zawierający zestaw danych szkoleniowych. Zobacz Tworzenie i trenowanie niestandardowego modelu , aby uzyskać porady i opcje łączenia zestawu danych treningowych. W tym projekcie możesz użyć plików w folderze Train (Trenowanie ) przykładowego zestawu danych. Pobierz i wyodrębnij sample_data.zip.
Zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz zasób analizy dokumentów w witrynie Azure Portal. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Konfigurowanie środowiska programowania
Zainstaluj bibliotekę klienta i utwórz aplikację w języku Python.
Instalowanie biblioteki klienta
Po zainstalowaniu języka Python uruchom następujące polecenie, aby zainstalować najnowszą wersję biblioteki klienta usługi Document Intelligence.
pip install azure-ai-formrecognizer
Tworzenie aplikacji w języku Python
Utwórz aplikację w języku Python o nazwie form-recognizer.py w edytorze lub środowisku IDE.
Zaimportuj następujące biblioteki.
import os from azure.core.exceptions import ResourceNotFoundError from azure.ai.formrecognizer import FormRecognizerClient from azure.ai.formrecognizer import FormTrainingClient from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredentialUtwórz zmienne dla klucza i punktu końcowego platformy Azure zasobu.
endpoint = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_ENDPOINT_HERE" key = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY_HERE"
Korzystanie z modelu obiektów
Za pomocą analizy dokumentów można utworzyć dwa różne typy klientów. Pierwszy element , wysyła zapytanie do usługi w form_recognizer_clientcelu rozpoznawania pól formularzy i zawartości. Drugi element , form_training_clienttworzy modele niestandardowe i zarządza nimi w celu poprawy rozpoznawania.
form_recognizer_client udostępnia następujące operacje:
- Rozpoznawanie pól formularzy i zawartości przy użyciu modeli niestandardowych wytrenowanych do analizowania formularzy niestandardowych.
- Rozpoznawanie zawartości formularza, w tym tabel, wierszy i wyrazów bez konieczności trenowania modelu.
- Rozpoznawanie typowych pól z paragonów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu paragonu w usłudze Analizy dokumentów.
form_training_client zapewnia następujące operacje:
- Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania wszystkich pól i wartości znalezionych w formularzach niestandardowych. Zobacz Trenowanie modelu bez etykiet w tym artykule.
- Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania określonych pól i wartości określonych przez etykietowanie formularzy niestandardowych. Zobacz Trenowanie modelu z etykietami w tym artykule.
- Zarządzanie modelami utworzonymi na koncie.
- Skopiuj model niestandardowy z jednego zasobu analizy dokumentów do innego.
Uwaga
Modele można również wytrenować przy użyciu graficznego interfejsu użytkownika, takiego jak narzędzie do etykietowania analizy dokumentów.
Uwierzytelnianie użytkownika
Uwierzytelnianie dwóch obiektów klienta przy użyciu zdefiniowanych wcześniej zmiennych subskrypcji. AzureKeyCredential Użyj obiektu, aby w razie potrzeby można zaktualizować klucz bez tworzenia nowych obiektów klienta.
form_recognizer_client = FormRecognizerClient(endpoint, AzureKeyCredential(key))
form_training_client = FormTrainingClient(endpoint, AzureKeyCredential(key))
Pobieranie zasobów na potrzeby testowania
Musisz dodać odwołania do adresów URL dla danych szkoleniowych i testowych.
Aby pobrać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego dla danych trenowania modelu niestandardowego, przejdź do zasobu magazynu w witrynie Azure Portal i wybierz pozycję Kontenery magazynu>danych.
Przejdź do kontenera, kliknij prawym przyciskiem myszy i wybierz pozycję Generuj sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego.
Pobierz sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego dla kontenera, a nie dla samego konta magazynu.
Upewnij się, że wybrano uprawnienia Odczyt, Zapis, Usuwanie i Lista , a następnie wybierz pozycję Generuj token SAS i adres URL.
Skopiuj wartość w sekcji Adres URL do lokalizacji tymczasowej. Powinna ona mieć postać:
https://<storage account>.blob.core.windows.net/<container name>?<SAS value>.
Użyj przykładowego formularza i obrazów paragonów zawartych w przykładach, które są również dostępne w usłudze GitHub. Możesz też użyć powyższych kroków, aby uzyskać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego pojedynczego dokumentu w magazynie obiektów blob.
Uwaga
Fragmenty kodu w tym projekcie używają formularzy zdalnych używanych przez adresy URL. Jeśli zamiast tego chcesz przetworzyć dokumenty lokalne, zapoznaj się z powiązanymi metodami w dokumentacji referencyjnej i przykładach.
Analizowanie układu
Analiza dokumentów umożliwia analizowanie tabel, wierszy i słów w dokumentach bez konieczności trenowania modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat wyodrębniania układu, zobacz model układu analizy dokumentów.
Aby przeanalizować zawartość pliku pod danym adresem URL, użyj begin_recognize_content_from_url metody . Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją FormPage obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej strony w przesłanym dokumencie. Poniższy kod wykonuje iterację po tych obiektach i drukuje wyodrębnione pary klucz/wartość i dane tabeli.
formUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-python/master/sdk/formrecognizer/azure-ai-formrecognizer/tests/sample_forms/forms/Form_1.jpg"
poller = form_recognizer_client.begin_recognize_content_from_url(formUrl)
page = poller.result()
table = page[0].tables[0] # page 1, table 1
print("Table found on page {}:".format(table.page_number))
for cell in table.cells:
print("Cell text: {}".format(cell.text))
print("Location: {}".format(cell.bounding_box))
print("Confidence score: {}\n".format(cell.confidence))
Napiwek
Możesz również pobrać zawartość z obrazów lokalnych za pomocą metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak begin_recognize_content.
Table found on page 1:
Cell text: Invoice Number
Location: [Point(x=0.5075, y=2.8088), Point(x=1.9061, y=2.8088), Point(x=1.9061, y=3.3219), Point(x=0.5075, y=3.3219)]
Confidence score: 1.0
Cell text: Invoice Date
Location: [Point(x=1.9061, y=2.8088), Point(x=3.3074, y=2.8088), Point(x=3.3074, y=3.3219), Point(x=1.9061, y=3.3219)]
Confidence score: 1.0
Cell text: Invoice Due Date
Location: [Point(x=3.3074, y=2.8088), Point(x=4.7074, y=2.8088), Point(x=4.7074, y=3.3219), Point(x=3.3074, y=3.3219)]
Confidence score: 1.0
Cell text: Charges
Location: [Point(x=4.7074, y=2.8088), Point(x=5.386, y=2.8088), Point(x=5.386, y=3.3219), Point(x=4.7074, y=3.3219)]
Confidence score: 1.0
...
Analizowanie paragonów
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z amerykańskich paragonów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu paragonu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy paragonów, zobacz Model paragonu analizy dokumentów. Aby analizować paragony z adresu URL, użyj begin_recognize_receipts_from_url metody .
receiptUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-python/master/sdk/formrecognizer/azure-ai-formrecognizer/tests/sample_forms/receipt/contoso-receipt.png"
poller = form_recognizer_client.begin_recognize_receipts_from_url(receiptUrl)
result = poller.result()
for receipt in result:
for name, field in receipt.fields.items():
if name == "Items":
print("Receipt Items:")
for idx, items in enumerate(field.value):
print("...Item #{}".format(idx + 1))
for item_name, item in items.value.items():
print("......{}: {} has confidence {}".format(item_name, item.value, item.confidence))
else:
print("{}: {} has confidence {}".format(name, field.value, field.confidence))
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy paragonów przy użyciu metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak begin_recognize_receipts.
ReceiptType: Itemized has confidence 0.659
MerchantName: Contoso Contoso has confidence 0.516
MerchantAddress: 123 Main Street Redmond, WA 98052 has confidence 0.986
MerchantPhoneNumber: None has confidence 0.99
TransactionDate: 2019-06-10 has confidence 0.985
TransactionTime: 13:59:00 has confidence 0.968
Receipt Items:
...Item #1
......Name: 8GB RAM (Black) has confidence 0.916
......TotalPrice: 999.0 has confidence 0.559
...Item #2
......Quantity: None has confidence 0.858
......Name: SurfacePen has confidence 0.858
......TotalPrice: 99.99 has confidence 0.386
Subtotal: 1098.99 has confidence 0.964
Tax: 104.4 has confidence 0.713
Total: 1203.39 has confidence 0.774
Analizowanie wizytówek
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z angielskich wizytówek przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy wizytówek, zobacz Model wizytówek analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować wizytówki z adresu URL, użyj begin_recognize_business_cards_from_url metody .
bcUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-python/master/sdk/formrecognizer/azure-ai-formrecognizer/samples/sample_forms/business_cards/business-card-english.jpg"
poller = form_recognizer_client.begin_recognize_business_cards_from_url(bcUrl)
business_cards = poller.result()
for idx, business_card in enumerate(business_cards):
print("--------Recognizing business card #{}--------".format(idx+1))
contact_names = business_card.fields.get("ContactNames")
if contact_names:
for contact_name in contact_names.value:
print("Contact First Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
contact_name.value["FirstName"].value, contact_name.value["FirstName"].confidence
))
print("Contact Last Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(
contact_name.value["LastName"].value, contact_name.value["LastName"].confidence
))
company_names = business_card.fields.get("CompanyNames")
if company_names:
for company_name in company_names.value:
print("Company Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(company_name.value, company_name.confidence))
departments = business_card.fields.get("Departments")
if departments:
for department in departments.value:
print("Department: {} has confidence: {}".format(department.value, department.confidence))
job_titles = business_card.fields.get("JobTitles")
if job_titles:
for job_title in job_titles.value:
print("Job Title: {} has confidence: {}".format(job_title.value, job_title.confidence))
emails = business_card.fields.get("Emails")
if emails:
for email in emails.value:
print("Email: {} has confidence: {}".format(email.value, email.confidence))
websites = business_card.fields.get("Websites")
if websites:
for website in websites.value:
print("Website: {} has confidence: {}".format(website.value, website.confidence))
addresses = business_card.fields.get("Addresses")
if addresses:
for address in addresses.value:
print("Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(address.value, address.confidence))
mobile_phones = business_card.fields.get("MobilePhones")
if mobile_phones:
for phone in mobile_phones.value:
print("Mobile phone number: {} has confidence: {}".format(phone.value, phone.confidence))
faxes = business_card.fields.get("Faxes")
if faxes:
for fax in faxes.value:
print("Fax number: {} has confidence: {}".format(fax.value, fax.confidence))
work_phones = business_card.fields.get("WorkPhones")
if work_phones:
for work_phone in work_phones.value:
print("Work phone number: {} has confidence: {}".format(work_phone.value, work_phone.confidence))
other_phones = business_card.fields.get("OtherPhones")
if other_phones:
for other_phone in other_phones.value:
print("Other phone number: {} has confidence: {}".format(other_phone.value, other_phone.confidence))
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy wizytówek za pomocą metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak begin_recognize_business_cards.
Analizowanie faktur
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z faktur sprzedaży przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy faktur, zobacz Model faktury analizy dokumentów.
Aby analizować faktury z adresu URL, użyj begin_recognize_invoices_from_url metody .
invoiceUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/simple-invoice.png"
poller = form_recognizer_client.begin_recognize_invoices_from_url(invoiceUrl)
invoices = poller.result()
for idx, invoice in enumerate(invoices):
print("--------Recognizing invoice #{}--------".format(idx+1))
vendor_name = invoice.fields.get("VendorName")
if vendor_name:
print("Vendor Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(vendor_name.value, vendor_name.confidence))
vendor_address = invoice.fields.get("VendorAddress")
if vendor_address:
print("Vendor Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(vendor_address.value, vendor_address.confidence))
customer_name = invoice.fields.get("CustomerName")
if customer_name:
print("Customer Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(customer_name.value, customer_name.confidence))
customer_address = invoice.fields.get("CustomerAddress")
if customer_address:
print("Customer Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(customer_address.value, customer_address.confidence))
customer_address_recipient = invoice.fields.get("CustomerAddressRecipient")
if customer_address_recipient:
print("Customer Address Recipient: {} has confidence: {}".format(customer_address_recipient.value, customer_address_recipient.confidence))
invoice_id = invoice.fields.get("InvoiceId")
if invoice_id:
print("Invoice Id: {} has confidence: {}".format(invoice_id.value, invoice_id.confidence))
invoice_date = invoice.fields.get("InvoiceDate")
if invoice_date:
print("Invoice Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(invoice_date.value, invoice_date.confidence))
invoice_total = invoice.fields.get("InvoiceTotal")
if invoice_total:
print("Invoice Total: {} has confidence: {}".format(invoice_total.value, invoice_total.confidence))
due_date = invoice.fields.get("DueDate")
if due_date:
print("Due Date: {} has confidence: {}".format(due_date.value, due_date.confidence))
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować lokalne obrazy faktur przy użyciu metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak begin_recognize_invoices.
Analizowanie dokumentów identyfikatorów
W tej sekcji przedstawiono sposób analizowania i wyodrębniania kluczowych informacji z dokumentów identyfikacyjnych wystawionych przez instytucje rządowe, w tym paszportów na całym świecie i licencji kierowców USA, przy użyciu wstępnie utworzonego modelu identyfikatora analizy dokumentów. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy dokumentów identyfikatorów, zobacz model dokumentu identyfikatora analizy dokumentów.
Aby przeanalizować dokumenty identyfikatorów z adresu URL, użyj begin_recognize_id_documents_from_url metody .
idURL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-REST-api-samples/master/curl/form-recognizer/id-license.jpg"
for idx, id_document in enumerate(id_documents):
print("--------Recognizing ID document #{}--------".format(idx+1))
first_name = id_document.fields.get("FirstName")
if first_name:
print("First Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(first_name.value, first_name.confidence))
last_name = id_document.fields.get("LastName")
if last_name:
print("Last Name: {} has confidence: {}".format(last_name.value, last_name.confidence))
document_number = id_document.fields.get("DocumentNumber")
if document_number:
print("Document Number: {} has confidence: {}".format(document_number.value, document_number.confidence))
dob = id_document.fields.get("DateOfBirth")
if dob:
print("Date of Birth: {} has confidence: {}".format(dob.value, dob.confidence))
doe = id_document.fields.get("DateOfExpiration")
if doe:
print("Date of Expiration: {} has confidence: {}".format(doe.value, doe.confidence))
sex = id_document.fields.get("Sex")
if sex:
print("Sex: {} has confidence: {}".format(sex.value, sex.confidence))
address = id_document.fields.get("Address")
if address:
print("Address: {} has confidence: {}".format(address.value, address.confidence))
country_region = id_document.fields.get("CountryRegion")
if country_region:
print("Country/Region: {} has confidence: {}".format(country_region.value, country_region.confidence))
region = id_document.fields.get("Region")
if region:
print("Region: {} has confidence: {}".format(region.value, region.confidence))
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować obrazy dokumentów identyfikatorów za pomocą metod FormRecognizerClient , takich jak begin_recognize_identity_documents.
Trenowanie modelu niestandardowego
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak wytrenować model przy użyciu własnych danych. Wytrenowany model może wyświetlać dane ustrukturyzowane, które zawierają relacje klucz/wartość w oryginalnym dokumencie. Po wytrenowania modelu można testować, ponownie trenować i w końcu używać go do niezawodnego wyodrębniania danych z większej liczby formularzy zgodnie z potrzebami.
Uwaga
Modele można również trenować za pomocą graficznego interfejsu użytkownika, takiego jak narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów.
Trenowanie modelu bez etykiet
Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych w celu analizowania wszystkich pól i wartości znalezionych w formularzach niestandardowych bez ręcznego etykietowania dokumentów szkoleniowych.
Poniższy kod używa klienta szkoleniowego begin_training z funkcją do trenowania modelu na danym zestawie dokumentów. Zwrócony CustomFormModel obiekt zawiera informacje na temat typów formularzy, które model może analizować, a pola, które mogą wyodrębniać z każdego typu formularza. Poniższy blok kodu wyświetla te informacje w konsoli programu .
# To train a model you need an Azure Storage account.
# Use the SAS URL to access your training files.
trainingDataUrl = "PASTE_YOUR_SAS_URL_OF_YOUR_FORM_FOLDER_IN_BLOB_STORAGE_HERE"
poller = form_training_client.begin_training(trainingDataUrl, use_training_labels=False)
model = poller.result()
print("Model ID: {}".format(model.model_id))
print("Status: {}".format(model.status))
print("Training started on: {}".format(model.training_started_on))
print("Training completed on: {}".format(model.training_completed_on))
print("\nRecognized fields:")
for submodel in model.submodels:
print(
"The submodel with form type '{}' has recognized the following fields: {}".format(
submodel.form_type,
", ".join(
[
field.label if field.label else name
for name, field in submodel.fields.items()
]
),
)
)
# Training result information
for doc in model.training_documents:
print("Document name: {}".format(doc.name))
print("Document status: {}".format(doc.status))
print("Document page count: {}".format(doc.page_count))
print("Document errors: {}".format(doc.errors))
Oto dane wyjściowe dla modelu wytrenowanego przy użyciu danych szkoleniowych dostępnych w zestawie SDK języka Python.
Model ID: 628739de-779c-473d-8214-d35c72d3d4f7
Status: ready
Training started on: 2020-08-20 23:16:51+00:00
Training completed on: 2020-08-20 23:16:59+00:00
Recognized fields:
The submodel with form type 'form-0' has recognized the following fields: Additional Notes:, Address:, Company Name:, Company Phone:, Dated As:, Details, Email:, Hero Limited, Name:, Phone:, Purchase Order, Purchase Order #:, Quantity, SUBTOTAL, Seattle, WA 93849 Phone:, Shipped From, Shipped To, TAX, TOTAL, Total, Unit Price, Vendor Name:, Website:
Document name: Form_1.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Document name: Form_2.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Document name: Form_3.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Document name: Form_4.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Document name: Form_5.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Trenowanie modelu przy użyciu etykiet
Modele niestandardowe można również trenować, ręcznie oznaczając dokumenty szkoleniowe. Trenowanie z etykietami prowadzi do lepszej wydajności w niektórych scenariuszach. Zwrócone CustomFormModel pole wskazuje pola, które model może wyodrębnić wraz z szacowaną dokładnością w każdym polu. Poniższy blok kodu wyświetla te informacje w konsoli programu .
Ważne
Aby wytrenować za pomocą etykiet, musisz mieć specjalne pliki informacyjne etykiet (<nazwa pliku>.pdf.labels.json) w kontenerze magazynu obiektów blob wraz z dokumentami szkoleniowymi. Narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów udostępnia interfejs użytkownika, który ułatwia tworzenie tych plików etykiet. Po ich otrzymaniu begin_training możesz wywołać funkcję z parametrem ustawionym use_training_labels na true.
# To train a model you need an Azure Storage account.
# Use the SAS URL to access your training files.
trainingDataUrl = "PASTE_YOUR_SAS_URL_OF_YOUR_FORM_FOLDER_IN_BLOB_STORAGE_HERE"
poller = form_training_client.begin_training(trainingDataUrl, use_training_labels=True)
model = poller.result()
trained_model_id = model.model_id
print("Model ID: {}".format(trained_model_id))
print("Status: {}".format(model.status))
print("Training started on: {}".format(model.training_started_on))
print("Training completed on: {}".format(model.training_completed_on))
print("\nRecognized fields:")
for submodel in model.submodels:
print(
"The submodel with form type '{}' has recognized the following fields: {}".format(
submodel.form_type,
", ".join(
[
field.label if field.label else name
for name, field in submodel.fields.items()
]
),
)
)
# Training result information
for doc in model.training_documents:
print("Document name: {}".format(doc.name))
print("Document status: {}".format(doc.status))
print("Document page count: {}".format(doc.page_count))
print("Document errors: {}".format(doc.errors))
Oto dane wyjściowe dla modelu wytrenowanego przy użyciu danych szkoleniowych dostępnych w zestawie SDK języka Python.
Model ID: ae636292-0b14-4e26-81a7-a0bfcbaf7c91
Status: ready
Training started on: 2020-08-20 23:20:56+00:00
Training completed on: 2020-08-20 23:20:57+00:00
Recognized fields:
The submodel with form type 'form-ae636292-0b14-4e26-81a7-a0bfcbaf7c91' has recognized the following fields: CompanyAddress, CompanyName, CompanyPhoneNumber, DatedAs, Email, Merchant, PhoneNumber, PurchaseOrderNumber, Quantity, Signature, Subtotal, Tax, Total, VendorName, Website
Document name: Form_1.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Document name: Form_2.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Document name: Form_3.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Document name: Form_4.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Document name: Form_5.jpg
Document status: succeeded
Document page count: 1
Document errors: []
Analizowanie formularzy przy użyciu modelu niestandardowego
W tej sekcji przedstawiono sposób wyodrębniania informacji o klucz/wartość i innej zawartości z niestandardowych typów szablonów przy użyciu modeli wytrenowanych przy użyciu własnych formularzy.
Ważne
Aby zaimplementować ten scenariusz, musisz mieć już wytrenowany model, aby można było przekazać jego identyfikator do operacji metody. Zobacz sekcję Train a model (Trenowanie modelu ).
Należy użyć begin_recognize_custom_forms_from_url metody . Zwracana wartość jest kolekcją RecognizedForm obiektów. Istnieje jeden obiekt dla każdej strony w przesłanym dokumencie. Poniższy kod wyświetla wyniki analizy w konsoli programu . Drukuje każde rozpoznane pole i odpowiadającą mu wartość wraz z współczynnikiem ufności.
poller = form_recognizer_client.begin_recognize_custom_forms_from_url(
model_id=trained_model_id, form_url=formUrl)
result = poller.result()
for recognized_form in result:
print("Form type: {}".format(recognized_form.form_type))
for name, field in recognized_form.fields.items():
print("Field '{}' has label '{}' with value '{}' and a confidence score of {}".format(
name,
field.label_data.text if field.label_data else name,
field.value,
field.confidence
))
Napiwek
Możesz również analizować obrazy lokalne. Zobacz metody FormRecognizerClient, takie jak begin_recognize_custom_forms. Możesz też zapoznać się z przykładowym kodem w usłudze GitHub , aby zapoznać się ze scenariuszami obejmującymi obrazy lokalne.
Model z poprzedniego przykładu renderuje następujące dane wyjściowe:
Form type: form-ae636292-0b14-4e26-81a7-a0bfcbaf7c91
Field 'Merchant' has label 'Merchant' with value 'Invoice For:' and a confidence score of 0.116
Field 'CompanyAddress' has label 'CompanyAddress' with value '1 Redmond way Suite 6000 Redmond, WA' and a confidence score of 0.258
Field 'Website' has label 'Website' with value '99243' and a confidence score of 0.114
Field 'VendorName' has label 'VendorName' with value 'Charges' and a confidence score of 0.145
Field 'CompanyPhoneNumber' has label 'CompanyPhoneNumber' with value '$56,651.49' and a confidence score of 0.249
Field 'CompanyName' has label 'CompanyName' with value 'PT' and a confidence score of 0.245
Field 'DatedAs' has label 'DatedAs' with value 'None' and a confidence score of None
Field 'Email' has label 'Email' with value 'None' and a confidence score of None
Field 'PhoneNumber' has label 'PhoneNumber' with value 'None' and a confidence score of None
Field 'PurchaseOrderNumber' has label 'PurchaseOrderNumber' with value 'None' and a confidence score of None
Field 'Quantity' has label 'Quantity' with value 'None' and a confidence score of None
Field 'Signature' has label 'Signature' with value 'None' and a confidence score of None
Field 'Subtotal' has label 'Subtotal' with value 'None' and a confidence score of None
Field 'Tax' has label 'Tax' with value 'None' and a confidence score of None
Field 'Total' has label 'Total' with value 'None' and a confidence score of None
Zarządzanie modelami niestandardowymi
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak zarządzać modelami niestandardowymi przechowywanymi na koncie.
Sprawdzanie liczby modeli na koncie zasobu FormRecognizer
Poniższy blok kodu sprawdza liczbę modeli zapisanych na koncie analizy dokumentów i porównuje je z limitem konta.
account_properties = form_training_client.get_account_properties()
print("Our account has {} custom models, and we can have at most {} custom models".format(
account_properties.custom_model_count, account_properties.custom_model_limit
))
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Our account has 5 custom models, and we can have at most 5000 custom models
Wyświetlanie listy modeli aktualnie przechowywanych na koncie zasobu
Poniższy kod blokuje bieżące modele na twoim koncie i wyświetla ich szczegóły w konsoli. Zapisuje również odwołanie do pierwszego modelu.
# Next, we get a paged list of all of our custom models
custom_models = form_training_client.list_custom_models()
print("We have models with the following ids:")
# Let's pull out the first model
first_model = next(custom_models)
print(first_model.model_id)
for model in custom_models:
print(model.model_id)
Wynik wygląda podobnie do poniższych danych wyjściowych.
Oto przykładowe dane wyjściowe dla konta testowego.
We have models with the following ids:
453cc2e6-e3eb-4e9f-aab6-e1ac7b87e09e
628739de-779c-473d-8214-d35c72d3d4f7
ae636292-0b14-4e26-81a7-a0bfcbaf7c91
b4b5df77-8538-4ffb-a996-f67158ecd305
c6309148-6b64-4fef-aea0-d39521452699
Pobieranie określonego modelu przy użyciu identyfikatora modelu
Poniższy blok kodu używa identyfikatora modelu zapisanego w poprzedniej sekcji i używa go do pobierania szczegółów dotyczących modelu.
custom_model = form_training_client.get_custom_model(model_id=trained_model_id)
print("Model ID: {}".format(custom_model.model_id))
print("Status: {}".format(custom_model.status))
print("Training started on: {}".format(custom_model.training_started_on))
print("Training completed on: {}".format(custom_model.training_completed_on))
Oto przykładowe dane wyjściowe dla modelu niestandardowego utworzonego w poprzednim przykładzie.
Model ID: ae636292-0b14-4e26-81a7-a0bfcbaf7c91
Status: ready
Training started on: 2020-08-20 23:20:56+00:00
Training completed on: 2020-08-20 23:20:57+00:00
Usuwanie modelu z konta zasobu
Możesz również usunąć model z konta, odwołując się do jego identyfikatora. Ten kod usuwa model używany w poprzedniej sekcji.
form_training_client.delete_model(model_id=custom_model.model_id)
try:
form_training_client.get_custom_model(model_id=custom_model.model_id)
except ResourceNotFoundError:
print("Successfully deleted model with id {}".format(custom_model.model_id))
Uruchamianie aplikacji
Uruchom aplikację za python pomocą polecenia :
python form-recognizer.py
Czyszczenie zasobów
Jeśli chcesz wyczyścić i usunąć subskrypcję usług Azure AI, możesz usunąć zasób lub grupę zasobów. Usunięcie grupy zasobów powoduje również usunięcie wszelkich innych skojarzonych z nią zasobów.
Rozwiązywanie problemów
Te problemy mogą być przydatne podczas rozwiązywania problemów.
Ogólne
Biblioteka klienta analizy dokumentów zgłasza wyjątki zdefiniowane w usłudze Azure Core.
Rejestrowanie
Ta biblioteka używa standardowej biblioteki rejestrowania do rejestrowania. Podstawowe informacje o sesjach HTTP, takich jak adresy URL i nagłówki, są rejestrowane na poziomie INFORMACJI.
Szczegółowe rejestrowanie na poziomie DEBUG, w tym treść żądania/odpowiedzi i nieredagowane nagłówki, można włączyć na kliencie z argumentem słowa kluczowego logging_enable :
import sys
import logging
from azure.ai.formrecognizer import FormRecognizerClient
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
# Create a logger for the 'azure' SDK
logger = logging.getLogger('azure')
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# Configure a console output
handler = logging.StreamHandler(stream=sys.stdout)
logger.addHandler(handler)
endpoint = "PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_ENDPOINT_HERE"
credential = AzureKeyCredential("PASTE_YOUR_FORM_RECOGNIZER_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY_HERE")
# This client will log detailed information about its HTTP sessions, at DEBUG level
form_recognizer_client = FormRecognizerClient(endpoint, credential, logging_enable=True)
logging_enable Podobnie można włączyć szczegółowe rejestrowanie dla pojedynczej operacji, nawet jeśli nie jest włączona dla klienta:
receiptUrl = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-python/master/sdk/formrecognizer/azure-ai-formrecognizer/tests/sample_forms/receipt/contoso-receipt.png"
poller = form_recognizer_client.begin_recognize_receipts_from_url(receiptUrl, logging_enable=True)
Przykłady REST w usłudze GitHub
- Wyodrębnianie tekstu, znaczników zaznaczenia i struktury tabeli z dokumentów: wyodrębnianie danych układu — Python
- Trenowanie modeli niestandardowych i wyodrębnianie niestandardowych danych formularza:
- Wyodrębnianie danych z faktur: wyodrębnianie danych faktury — Python
- Wyodrębnianie danych z paragonów sprzedaży: wyodrębnianie danych paragonu — Python
- Wyodrębnianie danych z wizytówek: wyodrębnianie danych wizytówek — Python
Następne kroki
W tym projekcie użyto biblioteki klienta Document Intelligence Python do trenowania modeli i analizowania formularzy na różne sposoby. Następnie dowiedz się więcej na temat tworzenia lepszego zestawu danych treningowych i tworzenia bardziej dokładnych modeli.
Przykładowy kod dla tego projektu można znaleźć w witrynie GitHub.
Uwaga
Ten projekt jest przeznaczony dla interfejsu API analizy dokumentów usługi Azure AI w wersji 2.1 przy użyciu biblioteki cURL do wykonywania wywołań interfejsu API REST.
Dokumentacja interfejsu API REST interfejsu API | REST analizy dokumentów
Wymagania wstępne
Subskrypcja platformy Azure — utwórz bezpłatnie.
Zainstalowane narzędzie wiersza polecenia cURL. Systemy Windows 10 i Windows 11 są dostarczane z kopią biblioteki cURL. W wierszu polecenia wpisz następujące polecenie cURL. Jeśli są wyświetlane opcje pomocy, program cURL jest zainstalowany w środowisku systemu Windows.
curl -helpJeśli nie zainstalowano biblioteki cURL, możesz ją uzyskać tutaj:
PowerShell w wersji 6.0 lub podobnej aplikacji wiersza polecenia.
Obiekt blob usługi Azure Storage zawierający zestaw danych szkoleniowych. Zobacz Tworzenie i trenowanie niestandardowego modelu , aby uzyskać porady i opcje łączenia zestawu danych treningowych. Możesz użyć plików w folderze Train (Trenowanie) przykładowego zestawu danych. Pobierz i wyodrębnij sample_data.zip.
Usługi azure AI lub zasób analizy dokumentów. Utwórz pojedynczą usługę lub wiele usług. Możesz użyć warstwy cenowej bezpłatna (
F0), aby wypróbować usługę, a następnie uaktualnić ją do warstwy płatnej dla środowiska produkcyjnego.Klucz i punkt końcowy z utworzonego zasobu w celu połączenia aplikacji z usługą Azure Document Intelligence.
- Po wdrożeniu zasobu wybierz pozycję Przejdź do zasobu.
- W menu nawigacji po lewej stronie wybierz pozycję Klucze i punkt końcowy.
- Skopiuj jeden z kluczy i punkt końcowy do użycia w dalszej części tego artykułu.

Adres URL obrazu paragonu. Możesz użyć przykładowego obrazu.
Adres URL obrazu wizytówki. Możesz użyć przykładowego obrazu.
Adres URL obrazu faktury. Możesz użyć przykładowego dokumentu.
Adres URL obrazu dokumentu o identyfikatorze. Możesz użyć przykładowego obrazu
Analizowanie układu
Za pomocą analizy dokumentów można analizować i wyodrębniać tabele, znaczniki zaznaczenia, tekst i strukturę w dokumentach bez konieczności trenowania modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat wyodrębniania układu, zobacz model układu analizy dokumentów.
Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <klucz> kluczem skopiowanymi z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <ciąg your-document-url> jednym z przykładowych adresów URL.
curl -v -i POST "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/layout/analyze" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>" --data-ascii "{'source': '<your-document-url>'}"
Otrzymasz odpowiedź zawierającą 202 (Success) nagłówek tylko do Operation-Location odczytu. Wartość tego nagłówka zawiera element resultId , który można wysłać do zapytania w celu uzyskania stanu operacji asynchronicznej i pobrania wyników przy użyciu żądania GET z tym samym kluczem subskrypcji zasobu:
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2.1/layout/analyzeResults/<resultId>
W poniższym przykładzie jako część adresu URL ciąg po analyzeResults/ jest identyfikatorem wyniku.
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2/layout/analyzeResults/54f0b076-4e38-43e5-81bd-b85b8835fdfb
Pobieranie wyników układu
Po wywołaniu interfejsu API analizowania układu sonduj interfejs API uzyskiwania wyników układu analizy, aby uzyskać stan operacji i wyodrębnione dane. Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <klucz> kluczem skopiowanymi z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <element resultId> identyfikatorem wyniku z poprzedniego kroku.
curl -v -X GET "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/layout/analyzeResults/<resultId>" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
Otrzymasz odpowiedź z zawartością 200 (success) JSON.
Zobacz poniższy obraz faktury i odpowiadające mu dane wyjściowe JSON.
- Węzeł
"readResults"zawiera każdy wiersz tekstu z odpowiednim umieszczeniem pola ograniczenia na stronie. - Węzeł
selectionMarkspokazuje każdy znacznik zaznaczenia (pole wyboru, znacznik radiowy) i określa, czy jego stan toselected, czyunselected. - Sekcja
"pageResults"zawiera wyodrębnione tabele. Dla każdej tabeli wyodrębniono tekst, wiersz i indeks kolumn, zakres wierszy i kolumn, pole ograniczenia i nie tylko.
Te dane wyjściowe treści odpowiedzi zostały skrócone dla uproszczenia. Zobacz pełne przykładowe dane wyjściowe w witrynie GitHub.
{
"status": "succeeded",
"createdDateTime": "2020-08-20T20:40:50Z",
"lastUpdatedDateTime": "2020-08-20T20:40:55Z",
"analyzeResult": {
"version": "2.1.0",
"readResults": [
{
"page": 1,
"angle": 0,
"width": 8.5,
"height": 11,
"unit": "inch",
"lines": [
{
"boundingBox": [
0.5826,
0.4411,
2.3387,
0.4411,
2.3387,
0.7969,
0.5826,
0.7969
],
"text": "Contoso, Ltd.",
"words": [
{
"boundingBox": [
0.5826,
0.4411,
1.744,
0.4411,
1.744,
0.7969,
0.5826,
0.7969
],
"text": "Contoso,",
"confidence": 1
},
{
"boundingBox": [
1.8448,
0.4446,
2.3387,
0.4446,
2.3387,
0.7631,
1.8448,
0.7631
],
"text": "Ltd.",
"confidence": 1
}
]
},
...
]
}
],
"selectionMarks": [
{
"boundingBox": [
3.9737,
3.7475,
4.1693,
3.7475,
4.1693,
3.9428,
3.9737,
3.9428
],
"confidence": 0.989,
"state": "selected"
},
...
]
}
],
"pageResults": [
{
"page": 1,
"tables": [
{
"rows": 5,
"columns": 5,
"cells": [
{
"rowIndex": 0,
"columnIndex": 0,
"text": "Training Date",
"boundingBox": [
0.5133,
4.2167,
1.7567,
4.2167,
1.7567,
4.4492,
0.5133,
4.4492
],
"elements": [
"#/readResults/0/lines/12/words/0",
"#/readResults/0/lines/12/words/1"
]
},
...
]
},
...
]
}
]
}
}
Analizowanie paragonów
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z amerykańskich paragonów przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu paragonu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy paragonów, zobacz Model paragonu analizy dokumentów. Aby rozpocząć analizowanie paragonu, wywołaj interfejs API analizowania paragonu przy użyciu polecenia cURL. Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <adres URL potwierdzenia adresem URL> obrazu potwierdzenia.
- Zastąp <klucz klucz> kluczem skopiowany z poprzedniego kroku.
curl -i -X POST "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/receipt/analyze" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>" --data-ascii "{ 'source': '<your receipt URL>'}"
202 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź zawierającą Operation-Location nagłówek. Wartość tego nagłówka zawiera identyfikator wyniku, którego można użyć do wykonywania zapytań o stan operacji asynchronicznej i uzyskiwania wyników:
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/receipt/analyzeResults/<resultId>
W poniższym przykładzie ciąg po operations/ jest identyfikatorem wyniku:
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/receipt/operations/aeb13e15-555d-4f02-ba47-04d89b487ed5
Pobieranie wyników paragonu
Po wywołaniu interfejsu API analizowania paragonu wywołaj interfejs API Uzyskiwanie wyniku paragonu, aby uzyskać stan operacji i wyodrębnione dane. Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym za pomocą klucza analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <element resultId> identyfikatorem wyniku z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <klucz> klucz kluczem.
curl -X GET "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/receipt/analyzeResults/<resultId>" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
200 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z danymi wyjściowymi JSON. Pierwsze pole , "status"wskazuje stan operacji. Jeśli operacja nie jest ukończona, wartość "status" to "running" lub "notStarted", a należy wywołać interfejs API ponownie, ręcznie lub za pomocą skryptu. Zalecamy interwał co najmniej jednej sekundy między wywołaniami.
Węzeł "readResults" zawiera cały rozpoznany tekst, jeśli ustawisz opcjonalny includeTextDetails parametr na truewartość ). Odpowiedź organizuje tekst według strony, a następnie według wierszy, a następnie poszczególnych wyrazów. Węzeł "documentResults" zawiera wartości specyficzne dla potwierdzenia wykryte przez model. Węzeł "documentResults" to miejsce, w którym można znaleźć przydatne pary klucz/wartość, takie jak podatek, suma, adres sprzedawcy itd.
Zobacz następujący obraz potwierdzenia i odpowiadające mu dane wyjściowe JSON.

Te dane wyjściowe treści odpowiedzi zostały skrócone pod kątem czytelności. Zobacz pełne przykładowe dane wyjściowe w witrynie GitHub.
{
"status":"succeeded",
"createdDateTime":"2019-12-17T04:11:24Z",
"lastUpdatedDateTime":"2019-12-17T04:11:32Z",
"analyzeResult":{
"version":"2.1.0",
"readResults":[
{
"page":1,
"angle":0.6893,
"width":1688,
"height":3000,
"unit":"pixel",
"language":"en",
"lines":[
{
"text":"Contoso",
"boundingBox":[
635,
510,
1086,
461,
1098,
558,
643,
604
],
"words":[
{
"text":"Contoso",
"boundingBox":[
639,
510,
1087,
461,
1098,
551,
646,
604
],
"confidence":0.955
}
]
},
...
]
}
],
"documentResults":[
{
"docType":"prebuilt:receipt",
"pageRange":[
1,
1
],
"fields":{
"ReceiptType":{
"type":"string",
"valueString":"Itemized",
"confidence":0.692
},
"MerchantName":{
"type":"string",
"valueString":"Contoso Contoso",
"text":"Contoso Contoso",
"boundingBox":[
378.2,
292.4,
1117.7,
468.3,
1035.7,
812.7,
296.3,
636.8
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.613,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/0/words/0",
"#/readResults/0/lines/1/words/0"
]
},
"MerchantAddress":{
"type":"string",
"valueString":"123 Main Street Redmond, WA 98052",
"text":"123 Main Street Redmond, WA 98052",
"boundingBox":[
302,
675.8,
848.1,
793.7,
809.9,
970.4,
263.9,
852.5
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.99,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/2/words/0",
"#/readResults/0/lines/2/words/1",
"#/readResults/0/lines/2/words/2",
"#/readResults/0/lines/3/words/0",
"#/readResults/0/lines/3/words/1",
"#/readResults/0/lines/3/words/2"
]
},
"MerchantPhoneNumber":{
"type":"phoneNumber",
"valuePhoneNumber":"+19876543210",
"text":"987-654-3210",
"boundingBox":[
278,
1004,
656.3,
1054.7,
646.8,
1125.3,
268.5,
1074.7
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.99,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/4/words/0"
]
},
"TransactionDate":{
"type":"date",
"valueDate":"2019-06-10",
"text":"6/10/2019",
"boundingBox":[
265.1,
1228.4,
525,
1247,
518.9,
1332.1,
259,
1313.5
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.99,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/5/words/0"
]
},
"TransactionTime":{
"type":"time",
"valueTime":"13:59:00",
"text":"13:59",
"boundingBox":[
541,
1248,
677.3,
1261.5,
668.9,
1346.5,
532.6,
1333
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.977,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/5/words/1"
]
},
"Items":{
"type":"array",
"valueArray":[
{
"type":"object",
"valueObject":{
"Quantity":{
"type":"number",
"text":"1",
"boundingBox":[
245.1,
1581.5,
300.9,
1585.1,
295,
1676,
239.2,
1672.4
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.92,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/7/words/0"
]
},
"Name":{
"type":"string",
"valueString":"Cappuccino",
"text":"Cappuccino",
"boundingBox":[
322,
1586,
654.2,
1601.1,
650,
1693,
317.8,
1678
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.923,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/7/words/1"
]
},
"TotalPrice":{
"type":"number",
"valueNumber":2.2,
"text":"$2.20",
"boundingBox":[
1107.7,
1584,
1263,
1574,
1268.3,
1656,
1113,
1666
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.918,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/8/words/0"
]
}
}
},
...
]
},
"Subtotal":{
"type":"number",
"valueNumber":11.7,
"text":"11.70",
"boundingBox":[
1146,
2221,
1297.3,
2223,
1296,
2319,
1144.7,
2317
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.955,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/13/words/1"
]
},
"Tax":{
"type":"number",
"valueNumber":1.17,
"text":"1.17",
"boundingBox":[
1190,
2359,
1304,
2359,
1304,
2456,
1190,
2456
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.979,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/15/words/1"
]
},
"Tip":{
"type":"number",
"valueNumber":1.63,
"text":"1.63",
"boundingBox":[
1094,
2479,
1267.7,
2485,
1264,
2591,
1090.3,
2585
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.941,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/17/words/1"
]
},
"Total":{
"type":"number",
"valueNumber":14.5,
"text":"$14.50",
"boundingBox":[
1034.2,
2617,
1387.5,
2638.2,
1380,
2763,
1026.7,
2741.8
],
"page":1,
"confidence":0.985,
"elements":[
"#/readResults/0/lines/19/words/0"
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
Analizowanie wizytówek
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak analizować i wyodrębniać typowe pola z angielskich wizytówek przy użyciu wstępnie wytrenowanego modelu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy wizytówek, zobacz Model wizytówek analizy dokumentów. Aby rozpocząć analizowanie wizytówki, należy wywołać interfejs API analizowania wizytówek przy użyciu polecenia cURL. Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <adres URL> wizytówki adresem URL obrazu potwierdzenia.
- Zastąp <klucz> kluczem skopiowanymi z poprzedniego kroku.
curl -i -X POST "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/businessCard/analyze" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>" --data-ascii "{ 'source': '<your receipt URL>'}"
Otrzymasz odpowiedź zawierającą 202 (Success)nagłówek Operation-Location . Wartość tego nagłówka zawiera identyfikator wyniku, którego można użyć do wykonywania zapytań o stan operacji asynchronicznej i uzyskiwania wyników:
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/businessCard/analyzeResults/<resultId>
W poniższym przykładzie jako część adresu URL ciąg po analyzeResults/ jest identyfikatorem wyniku.
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/businessCard/analyzeResults/54f0b076-4e38-43e5-81bd-b85b8835fdfb
Po wywołaniu interfejsu API analizowania wizytówek wywołaj interfejs API Uzyskiwanie wyników karty biznesowej, aby uzyskać stan operacji i wyodrębnione dane. Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym za pomocą klucza analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <element resultId> identyfikatorem wyniku z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <klucz> klucz kluczem.
curl -v -X GET https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/businessCard/analyzeResults/<resultId>"
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
200 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z danymi wyjściowymi JSON.
Węzeł "readResults" zawiera cały rozpoznany tekst. Odpowiedź organizuje tekst według strony, a następnie według wierszy, a następnie poszczególnych wyrazów. Węzeł "documentResults" zawiera wartości specyficzne dla wizytówki wykryte przez model. Węzeł "documentResults" to miejsce, w którym można znaleźć przydatne informacje kontaktowe, takie jak nazwa firmy, imię, nazwisko, numer telefonu itd.

Te przykładowe dane wyjściowe JSON zostały skrócone pod kątem czytelności. Zobacz pełne przykładowe dane wyjściowe w witrynie GitHub.
{
"status": "succeeded",
"createdDateTime":"2021-02-09T18:14:05Z",
"lastUpdatedDateTime":"2021-02-09T18:14:10Z",
"analyzeResult": {
"version": "2.1.0",
"readResults": [
{
"page":1,
"angle":-16.6836,
"width":4032,
"height":3024,
"unit":"pixel"
}
],
"documentResults": [
{
"docType": "prebuilt:businesscard",
"pageRange": [
1,
1
],
"fields": {
"ContactNames": {
"type": "array",
"valueArray": [
{
"type": "object",
"valueObject": {
"FirstName": {
"type": "string",
"valueString": "Avery",
"text": "Avery",
"boundingBox": [
703,
1096,
1134,
989,
1165,
1109,
733,
1206
],
"page": 1
},
"text": "Dr. Avery Smith",
"boundingBox": [
419.3,
1154.6,
1589.6,
877.9,
1618.9,
1001.7,
448.6,
1278.4
],
"confidence": 0.993
}
]
},
"Emails": {
"type": "array",
"valueArray": [
{
"type": "string",
"valueString": "avery.smith@contoso.com",
"text": "avery.smith@contoso.com",
"boundingBox": [
2107,
934,
2917,
696,
2935,
764,
2126,
995
],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.99
}
]
},
"Websites": {
"type": "array",
"valueArray": [
{
"type": "string",
"valueString": "https://www.contoso.com/",
"text": "https://www.contoso.com/",
"boundingBox": [
2121,
1002,
2992,
755,
3014,
826,
2143,
1077
],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.995
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
Skrypt wyświetla odpowiedzi na konsolę do momentu zakończenia operacji Analizowanie wizytówek.
Analizowanie faktur
Analiza dokumentów umożliwia wyodrębnianie tekstu pola i wartości semantycznych z danego dokumentu faktury. Aby rozpocząć analizowanie faktury, użyj polecenia cURL. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy faktur, zobacz Przewodnik koncepcyjny dotyczący faktury. Aby rozpocząć analizowanie faktury, wywołaj interfejs API analizowania faktur przy użyciu polecenia cURL.
Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <adres URL faktury adresem URL> dokumentu faktury.
- Zastąp <klucz> klucz kluczem.
curl -v -i POST https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/invoice/analyze" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>" --data-ascii "{'source': '<your invoice URL>'}"
202 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź zawierającą Operation-Location nagłówek. Wartość tego nagłówka zawiera identyfikator wyniku, którego można użyć do wykonywania zapytań o stan operacji asynchronicznej i uzyskiwania wyników:
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/receipt/analyzeResults/<resultId>
W poniższym przykładzie jako część adresu URL ciąg po analyzeResults/ jest identyfikatorem wyniku:
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/invoice/analyzeResults/54f0b076-4e38-43e5-81bd-b85b8835fdfb
Po wywołaniu interfejsu API analizowania faktur wywołaj interfejs API Pobierania wyniku faktury, aby uzyskać stan operacji i wyodrębnione dane.
Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym za pomocą klucza analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <element resultId> identyfikatorem wyniku z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <klucz> klucz kluczem.
curl -v -X GET "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/invoice/analyzeResults/<resultId>" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
200 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z danymi wyjściowymi JSON.
- Pole
"readResults"zawiera każdy wiersz tekstu wyodrębniony z faktury. - Element
"pageResults"zawiera tabele i znaczniki wyboru wyodrębnione z faktury. - Pole
"documentResults"zawiera informacje o kluczu/wartości dla najbardziej odpowiednich części faktury.
Zapoznaj się z następującym dokumentem faktury i odpowiadającymi mu danymi wyjściowymi JSON.
Ta zawartość JSON treści odpowiedzi została skrócona w celu zapewnienia czytelności. Zobacz pełne przykładowe dane wyjściowe w witrynie GitHub.
{
"status": "succeeded",
"createdDateTime": "2020-11-06T23:32:11Z",
"lastUpdatedDateTime": "2020-11-06T23:32:20Z",
"analyzeResult": {
"version": "2.1.0",
"readResults": [{
"page": 1,
"angle": 0,
"width": 8.5,
"height": 11,
"unit": "inch"
}],
"pageResults": [{
"page": 1,
"tables": [{
"rows": 3,
"columns": 4,
"cells": [{
"rowIndex": 0,
"columnIndex": 0,
"text": "QUANTITY",
"boundingBox": [0.4953,
5.7306,
1.8097,
5.7306,
1.7942,
6.0122,
0.4953,
6.0122]
},
{
"rowIndex": 0,
"columnIndex": 1,
"text": "DESCRIPTION",
"boundingBox": [1.8097,
5.7306,
5.7529,
5.7306,
5.7452,
6.0122,
1.7942,
6.0122]
},
...
],
"boundingBox": [0.4794,
5.7132,
8.0158,
5.714,
8.0118,
6.5627,
0.4757,
6.5619]
},
{
"rows": 2,
"columns": 6,
"cells": [{
"rowIndex": 0,
"columnIndex": 0,
"text": "SALESPERSON",
"boundingBox": [0.4979,
4.963,
1.8051,
4.963,
1.7975,
5.2398,
0.5056,
5.2398]
},
{
"rowIndex": 0,
"columnIndex": 1,
"text": "P.O. NUMBER",
"boundingBox": [1.8051,
4.963,
3.3047,
4.963,
3.3124,
5.2398,
1.7975,
5.2398]
},
...
],
"boundingBox": [0.4976,
4.961,
7.9959,
4.9606,
7.9959,
5.5204,
0.4972,
5.5209]
}]
}],
"documentResults": [{
"docType": "prebuilt:invoice",
"pageRange": [1,
1],
"fields": {
"AmountDue": {
"type": "number",
"valueNumber": 610,
"text": "$610.00",
"boundingBox": [7.3809,
7.8153,
7.9167,
7.8153,
7.9167,
7.9591,
7.3809,
7.9591],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.875
},
"BillingAddress": {
"type": "string",
"valueString": "123 Bill St, Redmond WA, 98052",
"text": "123 Bill St, Redmond WA, 98052",
"boundingBox": [0.594,
4.3724,
2.0125,
4.3724,
2.0125,
4.7125,
0.594,
4.7125],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.997
},
"BillingAddressRecipient": {
"type": "string",
"valueString": "Microsoft Finance",
"text": "Microsoft Finance",
"boundingBox": [0.594,
4.1684,
1.7907,
4.1684,
1.7907,
4.2837,
0.594,
4.2837],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.998
},
...
}
}]
}
}
Analizowanie dokumentów tożsamości
Aby rozpocząć analizowanie dokumentu identyfikacji (ID), użyj polecenia cURL. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat analizy dokumentów identyfikatorów, zobacz model dokumentu identyfikatora analizy dokumentów. Aby rozpocząć analizowanie dokumentu identyfikatora, należy wywołać interfejs API dokumentu Analyze ID przy użyciu polecenia cURL.
Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <adres URL> dokumentu identyfikatora adresem URL obrazu potwierdzenia.
- Zastąp <klucz> kluczem skopiowanymi z poprzedniego kroku.
curl -i -X POST "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/idDocument/analyze" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>" --data-ascii "{ 'source': '<your ID document URL>'}"
202 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź zawierającą Operation-Location nagłówek. Wartość tego nagłówka zawiera identyfikator wyniku, którego można użyć do wykonywania zapytań o stan operacji asynchronicznej i uzyskiwania wyników:
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/documentId/analyzeResults/<resultId>
W poniższym przykładzie ciąg po analyzeResults/ jest identyfikatorem wyniku:
https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/idDocument/analyzeResults/3bc1d6e0-e24c-41d2-8c50-14e9edc336d1
Uzyskiwanie wyniku dokumentu analizy identyfikatora
Po wywołaniu interfejsu API dokumentu Analizuj identyfikator wywołaj interfejs API Uzyskiwanie wyniku dokumentu identyfikatora analizy, aby uzyskać stan operacji i wyodrębnionych danych. Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym za pomocą klucza analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <element resultId> identyfikatorem wyniku z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <klucz> klucz kluczem.
curl -X GET "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/prebuilt/idDocument/analyzeResults/<resultId>" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
200 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z danymi wyjściowymi JSON. Pierwsze pole , "status"wskazuje stan operacji. Jeśli operacja nie została ukończona, wartość to "status""running" lub "notStarted". Wywołaj ponownie interfejs API ręcznie lub za pomocą skryptu succeeded , dopóki nie otrzymasz wartości. Zalecamy interwał co najmniej jednej sekundy między wywołaniami.
- Pole
"readResults"zawiera każdy wiersz tekstu wyodrębniony z dokumentu o identyfikatorze. - Pole
"documentResults"zawiera tablicę obiektów, z których każdy reprezentuje dokument o identyfikatorze wykrytym w dokumencie wejściowym.
Oto przykładowy dokument o identyfikatorze i odpowiadających mu danych wyjściowych JSON.

Oto treść odpowiedzi.
{
"status": "succeeded",
"createdDateTime": "2021-04-13T17:24:52Z",
"lastUpdatedDateTime": "2021-04-13T17:24:55Z",
"analyzeResult": {
"version": "2.1.0",
"readResults": [
{
"page": 1,
"angle": -0.2823,
"width": 450,
"height": 294,
"unit": "pixel"
}
],
"documentResults": [
{
"docType": "prebuilt:idDocument:driverLicense",
"docTypeConfidence": 0.995,
"pageRange": [
1,
1
],
"fields": {
"Address": {
"type": "string",
"valueString": "123 STREET ADDRESS YOUR CITY WA 99999-1234",
"text": "123 STREET ADDRESS YOUR CITY WA 99999-1234",
"boundingBox": [
158,
151,
326,
151,
326,
177,
158,
177
],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.965
},
"CountryRegion": {
"type": "countryRegion",
"valueCountryRegion": "USA",
"confidence": 0.99
},
"DateOfBirth": {
"type": "date",
"valueDate": "1958-01-06",
"text": "01/06/1958",
"boundingBox": [
187,
133,
272,
132,
272,
148,
187,
149
],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.99
},
"DateOfExpiration": {
"type": "date",
"valueDate": "2020-08-12",
"text": "08/12/2020",
"boundingBox": [
332,
230,
414,
228,
414,
244,
332,
245
],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.99
},
"DocumentNumber": {
"type": "string",
"valueString": "LICWDLACD5DG",
"text": "LIC#WDLABCD456DG",
"boundingBox": [
162,
70,
307,
68,
307,
84,
163,
85
],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.99
},
"FirstName": {
"type": "string",
"valueString": "LIAM R.",
"text": "LIAM R.",
"boundingBox": [
158,
102,
216,
102,
216,
116,
158,
116
],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.985
},
"LastName": {
"type": "string",
"valueString": "TALBOT",
"text": "TALBOT",
"boundingBox": [
160,
86,
213,
85,
213,
99,
160,
100
],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.987
},
"Region": {
"type": "string",
"valueString": "Washington",
"confidence": 0.99
},
"Sex": {
"type": "string",
"valueString": "M",
"text": "M",
"boundingBox": [
226,
190,
232,
190,
233,
201,
226,
201
],
"page": 1,
"confidence": 0.99
}
}
}
]
}
}
Trenowanie modelu niestandardowego
Aby wytrenować model niestandardowy, potrzebny jest zestaw danych szkoleniowych w obiekcie blob usługi Azure Storage. Potrzebujesz co najmniej pięciu wypełnionych formularzy (dokumentów PDF i/lub obrazów) tego samego typu/struktury. Zobacz Tworzenie i trenowanie niestandardowego modelu , aby uzyskać porady i opcje łączenia danych szkoleniowych.
Trenowanie bez danych oznaczonych etykietami jest operacją domyślną i jest prostsze. Alternatywnie możesz ręcznie oznaczyć niektóre lub wszystkie dane treningowe wcześniej. Etykietowanie ręczne jest bardziej złożonym procesem, ale skutkuje lepszym wytrenowanym modelem.
Uwaga
Modele można również trenować za pomocą graficznego interfejsu użytkownika, takiego jak narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów.
Trenowanie modelu bez etykiet
Aby wytrenować model analizy dokumentów przy użyciu dokumentów w kontenerze obiektów blob platformy Azure, wywołaj interfejs API trenowania modelu niestandardowego, uruchamiając następujące polecenie cURL. Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <klucz> kluczem skopiowanymi z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <adres URL> sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego (SAS) kontenera usługi Azure Blob Storage.
Aby pobrać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego dla danych trenowania modelu niestandardowego:
Przejdź do zasobu magazynu w witrynie Azure Portal i wybierz pozycję Kontenery magazynu>danych.
Przejdź do kontenera, kliknij prawym przyciskiem myszy i wybierz pozycję Generuj sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego.
Pobierz sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego dla kontenera, a nie dla samego konta magazynu.
Upewnij się, że wybrano uprawnienia Odczyt, Zapis, Usuwanie i Lista , a następnie wybierz pozycję Generuj token SAS i adres URL.
Skopiuj wartość w sekcji Adres URL do lokalizacji tymczasowej. Powinna ona mieć postać:
https://<storage account>.blob.core.windows.net/<container name>?<SAS value>.
Wprowadź zmiany, a następnie uruchom polecenie:
curl -i -X POST "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>" --data-ascii "{ 'source': '<SAS URL>'}"
201 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z nagłówkiemLocation. Wartość tego nagłówka zawiera identyfikator modelu dla nowo wytrenowanego modelu, którego można użyć do wykonywania zapytań o stan operacji i uzyskiwania wyników:
https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/<modelId>
W poniższym przykładzie jako część adresu URL ciąg po models/ jest identyfikatorem modelu.
https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/77d8ecad-b8c1-427e-ac20-a3fe4af503e9
Trenowanie modelu przy użyciu etykiet
Aby wytrenować za pomocą etykiet, musisz mieć specjalne pliki informacyjne etykiet (<nazwa pliku>.pdf.labels.json) w kontenerze magazynu obiektów blob wraz z dokumentami szkoleniowymi. Narzędzie do etykietowania przykładowego analizy dokumentów udostępnia interfejs użytkownika, który ułatwia tworzenie tych plików etykiet. Po ich otrzymaniu wywołaj interfejs API Train Custom Model (Trenowanie niestandardowego modelu ) z parametrem ustawionym "useLabelFile" na true wartość w treści JSON.
Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <klucz> kluczem skopiowanymi z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <adres URL> sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego (SAS) kontenera usługi Azure Blob Storage.
Aby pobrać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego dla danych trenowania modelu niestandardowego:
Przejdź do zasobu magazynu w witrynie Azure Portal i wybierz pozycję Kontenery magazynu>danych.1. Przejdź do kontenera, kliknij prawym przyciskiem myszy i wybierz pozycję Generuj sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego.
Pobierz sygnaturę dostępu współdzielonego dla kontenera, a nie dla samego konta magazynu.
Upewnij się, że wybrano uprawnienia Odczyt, Zapis, Usuwanie i Lista , a następnie wybierz pozycję Generuj token SAS i adres URL.
Skopiuj wartość w sekcji Adres URL do lokalizacji tymczasowej. Powinna ona mieć postać:
https://<storage account>.blob.core.windows.net/<container name>?<SAS value>.
Wprowadź zmiany, a następnie uruchom polecenie:
curl -i -X POST "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>" --data-ascii "{ 'source': '<SAS URL>', 'useLabelFile':true}"
201 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z nagłówkiemLocation. Wartość tego nagłówka zawiera identyfikator modelu dla nowo wytrenowanego modelu, którego można użyć do wykonywania zapytań o stan operacji i uzyskiwania wyników:
https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/<modelId>
W poniższym przykładzie jako część adresu URL ciąg po models/ jest identyfikatorem modelu.
https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/62e79d93-78a7-4d18-85be-9540dbb8e792
Po rozpoczęciu operacji trenowania użyj polecenia Pobierz model niestandardowy, aby sprawdzić stan trenowania. Przekaż identyfikator modelu do żądania interfejsu API, aby sprawdzić stan trenowania:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym za pomocą klucza analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <klucz> klucz kluczem
- Zamień <identyfikator> modelu na identyfikator modelu otrzymany w poprzednim kroku
curl -X GET "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/<modelId>" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
Analizowanie formularzy przy użyciu modelu niestandardowego
Następnie użyj nowo wytrenowanego modelu, aby przeanalizować dokument i wyodrębnić z niego pola i tabele. Wywołaj interfejs API analizowania formularza , uruchamiając następujące polecenie cURL. Przed uruchomieniem polecenia wprowadź następujące zmiany:
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym z klucza analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <wartość identyfikator modelu identyfikatorem> modelu otrzymaną w poprzedniej sekcji.
- Zastąp <adres URL> sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego adresem URL do pliku w usłudze Azure Storage. Wykonaj kroki opisane w sekcji Trenowanie, ale zamiast pobierać adres URL sygnatury dostępu współdzielonego dla całego kontenera obiektów blob, uzyskaj jeden dla określonego pliku, który chcesz przeanalizować.
- Zastąp <klucz> klucz kluczem.
curl -v "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/<modelId>/analyze?includeTextDetails=true" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>" -d "{ 'source': '<SAS URL>' } "
202 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z nagłówkiemOperation-Location. Wartość tego nagłówka zawiera identyfikator wyniku używany do śledzenia wyników operacji Analizuj:
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/<modelId>/analyzeResults/<resultId>
W poniższym przykładzie jako część adresu URL ciąg po analyzeResults/ jest identyfikatorem wyniku.
https://cognitiveservice/formrecognizer/v2/layout/analyzeResults/e175e9db-d920-4c7d-bc44-71d1653cdd06
Zapisz ten identyfikator wyników dla następnego kroku.
Wywołaj interfejs API analizowania wyników formularza, aby wysłać zapytanie do wyników operacji Analizuj.
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym z klucza analizy dokumentów.
- Zamień <identyfikator> wyniku na identyfikator otrzymany w poprzedniej sekcji.
- Zastąp <klucz> klucz kluczem.
curl -X GET "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/<modelId>/analyzeResults/<resultId>" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
200 (Success) Otrzymasz odpowiedź z treścią JSON w następującym formacie. Dane wyjściowe zostały skrócone dla uproszczenia. Zwróć uwagę na "status" pole w dolnej części. To pole ma wartość "succeeded" po zakończeniu operacji Analizuj. Jeśli operacja Analizuj nie została ukończona, musisz ponownie wykonać zapytanie dotyczące usługi, uruchamiając ponownie polecenie. Zalecamy interwał co najmniej jednej sekundy między wywołaniami.
W modelach niestandardowych wytrenowanych bez etykiet skojarzenia par klucz/wartość i tabele znajdują się w węźle "pageResults" danych wyjściowych JSON. W modelach niestandardowych wytrenowanych za pomocą etykiet skojarzenia par klucz/wartość znajdują się w węźle "documentResults" . Jeśli określono również wyodrębnianie zwykłego tekstu za pomocą parametru includeTextDetails URL, "readResults" węzeł wyświetli zawartość i pozycje całego tekstu w dokumencie.
Te przykładowe dane wyjściowe JSON zostały skrócone dla uproszczenia. Zobacz pełne przykładowe dane wyjściowe w witrynie GitHub.
{
"status": "succeeded",
"createdDateTime": "2020-08-21T01:13:28Z",
"lastUpdatedDateTime": "2020-08-21T01:13:42Z",
"analyzeResult": {
"version": "2.1.0",
"readResults": [
{
"page": 1,
"angle": 0,
"width": 8.5,
"height": 11,
"unit": "inch",
"lines": [
{
"text": "Project Statement",
"boundingBox": [
5.0444,
0.3613,
8.0917,
0.3613,
8.0917,
0.6718,
5.0444,
0.6718
],
"words": [
{
"text": "Project",
"boundingBox": [
5.0444,
0.3587,
6.2264,
0.3587,
6.2264,
0.708,
5.0444,
0.708
]
},
{
"text": "Statement",
"boundingBox": [
6.3361,
0.3635,
8.0917,
0.3635,
8.0917,
0.6396,
6.3361,
0.6396
]
}
]
},
...
]
}
],
"pageResults": [
{
"page": 1,
"keyValuePairs": [
{
"key": {
"text": "Date:",
"boundingBox": [
6.9833,
1.0615,
7.3333,
1.0615,
7.3333,
1.1649,
6.9833,
1.1649
],
"elements": [
"#/readResults/0/lines/2/words/0"
]
},
"value": {
"text": "9/10/2020",
"boundingBox": [
7.3833,
1.0802,
7.925,
1.0802,
7.925,
1.174,
7.3833,
1.174
],
"elements": [
"#/readResults/0/lines/3/words/0"
]
},
"confidence": 1
},
...
],
"tables": [
{
"rows": 5,
"columns": 5,
"cells": [
{
"text": "Training Date",
"rowIndex": 0,
"columnIndex": 0,
"boundingBox": [
0.6944,
4.2779,
1.5625,
4.2779,
1.5625,
4.4005,
0.6944,
4.4005
],
"confidence": 1,
"rowSpan": 1,
"columnSpan": 1,
"elements": [
"#/readResults/0/lines/15/words/0",
"#/readResults/0/lines/15/words/1"
],
"isHeader": true,
"isFooter": false
},
...
]
}
],
"clusterId": 0
}
],
"documentResults": [],
"errors": []
}
}
Ulepszanie wyników
"confidence" Sprawdź wartości dla każdego wyniku klucza/wartości w węźle"pageResults". Należy również przyjrzeć się współczynnikom ufności w węźle "readResults" , które odpowiadają operacji odczytu tekstu. Pewność wyników odczytu nie wpływa na pewność wyników wyodrębniania klucza/wartości, dlatego należy sprawdzić oba te wyniki.
- Jeśli wyniki ufności operacji odczytu są niskie, spróbuj poprawić jakość dokumentów wejściowych. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Wymagania dotyczące danych wejściowych.
- Jeśli wyniki ufności operacji wyodrębniania klucza/wartości są niskie, upewnij się, że analizowane dokumenty są tego samego typu co dokumenty używane w zestawie treningowym. Jeśli dokumenty w zestawie szkoleniowym mają zmiany wyglądu, rozważ podzielenie ich na różne foldery i trenowanie jednego modelu dla każdej odmiany.
Docelowe wyniki ufności zależą od przypadku użycia, ale zazwyczaj dobrym rozwiązaniem jest określenie wyniku 80 procent lub wyższego. W przypadku bardziej wrażliwych przypadków, takich jak odczytywanie dokumentacji medycznej lub oświadczeń rozliczeniowych, zalecamy ocenę 100 procent.
Zarządzanie modelami niestandardowymi
Użyj interfejsu API List Custom Models w poniższym poleceniu, aby zwrócić listę wszystkich modeli niestandardowych należących do subskrypcji.
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <klucz> kluczem skopiowanymi z poprzedniego kroku.
curl -v -X GET "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models?op=full"
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
Otrzymasz odpowiedź z informacją o powodzeniu 200 z danymi JSON, takimi jak poniżej. Element "modelList" zawiera wszystkie utworzone modele i ich informacje.
{
"summary": {
"count": 0,
"limit": 0,
"lastUpdatedDateTime": "string"
},
"modelList": [
{
"modelId": "string",
"status": "creating",
"createdDateTime": "string",
"lastUpdatedDateTime": "string"
}
],
"nextLink": "string"
}
Pobieranie określonego modelu
Aby pobrać szczegółowe informacje o określonym modelu niestandardowym, użyj interfejsu API Pobierz model niestandardowy w poniższym poleceniu.
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <klucz> kluczem skopiowanymi z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <wartość modelId> identyfikatorem modelu niestandardowego, który chcesz wyszukać.
curl -v -X GET "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/<modelId>" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
Otrzymasz odpowiedź na powodzenie 200 z danymi JSON treści żądania, takimi jak poniżej.
{
"modelInfo": {
"modelId": "string",
"status": "creating",
"createdDateTime": "string",
"lastUpdatedDateTime": "string"
},
"keys": {
"clusters": {}
},
"trainResult": {
"trainingDocuments": [
{
"documentName": "string",
"pages": 0,
"errors": [
"string"
],
"status": "succeeded"
}
],
"fields": [
{
"fieldName": "string",
"accuracy": 0.0
}
],
"averageModelAccuracy": 0.0,
"errors": [
{
"message": "string"
}
]
}
}
Usuwanie modelu z konta zasobu
Możesz również usunąć model z konta, odwołując się do jego identyfikatora. To polecenie wywołuje interfejs API Usuwania modelu niestandardowego, aby usunąć model używany w poprzedniej sekcji.
- Zastąp <punkt końcowy punktem końcowym> uzyskanym przy użyciu subskrypcji analizy dokumentów.
- Zastąp <klucz> kluczem skopiowanymi z poprzedniego kroku.
- Zastąp <wartość modelId> identyfikatorem modelu niestandardowego, który chcesz wyszukać.
curl -v -X DELETE "https://<endpoint>/formrecognizer/v2.1/custom/models/<modelId>" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <key>"
Otrzymasz odpowiedź z informacją o powodzeniu 204 wskazującą, że model jest oznaczony do usunięcia. Artefakty modelu są usuwane w ciągu 48 godzin.
Następne kroki
W tym projekcie użyto interfejsu API REST analizy dokumentów do analizowania formularzy na różne sposoby. Następnie zapoznaj się z dokumentacją referencyjną, aby dowiedzieć się więcej na temat interfejsu API analizy dokumentów.