Events
May 19, 6 PM - May 23, 12 AM
Calling all developers, creators, and AI innovators to join us in Seattle @Microsoft Build May 19-22.
Register todayThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Learn how to create a function in the Azure portal that is triggered when data is added to or changed in Azure Cosmos DB. To learn more about Azure Cosmos DB, see Azure Cosmos DB: Serverless database computing using Azure Functions.
Note
In-portal editing is only supported for JavaScript, PowerShell, and C# Script functions. Python in-portal editing is supported only when running in the Consumption plan. To create a C# Script app that supports in-portal editing, you must choose a runtime Version that supports the in-process model.
When possible, you should develop your functions locally.
To learn more about the limitations on editing function code in the Azure portal, see Development limitations in the Azure portal.
To complete this tutorial:
Note
Azure Cosmos DB bindings are only supported for use with Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL. Support for Azure Cosmos DB for Table is provided by using the Table storage bindings, starting with extension 5.x. For all other Azure Cosmos DB APIs, you should access the database from your function by using the static client for your API, including Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB, Azure Cosmos DB for Cassandra, and Azure Cosmos DB for Apache Gremlin.
Sign in to the Azure portal with your Azure account.
You must have an Azure Cosmos DB account that uses the SQL API before you create the trigger.
From the Azure portal menu or the Home page, select Create a resource.
Search for Azure Cosmos DB. Select Create > Azure Cosmos DB.
On the Create an Azure Cosmos DB account page, select the Create option within the Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL section.
Azure Cosmos DB provides several APIs:
To learn more about the API for NoSQL, see Welcome to Azure Cosmos DB.
In the Create Azure Cosmos DB Account page, enter the basic settings for the new Azure Cosmos DB account.
| Setting | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription | Subscription name | Select the Azure subscription that you want to use for this Azure Cosmos DB account. |
| Resource Group | Resource group name | Select a resource group, or select Create new, then enter a unique name for the new resource group. |
| Account Name | A unique name | Enter a name to identify your Azure Cosmos DB account. Because documents.azure.com is appended to the name that you provide to create your URI, use a unique name. The name can contain only lowercase letters, numbers, and the hyphen (-) character. It must be 3-44 characters. |
| Location | The region closest to your users | Select a geographic location to host your Azure Cosmos DB account. Use the location that is closest to your users to give them the fastest access to the data. |
| Capacity mode | Provisioned throughput or Serverless | Select Provisioned throughput to create an account in provisioned throughput mode. Select Serverless to create an account in serverless mode. |
| Apply Azure Cosmos DB free tier discount | Apply or Do not apply | With Azure Cosmos DB free tier, you get the first 1000 RU/s and 25 GB of storage for free in an account. Learn more about free tier. |
| Limit total account throughput | Selected or not | Limit the total amount of throughput that can be provisioned on this account. This limit prevents unexpected charges related to provisioned throughput. You can update or remove this limit after your account is created. |
You can have up to one free tier Azure Cosmos DB account per Azure subscription and must opt in when creating the account. If you don't see the option to apply the free tier discount, another account in the subscription has already been enabled with free tier.
Note
The following options are not available if you select Serverless as the Capacity mode:
In the Global Distribution tab, configure the following details. You can leave the default values for this quickstart:
| Setting | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Geo-Redundancy | Disable | Enable or disable global distribution on your account by pairing your region with a pair region. You can add more regions to your account later. |
| Multi-region Writes | Disable | Multi-region writes capability allows you to take advantage of the provisioned throughput for your databases and containers across the globe. |
| Availability Zones | Disable | Availability Zones help you further improve availability and resiliency of your application. |
Note
The following options are not available if you select Serverless as the Capacity mode in the previous Basics page:
Optionally, you can configure more details in the following tabs:
Select Review + create.
Review the account settings, and then select Create. It takes a few minutes to create the account. Wait for the portal page to display Your deployment is complete.
Select Go to resource to go to the Azure Cosmos DB account page.
From the Azure portal menu or the Home page, select Create a resource.
In the New page, select Compute > Function App.
Under Select a hosting option, select Consumption > Select to create your app in the default Consumption plan. In this serverless hosting option, you pay only for the time your functions run. Premium plan also offers dynamic scaling. When you run in an App Service plan, you must manage the scaling of your function app.
On the Basics page, use the function app settings as specified in the following table:
| Setting | Suggested value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription | Your subscription | The subscription under which you create your new function app. |
| Resource Group | myResourceGroup | Name for the new resource group in which you create your function app. You should create a new resource group because there are known limitations when creating new function apps in an existing resource group. |
| Function App name | Globally unique name | Name that identifies your new function app. Valid characters are a-z (case insensitive), 0-9, and -. |
| Runtime stack | Preferred language | Choose a runtime that supports your favorite function programming language. In-portal editing is only available for JavaScript, PowerShell, Python, TypeScript, and C# script. To create a C# Script app that supports in-portal editing, you must choose a runtime Version that supports the in-process model. C# class library and Java functions must be developed locally. |
| Version | Version number | Choose the version of your installed runtime. |
| Region | Preferred region | Select a region that's near you or near other services that your functions can access. |
| Operating system | Windows | An operating system is preselected for you based on your runtime stack selection, but you can change the setting if necessary. In-portal editing is only supported on Windows. |
Accept the default options in the remaining tabs, including the default behavior of creating a new storage account on the Storage tab and a new Application Insight instance on the Monitoring tab. You can also choose to use an existing storage account or Application Insights instance.
Select Review + create to review the app configuration you chose, and then select Create to provision and deploy the function app.
Select the Notifications icon in the upper-right corner of the portal and watch for the Deployment succeeded message.
Select Go to resource to view your new function app. You can also select Pin to dashboard. Pinning makes it easier to return to this function app resource from your dashboard.

Next, you create a function in the new function app.
In your function app, select Overview, and then select + Create under Functions.
Under Select a template, scroll down and choose the Azure Cosmos DB trigger template.
In Template details, configure the new trigger with the settings as specified in this table, then select Create:
| Setting | Suggested value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| New function | Accept the default name | The name of the function. |
| Azure Cosmos DB account connection | Accept the default new name | Select New, the Database Account you created earlier, and then OK. This action creates an application setting for your account connection. This setting is used by the binding to connection to the database. |
| Database name | Tasks | Name of the database that includes the collection to be monitored. |
| Collection name | Items | Name of the collection to be monitored. |
| Collection name for leases | leases | Name of the collection to store the leases. |
| Create lease collection if it does not exist | Yes | Checks for existence of the lease collection and automatically creates it. |
Azure creates the Azure Cosmos DB triggered function based on the provided values.
To display the template-based function code, select Code + Test.

This function template writes the number of documents and the first document ID to the logs.
Next, you connect to your Azure Cosmos DB account and create the Items container in the Tasks database.
Open a second instance of the Azure portal in a new tab in the browser.
On the left side of the portal, expand the icon bar, type cosmos in the search field, and select Azure Cosmos DB.
Choose your Azure Cosmos DB account, then select the Data Explorer.
Under SQL API, choose Tasks database and select New Container.

In Add Container, use the settings shown in the table below the image.

| Setting | Suggested value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Database ID | Tasks | The name for your new database. This must match the name defined in your function binding. |
| Container ID | Items | The name for the new container. This must match the name defined in your function binding. |
| Partition key | /category | A partition key that distributes data evenly to each partition. Selecting the correct partition key is important in creating a performant container. |
| Throughput | 400 RU | Use the default value. If you want to reduce latency, you can scale up the throughput later. |
Click OK to create the Items container. It may take a short time for the container to get created.
After the container specified in the function binding exists, you can test the function by adding items to this new container.
Expand the new Items container in Data Explorer, choose Items, then select New Item.

Replace the contents of the new item with the following content, then choose Save.
{
"id": "task1",
"category": "general",
"description": "some task"
}
Switch to the first browser tab that contains your function in the portal. Expand the function logs and verify that the new document has triggered the function. See that the task1 document ID value is written to the logs.

(Optional) Go back to your document, make a change, and click Update. Then, go back to the function logs and verify that the update has also triggered the function.
Other quickstarts in this collection build upon this quickstart. If you plan to work with subsequent quickstarts, tutorials, or with any of the services you've created in this quickstart, don't clean up the resources.
Resources in Azure refer to function apps, functions, storage accounts, and so forth. They're grouped into resource groups, and you can delete everything in a group by deleting the group.
You've created resources to complete these quickstarts. You might be billed for these resources, depending on your account status and service pricing. If you don't need the resources anymore, here's how to delete them:
In the Azure portal, go to the Resource group page.
To get to that page from the function app page, select the Overview tab, and then select the link under Resource group.
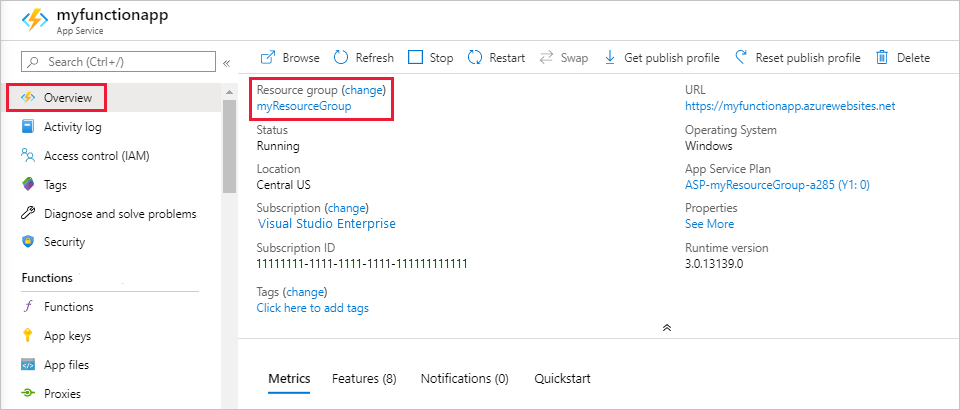
To get to that page from the dashboard, select Resource groups, and then select the resource group that you used for this article.
In the Resource group page, review the list of included resources, and verify that they're the ones you want to delete.
Select Delete resource group and follow the instructions.
Deletion might take a couple of minutes. When it's done, a notification appears for a few seconds. You can also select the bell icon at the top of the page to view the notification.
You have created a function that runs when a document is added or modified in your Azure Cosmos DB. For more information about Azure Cosmos DB triggers, see Azure Cosmos DB bindings for Azure Functions.
Now that you've created your first function, let's add an output binding to the function that writes a message to a Storage queue.
Events
May 19, 6 PM - May 23, 12 AM
Calling all developers, creators, and AI innovators to join us in Seattle @Microsoft Build May 19-22.
Register todayTraining
Module
Handle events with Azure Functions and Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL change feed - Training
Use Azure Functions bindings to integrate a function with Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL.
Certification
Microsoft Certified: Azure Cosmos DB Developer Specialty - Certifications
Write efficient queries, create indexing policies, manage, and provision resources in the SQL API and SDK with Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB.